MDM Capabilities
MDM embodies the best practices adapted toward an MDM project. It follows a model-driven architecture at its core and is essentially a domain-agnostic MDM, which enables developers to define a domain-specific MDM through models.
The following are the high-level MDM capabilities divided by type.
Model-driven architecture
Domain-agnostic MDM supports vertical models (metadata templates) that are domain-specific and can be customized and extended to fit particular project needs.
For detailed information about the architecture and model-driven nature of Ataccama MDM, see MDM Model.
Internal workflow and processing capabilities
The following are highlights of the MDM capabilities:
-
Out-of-the-box change detection on load. MDM is able to detect changes from source instance records fed to the MDM through a track of their unique source identifiers.
In addition, it can detect updates or differences on the different attributes, triggering the MDM process for that record in case it changed. The delta detection has an attribute-level granularity, hence developers can define a subset of attributes that should not trigger the MDM processing. All of them are considered by default.
-
Entity-by-entity-oriented processing. The processing of the MDM is done on entity level, that is, entities are processed in MDM in parallel as independent abstractions.
If any dependency between entities needs to be satisfied in order to process a subsequent phase of the MDM, MDM will create them according to the MDM operation plan.
-
Data transfer and linkage between entities. Entities can have their columns copied to other entities through their relationships.
This allows users to transfer values of importance to support MDM processes on a particular entity, for example, copying values from a supporting entity (on a 1:N relationship) to its parent entity, so the data can be used for matching.
-
Consistent MDM processes. This refers to data cleansing, matching and merging plans across all processing modes (batch, streaming, online, hybrid) and all source systems (through a common canonical model that accommodates all heterogeneous representations of the same entities).
The following diagram provides a high-level view of the internal workflow, including the MDM processes for master data consolidation.
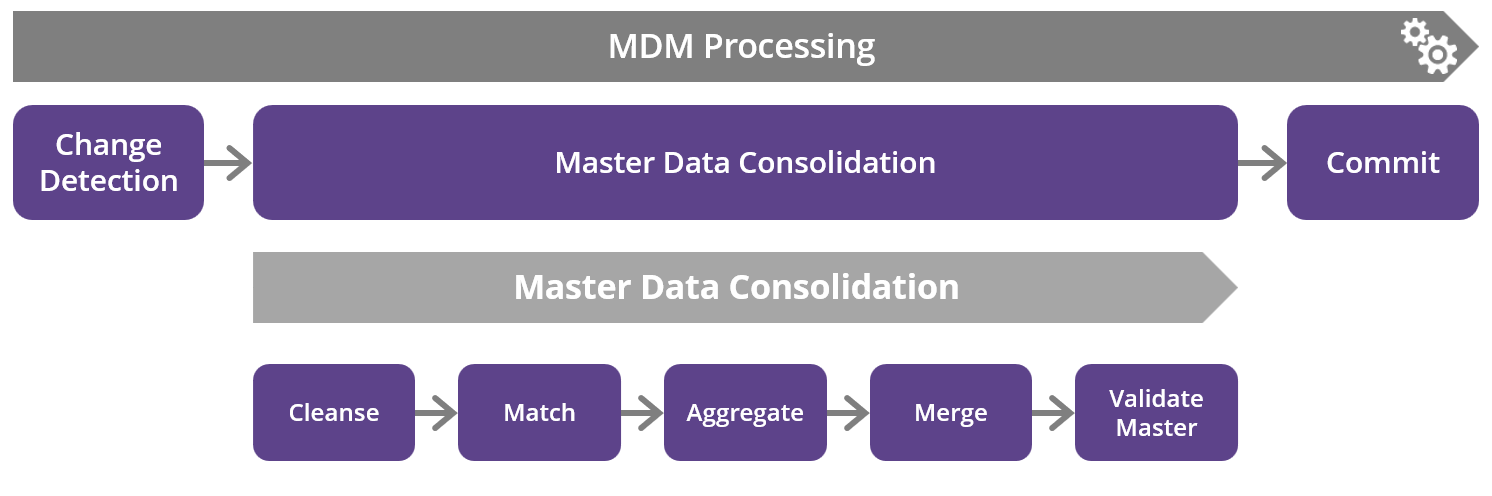
Integrated internal workflow with logical transaction
The integrated internal workflow of MDM automates and orchestrates the MDM processes transparently, enabling users to focus on the MDM processes themselves and not in the overhead of the integration and execution planning of those tasks.
At the same time, the logical transaction and the integrated workflow serve for the purposes of:
-
Enabling coexistence of batch, stream, and online processes. This allows for a hybrid deployment of MDM, and supports SOA-ready MDM that also interacts with legacy or not SOA-enabled systems through batch interfaces.
-
Parallel batch, streaming, and online processing. Mainly suitable for online parallel processing, including streams, but batch operations can also be processed in parallel.
-
Consistent data providing. Read-Only services are allowed to access actual data as providers, while Read-Write services are within the data scope of the logical transaction.
-
Data consistency. The logical transaction also secures rollback capability.
The following diagram shows an example of an MDM internal workflow on a Party entity (Customer) related data processing.
