SAP RFC
Prerequisites
To connect to your SAP application, SAP Java Connector binaries (sapjco3.jar and libsapjco3.so) must be provided to Data Processing Engine (DPE).
In on-premise deployments, data source drivers are located in the lib/jdbc folder in the DPE installation directory (typically /opt/ataccama/one/dpe).
| Ataccama cannot redistribute SAP Java Connector binaries. To obtain the required binaries, contact your SAP representative. |
| The SAP RFC connector does not support the definition of logon groups for logon load balancing. |
SAP RFC permissions
ONE reads data using the Z_READ_TABLE function, which in turn relies on the VIEW_AUTHORITY_CHECK call that is the standard SAP mechanism for access control.
You can grant access permissions to the user used to connect to SAP in one of the following ways:
-
Access only the selected table groups (
S_TABU_DISauthorization object). -
Access only individual tables (
S_TABU_NAMauthorization object).
As a prerequisite, your admin must ensure the user has appropriate access to the following tables:
-
DD02V - Table view used to store Generated Table for View data.
-
DD03L - Table used to store Table Fields data (structure definitions).
-
DD03M - Table use to store Table Fields data (text elements).
-
DD05Q - Table view on foreign key fields.
These tables contain metadata about the database schema. They are used by the Data Processing Engine (DPE) during connection browsing, metadata import, profiling, and DQ evaluation.
Create a source
To connect to SAP RFC:
-
Navigate to Data Catalog > Sources.
-
Select Create.
-
Provide the following:
-
Name: The source name.
-
Description: A description of the source.
-
Deployment (Optional): Choose the deployment type.
You can add new values if needed. See Lists of Values. -
Stewardship: The source owner and roles. For more information, see Stewardship.
-
| Alternatively, add a connection to an existing data source. See Connect to a Source. |
Add a connection
-
Select Add Connection.
-
In Select connection type, choose Others > SAP RFC.
-
Provide the following:
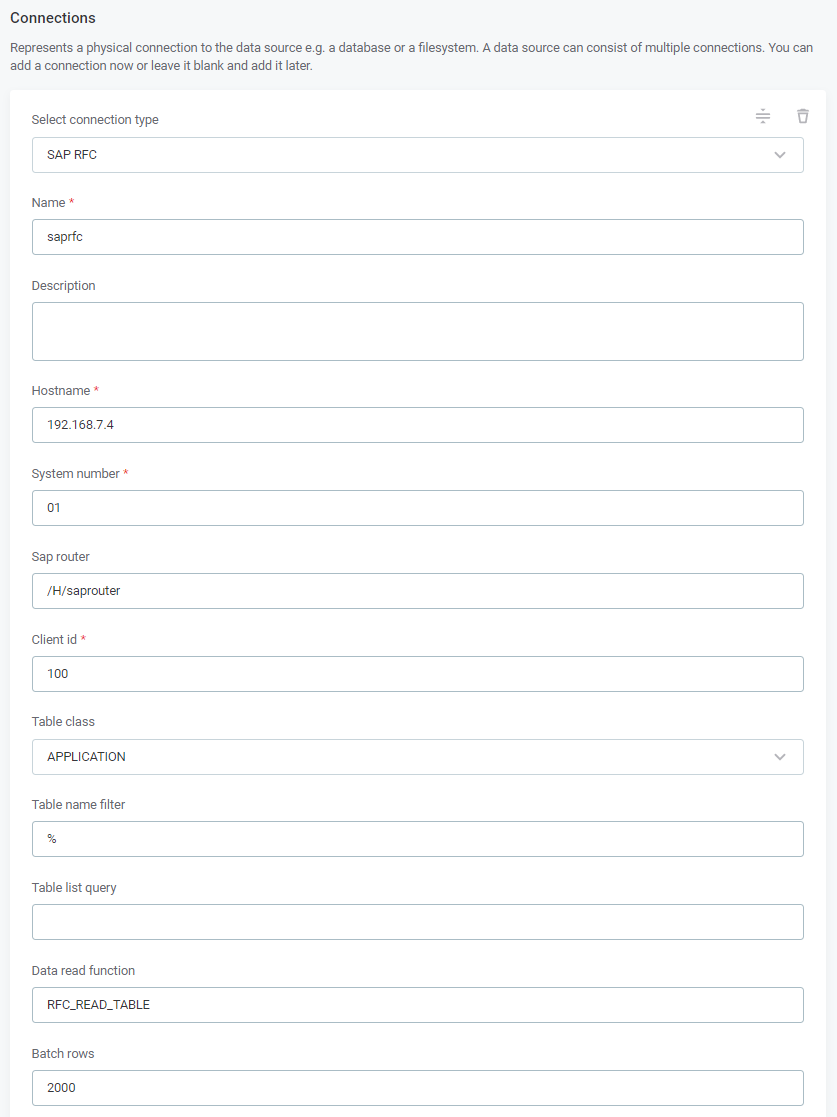
-
Name: A meaningful name for your connection. This is used to indicate the location of catalog items.
