Processors
A processor is a component of the Async Event Handler that controls how captured events are consumed and passed to publishers. Each event handler requires exactly one processor.
For an overview of processor types and their behavior, see Types of processors.
This article describes how to configure each processor type.
Before you start
-
Configure the instance layer model as described in Creating an Instance Layer Model using the top-down modeling approach.
-
Configure a master layer model as described in Creating a Master Data Layer Model using the top-down modeling approach.
| For more information, Creating a Logical Model. |
Batching event processor
-
Go to Output Interfaces > Event Handlers (right-click) > New Event Handler Definition.
-
Select
EventHandlerAsyncand confirm your choice. -
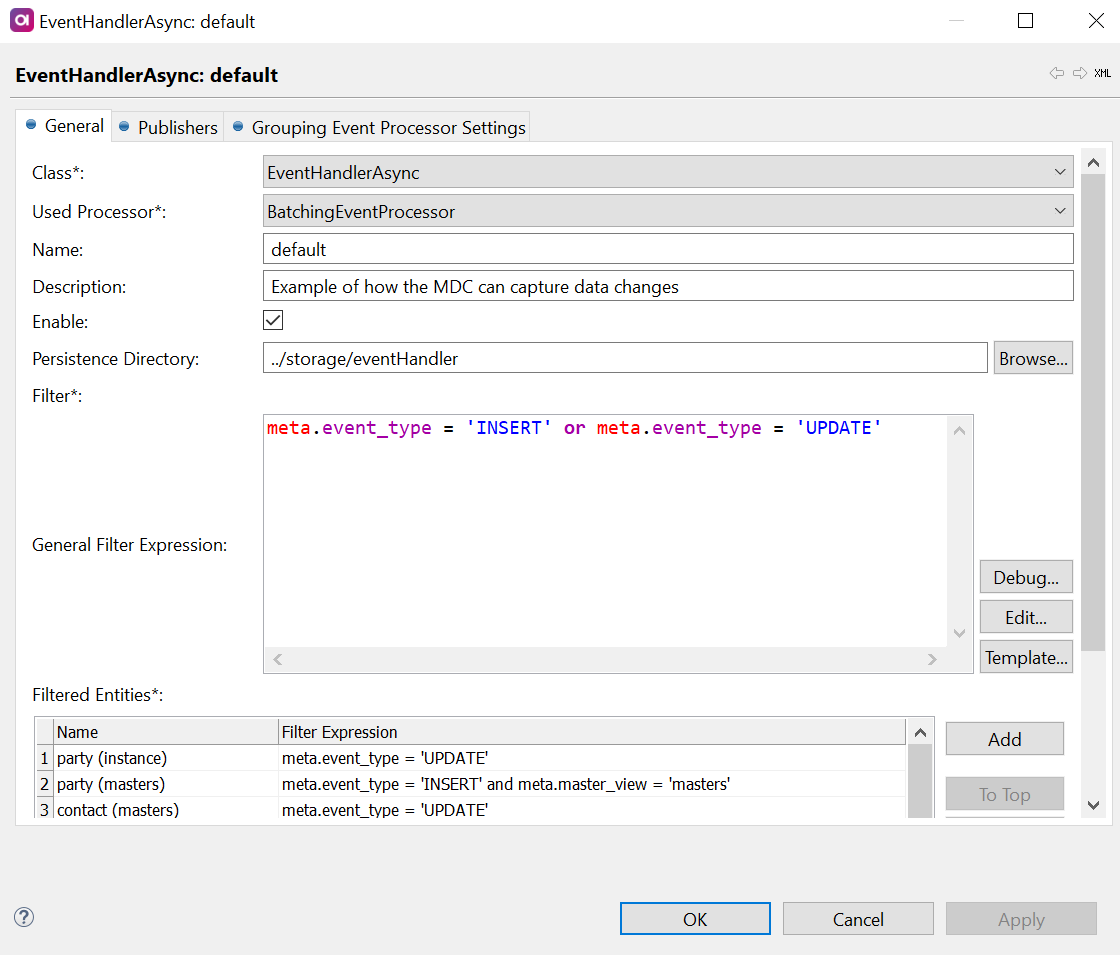
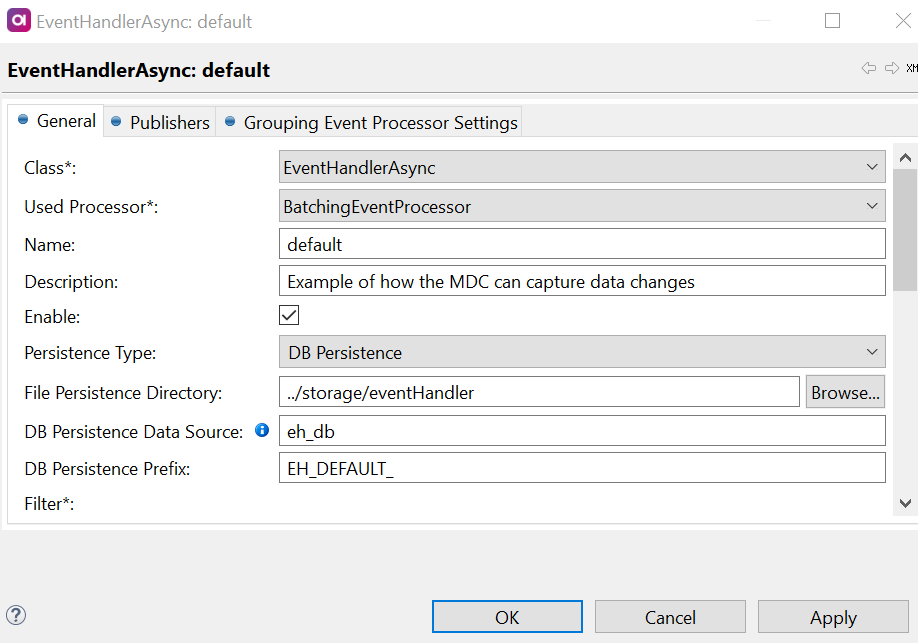
Set the following parameters:
-
Class - Filled in by default. The specific implementation of the data changes handler (
EventHandlerAsync). -
Used Processor - Select
BatchingEventProcessor. -
Name (optional) - Name to distinguish between multiple event handlers. If no name is entered, the Class type is used by default, but if multiple event handlers exist, providing names is required.
-
Description (optional) - Description of the handler.
-
Enable - Activate (
true) or deactivate (false) the event handler. -
Persistence Type, DB Persistence Data Source, and DB Persistence Prefix - See Event handler persistence.
-
Persistence Directory - Set a path to the folder for captured events before publishing.
-
Filter - Define a filter to preselect events (for example, only record updates). For details, see Filters.
-
-
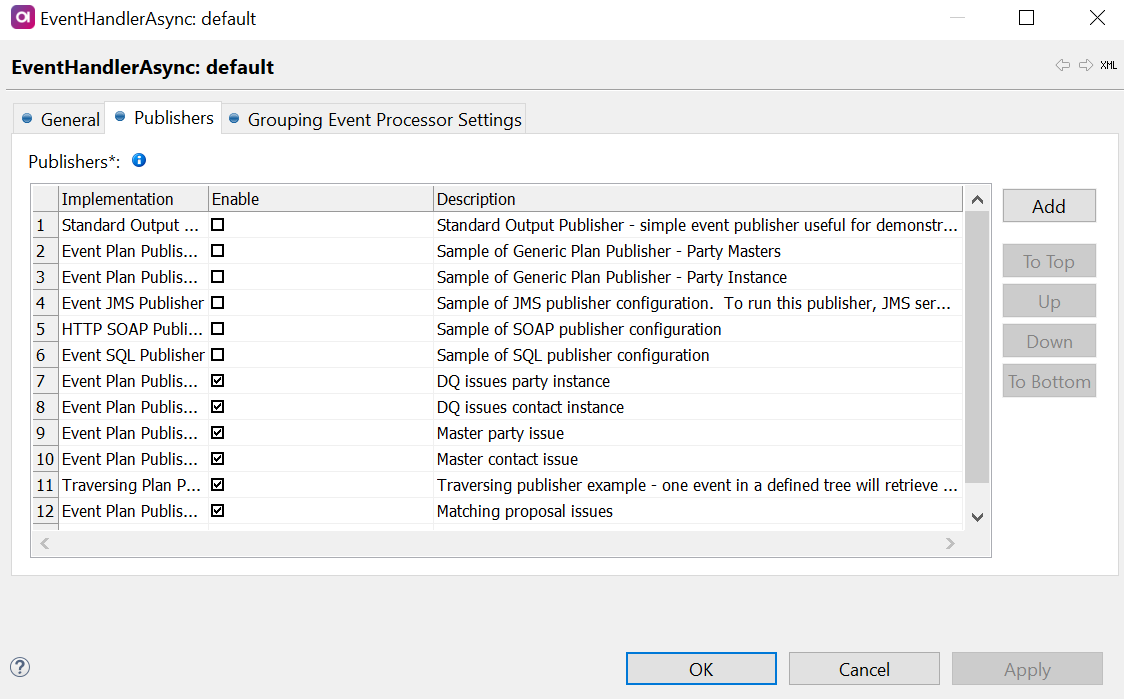
Go to the Publishers tab to define how event are distributed to external systems.
