Application Validation Checks
Overview
System validations check the internal consistency of data stored in the Metadata Management Module (MMM) database. In an ideal state, there are no inconsistencies in the MMM data. However, inconsistencies can be created under some circumstances, such as concurrent deletion of the same metadata node.
System validations are accessible for admin users at <ONE_URL>/organization/application/validations.
To run validation checks, you need superadmin permissions (MMM_admin or admin user roles).
|
You can view the recently run validations in any application mode in Global Settings > Validations in the Maintenance Center section.
Run validations
To run validations checks, select Run validations from the Validations screen:
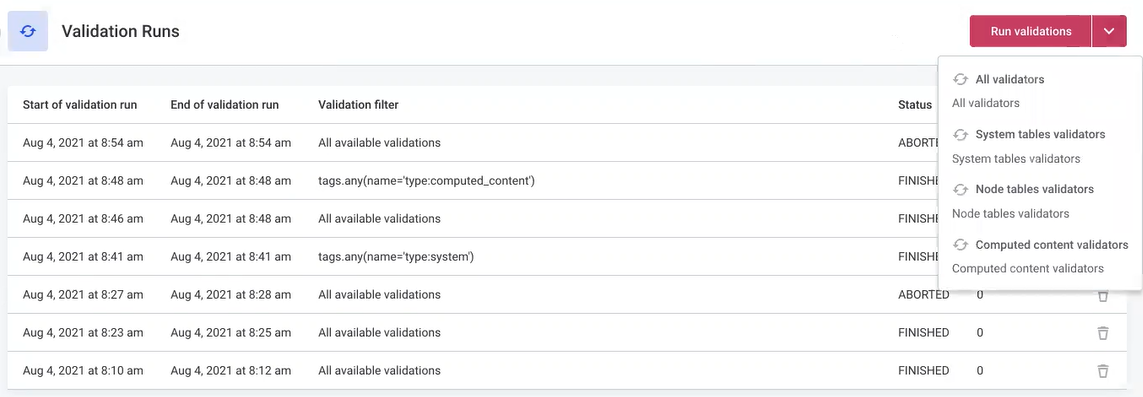
Validation options
From the Run validations options, run either all validation checks (All validators) or only some. The following validations are available:
-
System tables validators: Check pre-computed permission tables and dictionary tables storing type and path names as numbers.
-
Node tables validators: Check content of system columns of the data tables. For example, they check that
parent_id_iis not null and many other system column validations. -
