Snowflake Lineage Scanner
Scanned and supported objects
|
While we strive for comprehensive lineage capture, certain dataflows and transformations might be incomplete or unavailable due to technical constraints. We continuously work to expand coverage and accuracy. |
Supported statement types
The following statement types are supported:
-
CREATE TABLE AS SELECT(CTAS) -
CREATE VIEW -
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW -
INSERT -
MERGE -
SELECT -
UPDATE
Supported object types
The scanner supports the following Snowflake objects for Design Time Lineage:
-
Dynamic tables
-
Materialized views
-
Views
-
External tables
-
Iceberg tables
Lineage is also supported for stored procedures (SQL, Java, Python, Snowpark). If lineage information was captured from a procedure, the procedure name is present in the lineage. Currently, the procedure name is displayed as a comment in the SQL code preview (see View transformation context).
Lineage from procedures and other Snowflake objects is supported only indirectly, based on the captured queries in the Snowflake QUERY_HISTORY view.
|
Limitations
Lineage provided by Snowflake
Statements listed in this section are included in the lineage diagram but without expression details.
In these cases, the scanner extracts lineage collected by Snowflake (the same lineage that is available in Snowflake Horizon Catalog). See Snowflake lineage.
-
Statements containing the following SQL clauses or elements:
-
MATCH_RECOGNIZE -
Column rename in the
SELECTclause
-
-
Streams
For the cases described:
-
Snowflake Standard Edition: Lineage is not available.
-
Enterprise Edition: Lineage is available only for temporary views.
Lineage not supported
Certain statement types or features which might be relevant for lineage in specific use cases are currently not supported:
-
Statement types:
-
CLONEtable -
SWAPtables
-
-
Lineage from or to external stages (except AWS S3 buckets).
For example, the
COPYcommand for loading files from Azure ADLS storage into a Snowflake table is not supported. -
Semantic views
-
Lineage from user-defined table functions.
If a statement relevant for lineage (for example, CTAS) uses a user-defined table function as a source, the scanner doesn’t capture the objects accessed (read) by this function.
|
The following features are also not supported in the Snowflake built-in lineage (as of November 25, 2025):
|
Supported connectivity
-
Connector type: JDBC.
-
Authentication method:
-
Key-pair authentication (encrypted private keys are supported).
-
Snowflake permissions
The lineage scanner uses metadata from views located in the ACCOUNT_USAGE schema.
For details, see the official Snowflake documentation: Account Usage.
The IMPORTED PRIVILEGES privilege on the Snowflake database allows a role to access all required views in the ACCOUNT_USAGE schema.
This privilege does not grant access to table data.
| View name | Database role | Used in lineage toolkit | Enterprise Edition only | Purpose | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
Database metadata |
45 minutes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Database metadata |
90 minutes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Database metadata |
90 minutes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
SQL history |
90 minutes |
|
|
Yes, partially |
No |
Application name extraction |
3 hours |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Lineage information |
3 hours |
|
|
Optional |
No |
Lineage information |
2 hours |
To allow other roles to access the Snowflake database and query the views, run the following command with the ACCOUNTADMIN role:
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN;
GRANT IMPORTED PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE snowflake TO ROLE ata_mde_role;
If you do not require lineage for external stages or Snowpipe, you can grant the following three database roles to the scanner role instead of IMPORTED PRIVILEGES.
This limits the scanner access to views granted by the USAGE_VIEWER role.
|
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN;
GRANT GOVERNANCE_VIEWER ON DATABASE snowflake TO ROLE ata_mde_role;
GRANT OBJECT_VIEWER ON DATABASE snowflake TO ROLE ata_mde_role;
GRANT SECURITY_VIEWER ON DATABASE snowflake TO ROLE ata_mde_role;Optional privileges
- Execute privilege for function GET_LINEAGE (SNOWFLAKE.CORE)
-
By default, the
PUBLICrole can execute theGET_LINEAGEfunction, so no additional privilege is needed.The GET_LINEAGEfunction is used only to retrieve fallback lineage for database views and dynamic tables when the scanner is not able to derive detailed expression-level lineage. For example, for database views containingMATCH_RECOGNIZEclauses or queries reading from Snowflake streams. See Limitations. - Lineage for dynamic tables
-
To extract lineage for dynamic tables, the following additional privileges are required:
-
The
MONITORprivilege on dynamic tables. This is required for successfully executing theSHOW DYNAMIC TABLEScommand to construct lineage (see SHOW DYNAMIC TABLES).The command only returns objects for which the current role has at least one access privilege.
The scanner does not gather lineage for dynamic tables when these prerequisites are not satisfied. No errors or warnings are reported in this case.