-
Description (Optional): A short description of the connection.
-
Dpe label (Optional): Assign the processing of a data source to a particular data processing engine (DPE) by entering the DPE label assigned to the engine. For more information, see DPM and DPE Configuration in DPM Admin Console.
-
Hostname: The domain name or IP address of the SAP server.
-
System number: The application instance number of the SAP system. This is a two-digit number used for connecting to the server.
-
SAP router: Points to the SAProuter used to connect to the server. The following format is used:
(/H/host/S/service/W/pass)*. Both the service port (/S/) and the password (/W/) are optional. -
Client ID: A 3-digit number that specifies which profile is used when logging in the given user or group to the SAP server.
-
Table class: Specifies which tables are queried. The following options are available:
APPLICATION,CUSTOMER,VIEW,CUSTOM_QUERY,BAPI.If you select CUSTOM_QUERY, you also need to provide the query that will be applied in Table list query. -
Table name filter (Optional): Lets you filter tables by name. The default value is
%, which matches any string. -
Table list query: The table list query filter condition used to filter tables if
CUSTOM_QUERYis selected in Table class. See Table list query filter condition for detailed information about query syntax and examples. -
Data read function (Optional): The name of the SAP function for querying data. By default, the standard
RFC_READ_TABLEfunction is used. In some cases, this function might not support every table type. If necessary, consider creating a new function in SAP. For exampleZ_READ_TABLE, a custom implementation that has to be imported into SAP. -
Metadata read function (Optional): The name of the SAP function for querying metadata. It allows you to specify a custom function if necessary, as the data read function might not support all table types. Use this to read from table types that the data read function cannot handle, in situations such as:
-
The size of the table that can be read is limited (512-character row limit). Tables exceeding the limit are not supported by the data read function.
-
Paging is not supported by the data read function. Reading of bigger tables might fail.
-
The authorizations assigned to the user calling the function are not considered: SAP authorization checks are bypassed.
-
-
Batch rows (Optional): The number of records that are read in a single batch. Default value:
2000.
-
-
In Additional settings, select Enable exporting and loading of data if you want to export data from this connection and use it in ONE Data or outside of ONE.
If you want to export data to this source, you also need to configure write credentials. See Connection credentials.
Consider the security and privacy risks of allowing the export of data to other locations.
Table list query filter condition
When CUSTOM_QUERY is selected in the Table class field, you need to provide a query to filter which SAP tables are retrieved.
The query uses SAP Open SQL WHERE clause syntax without the WHERE keyword.
Syntax rules
-
Each condition line is limited to 72 characters maximum.
-
The
WHEREkeyword should NOT be included. -
Spaces are required around operators (e.g.,
TABNAME = 'TEST'notTABNAME='TEST'). -
Spaces are required after opening parenthesis and before closing parenthesis.
Available operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
|
Equal to |
|
Not equal to |
|
Less than |
|
Greater than |
|
Less than or equal to |
|
Greater than or equal to |
|
Pattern matching (use |
|
Negative pattern matching |
|
Value in list |
|
Value not in list |
|
Value between two values |
|
Logical AND |
|
Logical OR |
Common fields for filtering
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Table name |
|
Table class: |
|
Application class (module): |
|
Content/delivery flag: |
|
Authorization class |
Query examples
TABNAME = 'TEST'
Returns only the TEST table.
TABNAME LIKE 'Z%'
Returns all custom tables starting with Z.
TABNAME IN ( 'ONE', 'TWO', 'THREE' )
Returns only the specified tables.
TABCLASS = 'TRANSP'
Returns only transparent tables.