Computed content validators: Check if computed content nodes have correct SQL syntax.
-
Tables schema validators: Check if the tables generated by MMM have the expected definition.
-
Application validations validators: Check all PUBLISHED data stored in the MMM to ensure they satisfy the schema. These validations are executed after each editing of data in MMM. For example, they check if references point to existing nodes, if required properties have non-null values and if nodes are unique.
|
Running all validations might take a long time to complete, depending on the database size. |
View validation run results
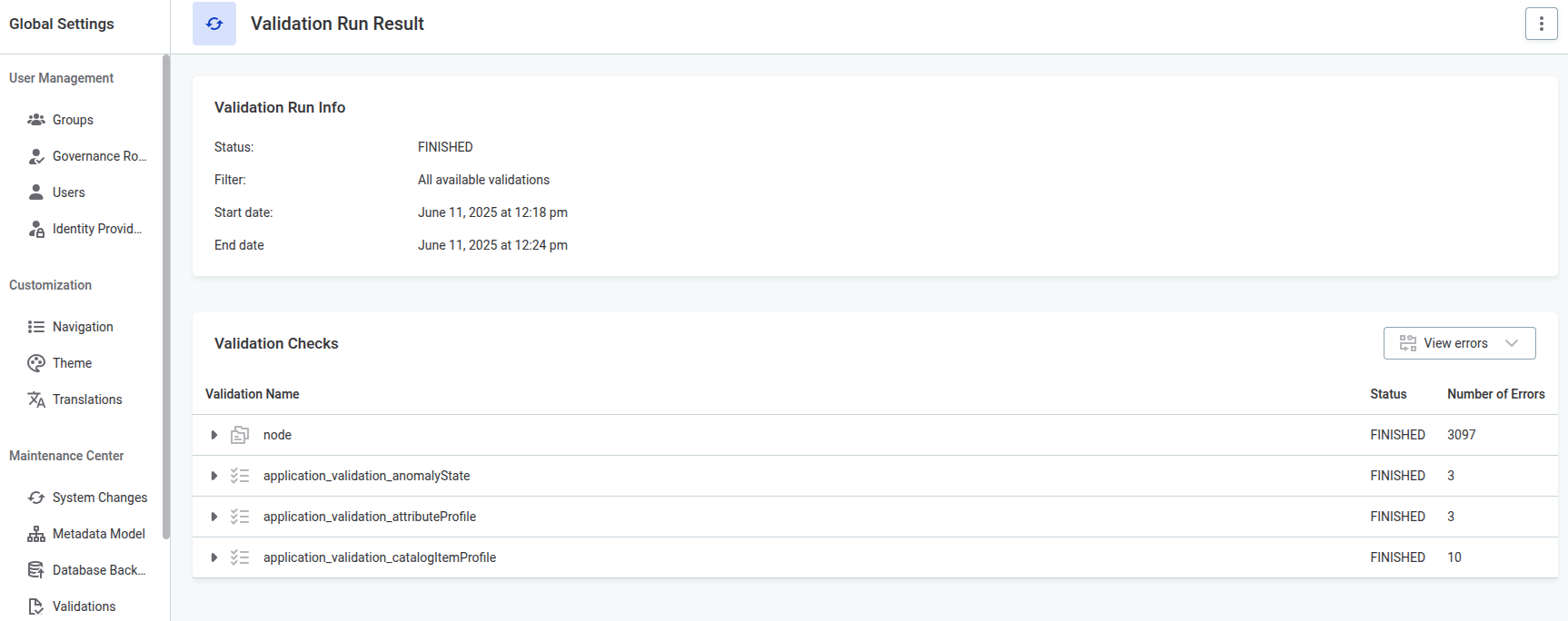
The Validation Runs tab displays a list of validation runs that can be executed manually or scheduled (usually once a day).
After the validation checks are complete, you can see the results on the Validation Runs tab. In Info, the status of the validation run and its start and end time are shown.
Validation run states
A validation run can end in the following states:
-
FINISHED: Validation run finished.
-
White row: No inconsistencies found.
-
Red row: Inconsistencies found.
-
-
ABORTED: Execution canceled, probably by a user.
-