-
- Cross lineage for Iceberg tables managed by AWS Glue Data Catalog
-
When the JSON property
icebergTablesExternalCatalogis set toAWS_GLUE, the scanner creates cross lineage (a link) between the Iceberg table definition in Snowflake and the corresponding AWS Glue Data Catalog definition. This is a prerequisite to create cross lineage between AWS Glue–managed and loaded Iceberg tables and their Snowflake representation (to provide Snowflake downstream lineage).The scanner user/role needs the
SELECTprivilege on all Iceberg tables that are in the scanner scope.If icebergTablesExternalCatalogis set toAWS_GLUEand the scanner role does not have theSELECTprivilege on any Iceberg table in the scan scope, the scanner terminates with a detailed error message to avoid creating incomplete lineage.
Scanner configuration
Online (JDBC-based) extraction connects to Snowflake and extracts the necessary metadata and query log from the database.
Basic configuration
The basic configuration contains:
-
Connection settings to Snowflake.
-
Filtering or specifying the lineage scope.
-
All filters are case-insensitive (for database, schema, and application).
-
The only filter that supports SQL wildcards is the application name filter. See also ILIKE:
-
An underscore (
_) matches any single character. -
A percent sign (
%) matches any sequence of zero or more characters.
-
-
All fields marked with an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
| Property | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Unique name for the scanner job. |
||||
|
Specifies the source type to be scanned.
Must contain |
||||
|
A human-readable description of the scan. |
||||
|
Snowflake account identifier. Displayed as the connection name on the Import Lineage screen in ONE. See the official Snowflake documentation: Account name in your organization. |
||||
|
Full JDBC connection string.
If |
||||
|
The part preceding For instance, if your access URL is To get the account identifier, you can also run the following query: |
||||
|
Snowflake username. |
||||
|
Snowflake private key used for key-pair authentication. |
||||
|
Password for the Snowflake private key, if encrypted. |
||||
|
Snowflake warehouse.
If not provided, the default warehouse assigned to the |
||||
|
Snowflake role.
If not provided, the default role assigned to the |
||||
|
Lineage history in days. For example, a value of The value of this property has a direct impact on both the scanner execution time and the lineage import time.
The execution time is driven primarily by the number of unique (deduplicated) SQL statements that need to be analyzed, not just by the number of days or the number of the queries in
You can then gradually increase the value (for example, from 2 to 7 or 30 days) based on:
|
||||
|
Restricts lineage extraction to a specified list of databases.
All source database objects (
|
||||
|
List of excluded databases.
If any source database object (
|
||||
|
Restricts lineage extraction to a specified list of schemas.
All source database objects (
|
||||
|
List of excluded schemas.
If any source schema (
|
||||
|
List of included applications.
Can be used to limit lineage extraction to specific applications.
This list is inclusive; for example, if you set this property to In addition, lineage is still extracted for design time objects (views, materialized views, dynamic tables) and lineage for external stages or Snowpipe, because the application information for these objects cannot always be determined precisely (unless lineage extraction for these object types is turned off). Example values:
|
||||
|
List of excluded applications.
Can be used to limit lineage extraction to specific applications.
A typical example is excluding all lineage from Snowsight (including user-defined worksheets) by excluding the application
Example values: |
Advanced configuration
All advanced configuration options are non-mandatory and have reasonable default values.
| Property | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Path to a catalog file for initialization. If not provided, an empty database is used. Used only for troubleshooting. |
||||
|
Scans external Iceberg tables.
Allowed values: Set this property to |
||||
|
Turns off extracting queries from Default value:
|
||||
|
If set to Default value: |
||||
|
If set to
Default value: |
||||
|
If set to
Default value: |
||||
|
If set to
Default value: |
Example JSON configurations
The following examples show how to extract lineage from the past five days for the whole account (for all databases) using account identifier or JDBC URL configuration.
{
"scannerConfigs": [
{
"name": "snowflake-lineage",
"accountIdentifier": "myorg-identifier",
"sourceType": "SNOWFLAKE",
"description": "Scan lineage demo export files",
"lineageFromPastNDays": 5,
"connection": {
"account": "myorg-identifier.us-west-1",
"username": "ATA_LINEAGE_EXTRACTION_USER",
"privateKey": "@@ref:ata:[SNOWFLAKE_KEY]"
}
}
]
}{
"scannerConfigs": [
{
"name": "snowflake-lineage",
"accountIdentifier": "myorg-identifier",
"sourceType": "SNOWFLAKE",
"description": "Snowflake lineage POC",
"lineageFromPastNDays": 5,
"connection": {
"jdbcUrl": "jdbc:snowflake://<account_identifier>.snowflakecomputing.com",
"username": "ATA_LINEAGE_EXTRACTION_USER",
"privateKey": "@@ref:ata:[SNOWFLAKE_KEY]"
}
}
]
}The following example illustrates advanced configuration for a medallion architecture where multiple environments (DEV, TEST, PROD) are configured under a single account, and lineage is extracted from the production environments.