( TABNAME LIKE 'Z%' OR TABNAME LIKE 'Y%' ) AND TABCLASS = 'TRANSP'
Returns custom transparent tables.
TABNAME NOT LIKE '%/%' AND TABCLASS = 'TRANSP' AND ( CONTFLAG = 'C' OR CONTFLAG = 'G' )
Excludes system tables, includes only transparent tables, and only customizing tables.
TABCLASS IN ( 'TRANSP', 'VIEW' )
RFC_READ_TABLE can only read transparent tables and views.
Pool and cluster tables require special handling.
Add credentials
Different sets of credentials can be used for different tasks. One set of credentials must be set as default for each connection.
To determine whether you need to configure more than a single set of credentials, see Connection credentials.
-
Select Add Credentials.
-
Provide the following:
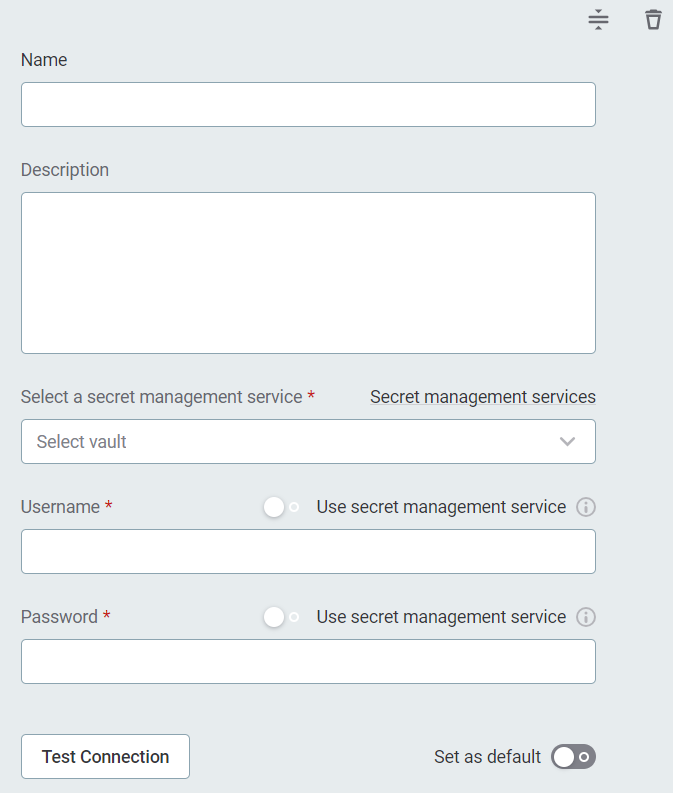
-
Name (Optional): A name for this set of credentials.
-
Description (Optional): A description for this set of credentials.
-
Select a secret management service (optional): If you want to use a secret management service to provide values for the following fields, specify which secret management service should be used. After you select the service, you can enable the Use secret management service toggle and provide instead the names the values are stored under in your key vault. For more information, see Secret Management Service.
-
Username: The username associated with the SAP account. Alternatively, enable Use secret management service and provide the name this value is stored under in your selected secret management service.
-
Password: The password for the SAP account. Alternatively, enable Use secret management service and provide the name this value is stored under in your selected secret management service.
-
-
Set the credentials to be used as default (Set as default).
See also Connection credentials.
Test the connection
To test and verify whether the data source connection has been correctly configured, select Test Connection.
If the connection is successful, continue with the following step. Otherwise, verify that your configuration is correct and that the data source is running.
Save and publish
Once you have configured your connection, save and publish your changes. If you provided all the required information, the connection is now available for other users in the application.
In case your configuration is missing required fields, you can view a list of detected errors instead. Review your configuration and resolve the issues before continuing.
Good to know
When running sample profiling on catalog items imported from SAP RFC, the whole table is read from the data source instead of only a selection of rows. Given the performance requirements and the limited insights it provides, we therefore do not recommend running sample profiling on SAP RFC data sources.
Keep in mind that pooled and cluster tables cannot be imported to ONE.
Next steps
You can now browse and profile assets from your SAP RFC connection.
In Data Catalog > Sources, find and open the source you just configured. Switch to the Connections tab and select Document. Alternatively, opt for Import or Discover documentation flow.
Or, to import or profile only some assets, select Browse on the Connections tab. Choose the assets you want to analyze and then the appropriate profiling option.
Was this page useful?