-
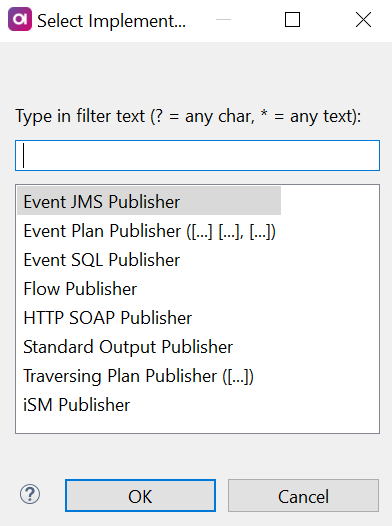
To add a new publisher, double-click the row number or select Add. Select the desired publisher from the list of available options.
-
Enable the publisher by selecting the option.
Each publisher has to be configured to connect to external systems. See the corresponding publisher configuration.
-
Simple event processor
We recommend using the event plan publisher with the simple event processor.
-
Go to Output Interfaces > Event Handlers (right-click) > New Event Handler Definition.
-
Select
EventHandlerAsyncand confirm your choice. -
Set the following parameters:
-
Class - Filled in by default. The specific implementation of the data changes handler (
EventHandlerAsync). -
Used Processor - Select
SimpleEventProcessor. -
Name (optional) - Name to distinguish between multiple event handlers.
-
Description (optional) - Description of the handler.
-
Enable - Activate (
true) or deactivate (false) the event handler. -
Persistence Type, DB Persistence Data Source, and DB Persistence Prefix - See Event handler persistence.
-
Persistence Directory - Set a path to the folder for captured events before publishing.
-
Filter - Define a filter to preselect events (for example, only record updates). For details, see Filters.
-
-
Go to the Publishers tab to define how event are distributed to external systems.
-
To add a new publisher, double-click the row number or select Add. Select the desired publisher from the list of available options.

-
Enable the publisher by selecting the option.
Each publisher has to be configured to connect to external systems. See the corresponding publisher configuration.
-
Grouping event processor
You can define the grouping event processor based on the traversing publisher configuration by choosing your traversing plan publisher in the Grouping Event Processor Settings. This requires having a traversing plan publisher defined beforehand.
It is possible to configure multiple grouping processors if needed.
We recommend using the traversing plan publisher with the grouping event processor to remove duplicate results.
-
Go to Output Interfaces > Event Handlers (right-click) > New Event Handler Definition.
-
Select
EventHandlerAsyncand confirm your choice. -
Set the following parameters:
-
Class - Filled in by default. The specific implementation of the data changes handler (
EventHandlerAsync). -
Used Processor - Select the Grouping Event Processor.
-
Name - Optional name to distinguish between multiple event handlers.
-
Description - Optional description of the handler.
-
Enable - Activate (
true) or deactivate (false) the event handler. -
Persistence Type, DB Persistence Data Source, and DB Persistence Prefix - See Event handler persistence.
-
Persistence Directory - Set a path to the folder for captured events before publishing.
-
Filter - Define a filter to preselect events (for example, only record updates). For details, see Filters.