FAILED: The run failed due to an unexpected error.
View all validations or the failed validations only (if there are any) by filtering the checks:
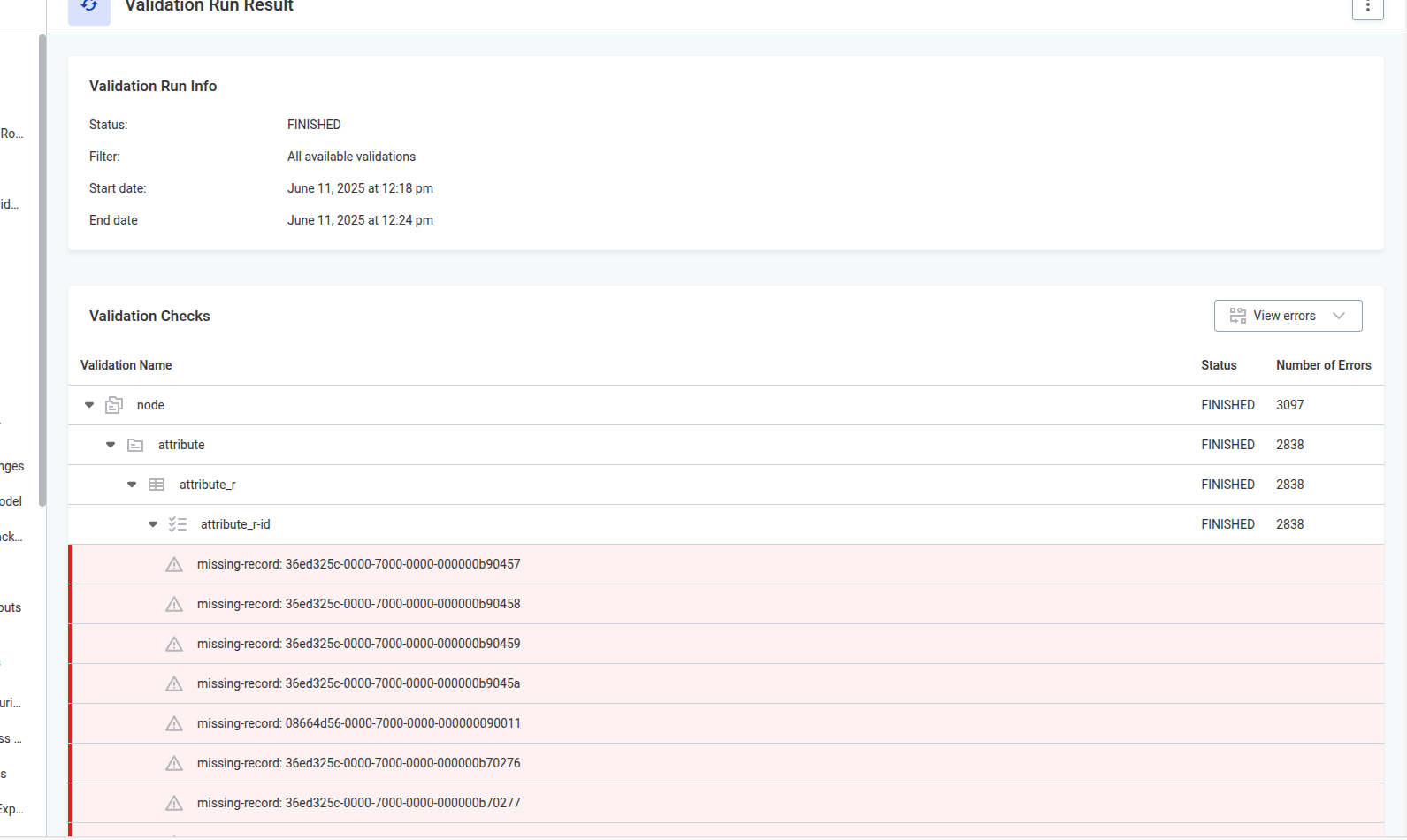
The Validation Checks section shows all performed validations with their status and error count:
Expand the validation groups to see each validation result:
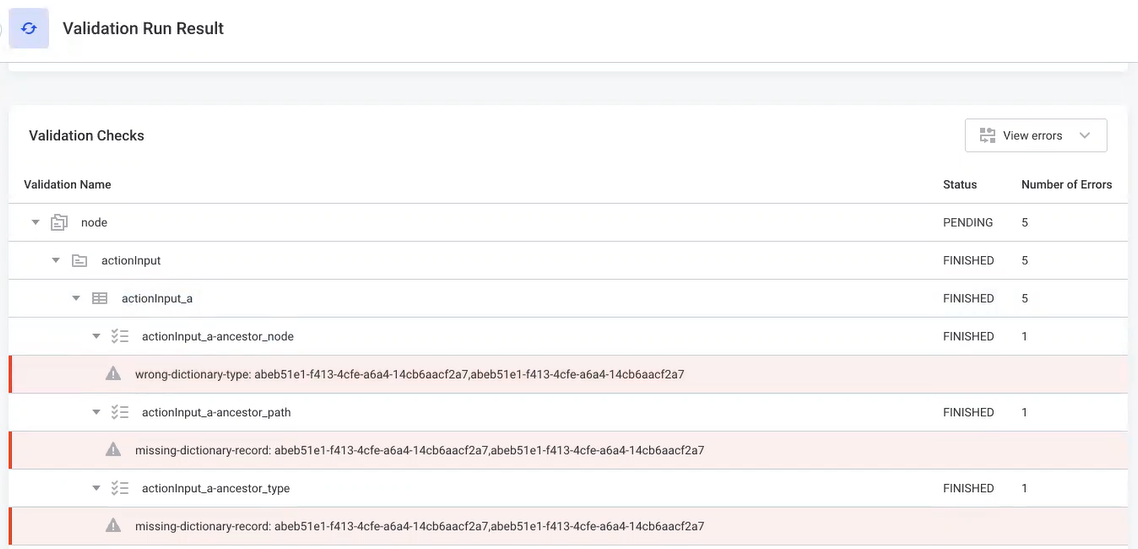
Validation categories
Under the node node, there are two main categories of validations:
-
Internal validations: Check for issues such as null system columns. Display one metadata node ID per row.
-
Application validations: Execute the same validations that run during editing of metadata nodes. These validations check PUBLISHED data stored in the MMM:
-
Property is required
-
Reference missing
-
Unique constraint is violated
-
| The two validation types display results in different formats. Internal validations list each affected metadata node on a separate row. Application validations group all affected nodes together by the constraint they violated, showing the list of IDs followed by the constraint details. |
Understanding error messages
When you expand an erroneous validation, the red rows show IDs of erroneous nodes followed by a message.
