Create Reference Data Tables
Reference data tables represent data you have stored in ONE. This guide shows you how to create new tables using different methods based on your data source.
|
This topic covers creating new tables. To import data into an existing table, see Import Data into Existing Tables. |
Next steps: After creating your first table, continue with Set Up Access and Governance to control who can access and modify your data.
Create tables
|
You can access the metadata of each reference data table in the Data Catalog as well (Catalog > Data Catalog > Published Reference Data). These tables appear as reference data catalog items. |
You can create new tables in one of the following ways:
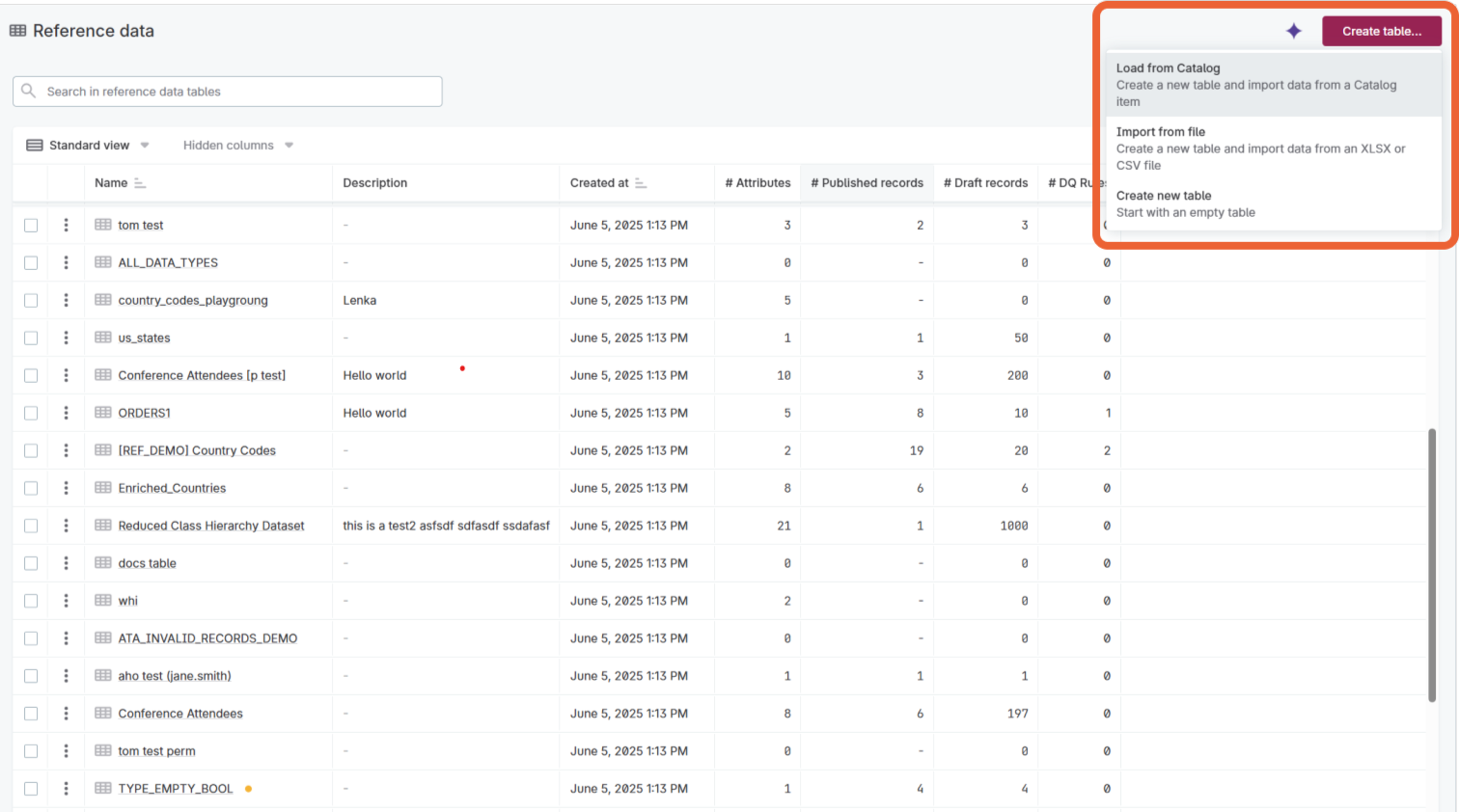
Create an empty table
You can create an empty table and fill in attributes and records manually.