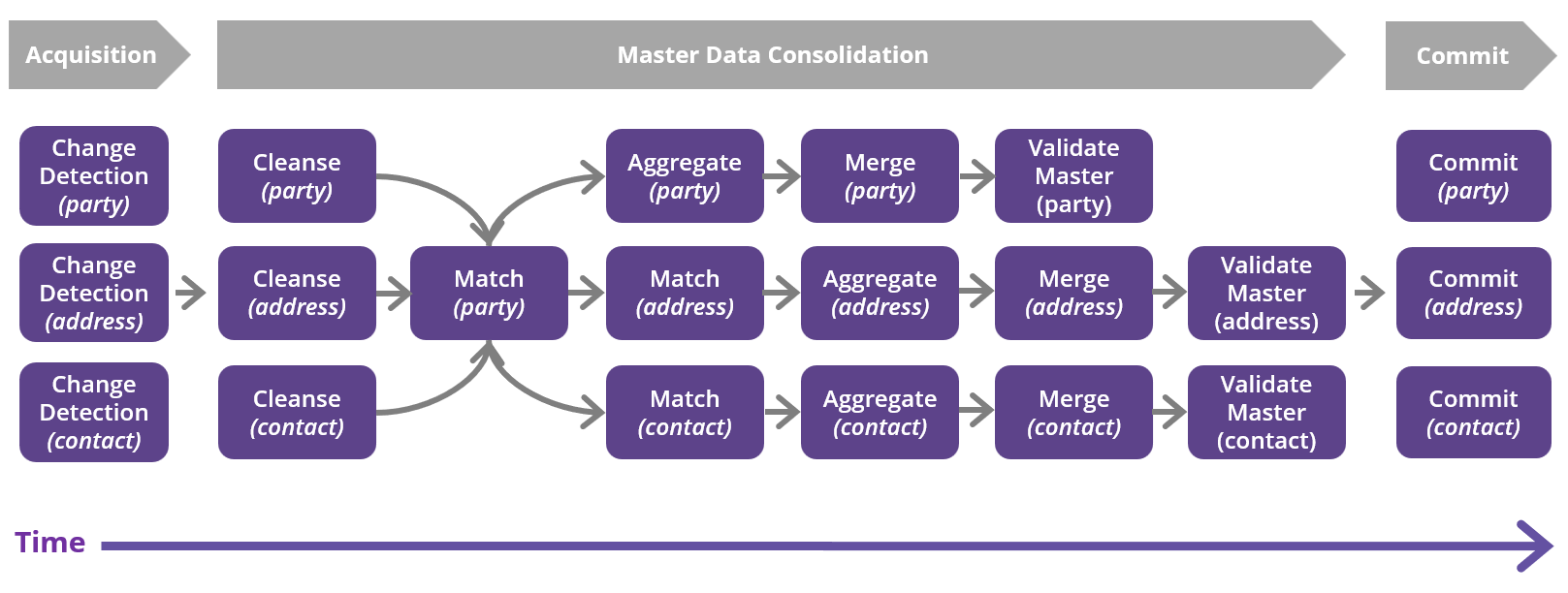
Business lineage and versioning
MDM stores data and supports both logical and physical deletes through housekeeping activities. It provides metadata engine flags to mark different statuses of records and enables activation and deactivation of selected records as per their source system updates. Historical record updates can be also stored if activated (not enabled by default).
Hence, MDM provides the following capabilities out-of-the-box:
-
Ability to maintain inactive records for business lineage through logical deletes. Different system-level handling for the active-inactive records.
-
Ability to capture changes and publish them, creating versioning history. Publishing is done to an external component of the architecture (for example, a data warehouse or database).
MDM is capable of publishing intra-day changes (using Event Publisher) or snapshots (using Batch Export).
-
Versioning records of selected entities and layers. History data can be provided by the native service interface and batch export.
The most common versioning setup would be publishing changes to an external component designated for this role.
Versioning records within MDM by using historical tables is possible, but it requires additional resources and extra database space. Using MDM as a data warehouse replacement is discouraged.
Reference data and related capabilities
MDM allows defining reference data as part of the mastering process, and within the same domain models. This enables validation against reference data out-of-the-box by mapping attributes to reference data dictionaries, also called lookups.
It also generates validations against those dictionaries automatically, leveraging the model and avoiding manual implementation of reference data checks.
-
Reference Data: Models include reference data models for defining dictionaries and their master versions, providing master reference data across sources, and effectively creating a bridge to master reference values on loading or cleansing processes.
Attributes defined in model entities can then be mapped to reference data dictionaries, with all logic being generated with the MDM process plans.
-
Refreshing: This feature serves for regenerating lookups when reference data is altered but uses a temporary copy of previous lookups until the new ones are made available. As such, it ensures business continuity and no downtime during lookup regeneration.
-
Reprocess: Existing data might need reprocessing after the reference data is changed, even if there are no updates coming from the original source systems.
MDM provides out-of-the-box options to trigger a reprocess, also enabling selective reprocessing based on metadata aspects (IDs, source systems, and so on).
For advanced administration and use of reference data, we recommend using Ataccama Reference Data Manager. This tool integrates seamlessly with Ataccama MDM to provide strong and tightly integrated master and reference data management. For more information about ONE RDM, see Welcome to RDM.
Disaster recovery and high availability
MDM Engine is designed to support both disaster recovery (DR) and high availability (HA), provided that all configuration requirements are satisfied. If set up, unfinished transactions can be rolled back and all states are saved to a storage.
Keep in mind that, for DR and HA to work, other components of the MDM solution need to be configured based on your specific use case (such as integration or orchestration), including infrastructure components and the database server.
Furthermore, different options are available for different deployment types. For optimal results, we strongly recommend having a member of Ataccama Professional Services team design the solution.
| If you are looking for assistance regarding the solution design, contact Ataccama Support. |
Was this page useful?