For this reason, an application filter is added on Snowsight (Snowflake Web App%) to exclude all manually created lineage (for example, temporary tables created for ad-hoc analysis).
{
"scannerConfigs": [
{
"name": "snowflake-lineage",
"accountIdentifier": "myorg-identifier",
"sourceType": "SNOWFLAKE",
"description": "Scan lineage production",
"lineageFromPastNDays": 30,
"includeDatabases": [
"BRONZE_PROD",
"SILVER_PROD",
"GOLD_PROD"
],
"excludeSchemas": [
"SANDBOX"
],
"excludeQueriesFromDbt": false,
"excludeApplications": [
"Snowflake Web App%"
],
"connection": {
"account": "myorg-identifier.us-west-1",
"username": "ATA_LINEAGE_EXTRACTION_USER",
"privateKey": "@@ref:ata:[SNOWFLAKE_KEY]",
"warehouse": "SMALL_WAREHOUSE",
"role": "ATA_LINEAGE_ROLE"
}
}
]
}Snowflake lineage from a cloned database
When, for security or other reasons, it is not possible to use the ACCOUNT_USAGE schema views in the Snowflake SNOWFLAKE database, lineage can be extracted from a cloned (or replicated) version of these views.
You can configure the database containing the cloned ACCOUNT_USAGE schema using the JSON property clonedDatabase.
The following views must be present in the ACCOUNT_USAGE schema of the cloned database:
-
TABLES -
COLUMNS -
VIEWS -
QUERY_HISTORY -
SESSIONS -
ACCESS_HISTORY -
COPY_HISTORY(optional; can be skipped whenskipCopyHistoryExtractionis set totrue).
SNOWFLAKE_CLONED_DB{
"scannerConfigs": [
{
"name": "snowflake-lineage",
"accountIdentifier": "myorg-identifier",
"sourceType": "SNOWFLAKE",
"description": "Snowflake lineage POC",
"lineageFromPastNDays": 5,
"clonedDatabase": "SNOWFLAKE_CLONED_DB",
"connection": {
"jdbcUrl": "some_jdbc",
"username": "ATA_LINEAGE_EXTRACTION_USER",
"privateKey": "@@ref:ata:[SNOWFLAKE_KEY]"
}
}
]
}
The schema name cannot be configured and must be set to ACCOUNT_USAGE.
In the example, the account usage views must be located in database SNOWFLAKE_CLONED_DB within schema ACCOUNT_USAGE (that is, SNOWFLAKE_CLONED_DB.ACCOUNT_USAGE.QUERY_HISTORY).
|
SQL anomaly detection
SQL anomaly detection helps you identify unused objects in complex SQL queries. This feature is part of the generic SQL scanner and available for all SQL-based scanners, including the Snowflake one.
Complex queries can contain tens of source tables or WITH clauses, making it difficult to spot unused objects manually (typically, around 0,5–2% of all scanned SQL statements will contain such queries).
Results of these SQL validations, which require semantic analysis of the SQL statements, are exported into CSV files in the exec_<date>_<id>/<scanner-name> folder:
-
Detection results of unreferenced (unused) tables: Available in the
NotUsedFromSources.csvfile. -
Detection results of orphaned WITH clauses: Available in the
NotReferencedWithClauses.csvfile.
Example: Table not referenced in SQL
In the following example, the table customers is joined in the SQL but not actually referenced in the SELECT list or in any filter.
As such, the table can be safely removed from the SQL.
Keeping such joins can cause performance issues or additional (cloud) costs.
Typically, this happens when the customers table was used in the past (for example, in an older version of the ETL) but is no longer required or was replaced with another source.
To quickly locate unused source tables or views in the exported SQL, search for the string <<.
All unused sources are wrapped in << >>, for example << customers >>.
SELECT
o.order_id,
-- c.name AS customer_name,
o.status,
e.first_name,
e.last_name
FROM orders o
LEFT JOIN employees e
ON e.employee_id = o.salesman_id
LEFT JOIN <<customers>> c
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
ORDER BY
o.order_date DESC;Example: WITH clause not used
In this example, the WITH clause avg_cost is never referenced in the final SELECT.
While it might have been used in the past and then forgotten, keeping the clause can lead to additional costs and incorrect impact analysis (creating a "false" dependency on the underlying tables).
To locate unreferenced or inaccessible WITH clauses in the exported SQL, search for the string NOT_REFERENCED_WITH_CLAUSE.