Application validation errors
Application validations display errors grouped by constraint violations:
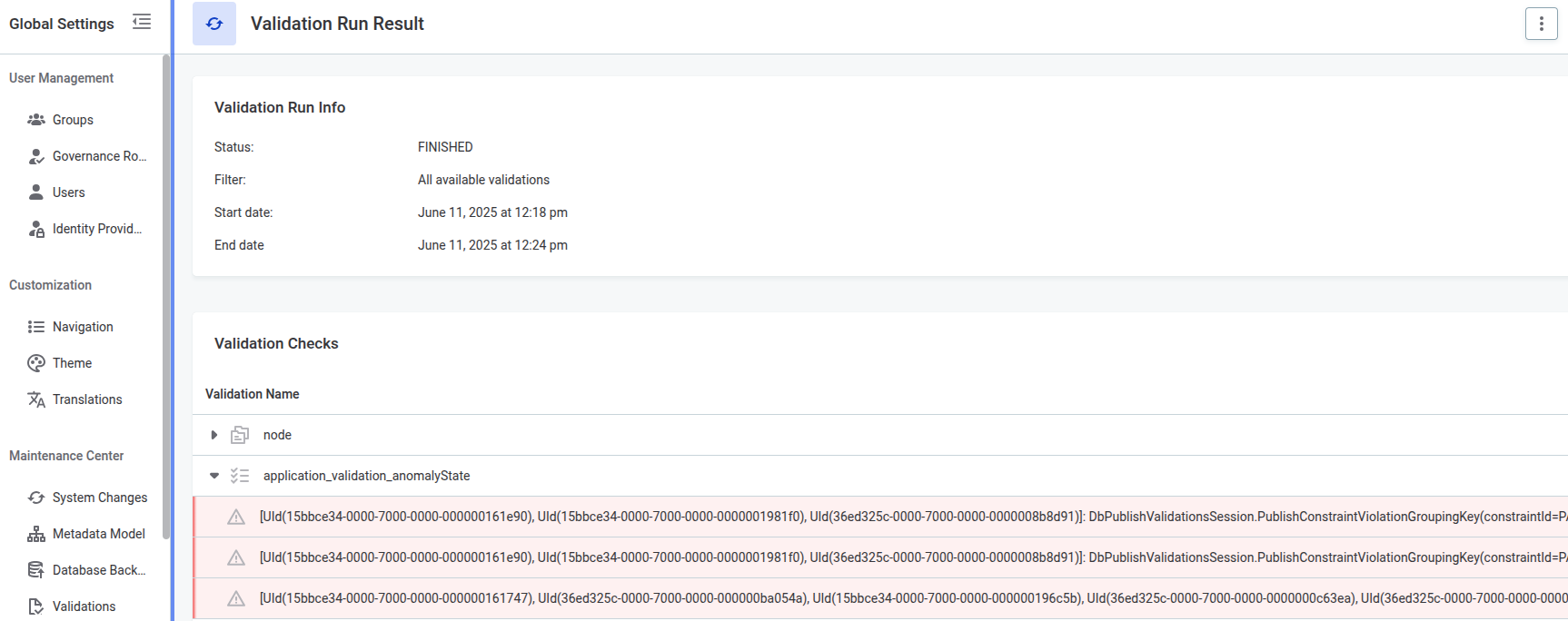
For example:
[UId(15bbce34-0000-7000-0000-000000161e90), UId(15bbce34-0000-7000-0000-0000001981f0), UId(36ed325c-0000-7000-0000-0000008b8d91)]: DbPublishValidationsSession.PublishConstraintViolationGroupingKey(constraintId=PARENT_EXISTS, nodePath=NodePath(path=/sources/workspace/catalogItems/profilingConfigurationInstances/profiles/anomalyState), constraintType=PARENT_EXISTS, code=PARENT_DOES_NOT_EXIST, entityName=anomalyState, propertyName=null, propertyNames=null)
In this example, the entity anomalyState does not have a parent.
The IDs show the exact metadata nodes that are missing parent nodes.
| The list of IDs can be duplicated. For the same entity, there can be multiple node paths. To get a unique set of affected nodes, collect all IDs and deduplicate them. |
Resolve errors
If the validation runs fail, expand the validation to see the error message.
-
If errors are found in validations for precomputed data stored in
_qtables, you can recalculate the ancestors using the following GraphQL mutation:mutation { _recalculateAncestors } -
If errors are found in other validations, the issues are in the database itself. Follow the error message to resolve the issue.