-
-
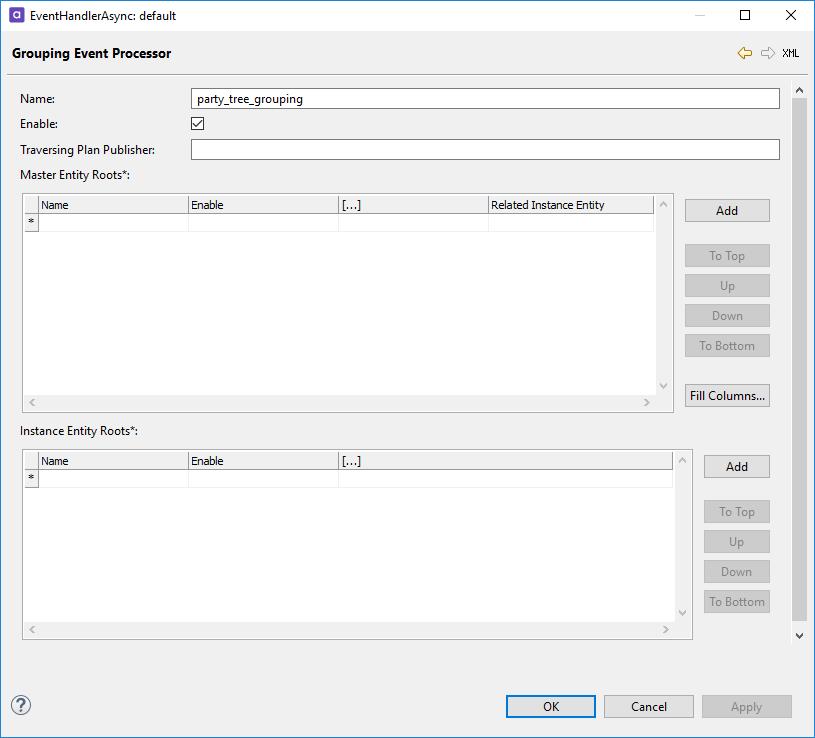
Open the Grouping Event Processor Settings tab to configure the entity tree model. Add a grouping event processor by clicking the asterisk (
*) next to the empty row. -
To configure the tree model, choose whether you wish to configure it for an instance entity root or a master entity root. Choose the Master Entity Roots or Instance Entity Roots tables accordingly.
-
To create a new root, select Add, or double-click the asterisk (
*) in the table row.Press Ctrl+Space in the Name column to see a list of all available entities.
-
Double-click the first row space in the […] column to open the configuration for related entities.
-
Add the related entities by double-clicking the asterisk (
*) in the table row and using Ctrl+Space to get a list of available child entities. -
Repeat the previous steps for as many roots as you wish to configure.
-
-
Go to the Publishers tab to define how event are distributed to external systems.
-
To add a new publisher, double-click the row number or select Add. Select the desired publisher from the list of available options.

-
Enable the publisher by selecting the option.
Each publisher has to be configured to connect to external systems. See the corresponding publisher configuration.
-
Filters
When defining a filter for events, specify the following:
-
General Filter Expression - A common filter based on metadata attributes: only the
metadot-source is supported here.A Boolean ONE expression can be specified. In that case, only the events for which the expression evaluates to
trueare accepted.If left empty, all events are accepted. See Event Handler > Evaluation of ONE expressions.
-
Filtered Entities - Define which entities should be monitored for data changes (events from all other entities are filtered out). Optionally, use a filter expression on the entity level:
meta,new, andolddot-sources are supported.Each entity is identified by its name, layer (instance or master), and, for master entities, the master view. This has to be an existing entity that has not been already filtered out earlier (usually by a filter on the parent element).
Each entity can have its own
filterExpressionthat works exactly like thefilterExpressionexcept all the data columns are available (old and new values of the changed records as well as metadata columns).
| For example, the event handler can be configured to do the following: "Capture all changes to the first_name attribute in the party entity and send a message to the JMS queue". This would be useful, for example, if your organization is a bank, as changes to attributes like first name and ID card number are suspicious and should be tracked. |
Event handler persistence
Event handlers can use file persistence (default) or database persistence.
Database persistence is generally slower than file persistence but it is easier to make it highly available (by using an HA database).
The following optimizations are available:
-
Adding events with batch inserts.
-
Adding index for selecting events.
| When switching the persistence type, ensure all events are published first. |
To define persistence for event handlers, go to Output interfaces > Event Handlers. Right-click the event handler and select Edit.
Select Persistence Type and fill in the necessary information. If you select DB Persistence, you need to define the DB Persistence Data Source and DB Persistence Prefix.
Was this page useful?