WITH
dept_costs AS (
SELECT dname, SUM(sal) AS dept_total
FROM emp e, dept d
WHERE e.deptno = d.deptno
GROUP BY dname
),
avg_cost AS (
SELECT
'NOT_REFERENCED_WITH_CLAUSE' AS generated_by_scanner,
SUM(dept_total) / COUNT(*) AS avg
FROM dept_costs
)
SELECT *
FROM dept_costs
WHERE dept_total > 100
ORDER BY dname;Troubleshooting
No active warehouse selected error
Problem: You received the following error when running the scanner:
No active warehouse selected in the current session. Select an active warehouse with the 'use warehouse' command.
Solution: Set the warehouse in the connection section of the JSON configuration file, then rerun the command.
JDBC driver communication error
Problem: You received the following error when running the scanner:
JDBC driver encountered communication error. Message: HTTP status=403.
Solution: This can indicate that the configuration parameter account contains only the Snowflake accountIdentifier (for example, myorg-identifier) instead of accountIdentifier together with the cloudRegion (for example, myorg-identifier.us-west-1).
Update the account parameter in the JSON configuration file to include the region, then rerun the command.
Analyzing missing or incomplete lineage
In most cases, the lineage coverage is expected to be more than 99,5%. To analyze and fix the root cause of missing or incomplete lineage, use the following steps:
-
In most cases, the root cause is related to the configured filters:
-
If you set
includeDatabasesorincludeSchemasfilters, check whether all source and target objects of the missing lineage statements are included. For example, the followingINSERTstatement is extracted by the scanner only if all three databases are included inincludeDatabases(CORE_DB,STAGE_DB,DIM_DB):INSERT INTO CORE_DB.DERIVED.CUSTOMER SELECT c.id, c.name, t.type_cd FROM STAGE_DB.SOURCE.CUSTOMER c LEFT JOIN DIM_DB.BASE.DIM_CUSTOMER_TYPE t ON t.ID = c.CUSTOMER_TYPE_ID
-
-
Check whether
lineageFromPastNDaysis correctly set.-
If it is set correctly, verify that the required SQL scripts, ETL processes, and dbt models have been executed in the past N days specified by this parameter.
-
On development and testing environments, where most ETLs are not executed regularly, this is often the main reason for missing lineage.
-
-
Check which object types the lineage is missing for. If lineage is missing for:
-
Object types that are not yet supported: For example, if lineage is not available for semantic views, this is expected. See Limitations.
-
Dynamic tables: Check the required permissions for dynamic table lineage (see Optional privileges).
-
Temporary views: Contact Ataccama Support (fallback lineage is currently not available for temporary views).
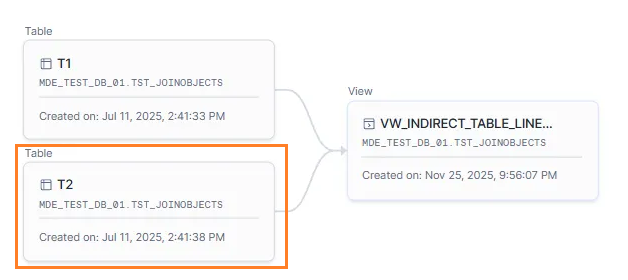
Snowflake does not display lineage for temporary tables (as of November 25, 2025). For database views, Snowflake lineage displays also the indirect lineage while Ataccama ONE displays only the direct lineage.
For other database object types, Snowflake displays direct lineage as well, so no differences are expected.
-
The following example illustrates the difference for views.
The table T2 participates only in indirect lineage, so it is not displayed on the Ataccama ONE lineage diagram.
CREATE VIEW VW_INDIRECT_TABLE_LINEAGE AS
SELECT
t1.c1
FROM T1 t1
LEFT JOIN T2 t2
ON t1.c2 = t2.c1;For comparison, you would see the following in Snowflake Horizon Catalog:
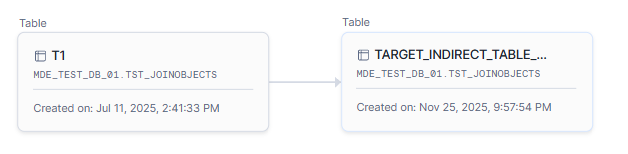
If you use the same SQL to create a table (instead of a view), Snowflake does not display table-level lineage for table T2.
In this case, the lineage is the same as in Ataccama ONE.
CREATE TABLE TARGET_INDIRECT_TABLE_LINEAGE AS
SELECT
t1.c1
FROM T1 t1
LEFT JOIN T2 t2
ON t1.c2 = t2.c1;For comparison, Snowflake Horizon Catalog would display the following:
Was this page useful?