For example, for missing parent errors such as
anomalyState, delete and publish the entities using GraphQL mutations.
GraphQL API for system validations
You can access and manage system validations through the GraphQL API. For more information about using GraphQL in ONE, see ONE API.
Query validation runs
Retrieve the most recent validation run with errors:
query e {
_systemValidationRuns(size: 1, withErrorsOnly: true) {
edges {
node {
errorsCount
start
status
id
checks {
edges {
node {
id
errorMessage
distinctErrorsCount
validator {
name
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}Query validation errors
Retrieve detailed error information for a specific validation check:
query e1 {
_systemValidationErrors(runId: "4155c8b9-0000-7000-0000-000000201aa0", checkId: "4155c8b9-0000-7000-0000-000000201b0b") {
edges {
node {
message
record
checkId
}
}
}
}Replace runId and checkId with the appropriate values from your validation run.
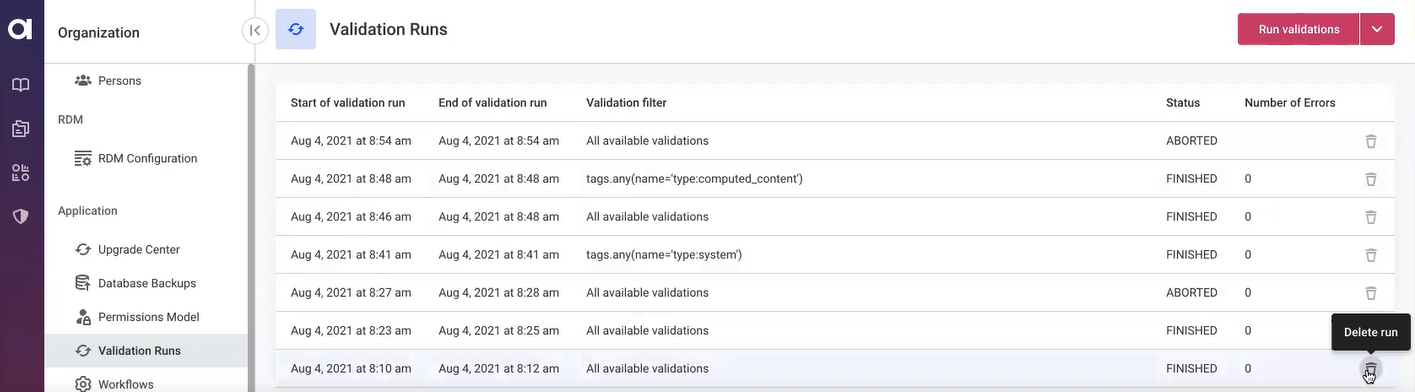
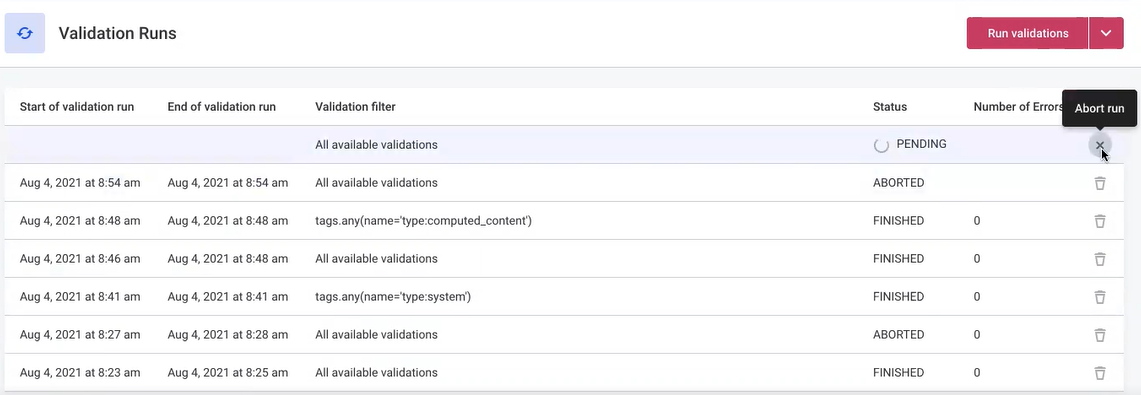
Delete and stop validation runs
You can delete a finished validation run and stop the running one.
-
To delete the old validation run, hover over the run and select the bin icon:
-
To stop the running validation, hover over the run and select the cross icon:
Was this page useful?