To create an empty table:
-
Go to Reference data > Tables.
-
Select Create table.
-
Select Create new table.
-
Enter a Table name.
-
Select Confirm.
After creating the empty table, it opens on the Data structure tab where you can continue with defining the table structure and adding records.
For next steps, see:
Create a table from catalog data
You can create a new reference data table by loading data from an existing catalog item. This approach lets you select specific columns and apply data transformations for advanced data preparation use cases.
|
Permissions: You need Full access or Editing access to Data Transformation plans to create reference data from catalog items. |
From the Reference data section
To create a table from a catalog item using the Reference data section:
-
Go to Reference data > Tables.
-
Select Create table.
-
Select Load from Catalog.
-
Select a catalog item from the list.
Use the search box to find the item you need. -
Select Next.
-
Configure Source and Target settings:
-
Source:
-
Selected Catalog item: Confirm the selected catalog item.
-
Import: Choose whether to import all attributes or selected attributes only.
-
-
Target:
-
Enter new table name: Enter a name for your new table.
-
Open the dataset in data transformations to prepare it before loading: Prepare the data using transformation steps.
-
-
-
Select Next.
-
(Optional) If you selected specific attributes, choose which ones to load.
-
Select Load data.
Your new table and its records are now created.
From a catalog item directly
You can also create reference data directly from a catalog item without going through the Reference data module:
-
In Catalog, find and open the catalog item you want to use as reference data.
-
Select the three-dots menu > Create reference data.
-
Configure the settings as described in Create a table from catalog data.
-
Select Load data.
This approach is useful when you’re already working with catalog items.
|
Both methods are equivalent - use whichever matches your workflow. If you’re in the Reference data module, use the first method. If you’re already in the catalog, use the second method. |
Create a table from a file
You can create new tables by importing XLSX and CSV files. Optionally, use AI to help design your table structure during import.
To create a table from a file:
-
Go to Reference data > Tables.
-
Select Create table.
-
Select Import from file.
-
Upload your file:
-
Drag and drop into the Source file area, or
-
Click Browse files and select from your system.
-
-
Configure import settings:
Import options are autodetected, which means you can usually leave them as is, unless you encounter issues. -
In the Source file section, you have the following options:
-
Remove: Removes source file and returns you to the beginning of the import flow.
-
Reset settings: Resets changed settings to the autodetected defaults.
-
Use first row as header: Select this if the first row of your table is a header row.
-
File encoding: Select the encoding type of your file.
-
Value separator: Enter the symbol that separates values in your table.
-
In Source file preview, you can change the labels of the header rows as needed.
-
-
-
Select Next.
-
On the Data Model step, you can optionally use AI to help structure your table, or make manual modifications:
You can manually rename tables and attributes, add table descriptions, and set up deduplication keys.
Note that data types cannot be changed during import. You’ll need to modify them after import on the Data structure tab. .. Select Model with AI to start AI analysis.
+ The AI analyzes your file and suggests an optimal data model structure.
-
(Optional) Refine the model using the chat interface:
-
Enter natural language instructions to modify the structure. Example prompts appear in the input field, such as:
-
"Add a new table for policies"
-
"Remove the status field"
The AI responds to conversational requests. Be specific about what you want to change.
-
-
-
Review the visual preview of your table structure on the canvas.
-
When satisfied, select Next to continue.
If you don’t use AI modeling, select Next to proceed with the default structure.
-
-
Configure table settings:
-
Provide the following information:
-
Name: Enter a name for your table.
-
Description: (Optional) Add a description to help others understand the table’s purpose. You can also select Generate to have AI create a description based on your data.
-
-
-
To finish the import, select Create reference data. This creates the table and imports your data.
The table structure and records are published immediately. Relationships are also published, unless the operation would result in loss of data.
Tips for using AI modeling
When using the Model with AI feature:
-
Clean headers help: Files with clear, descriptive column names produce better AI suggestions.
-
Be specific in chat: Instead of "improve this", say "make Frame 1 the primary key".
-
Review the preview: Check the visual canvas to understand the suggested structure before proceeding.
-
Use it for exploration: AI modeling is helpful when you’re uncertain about the optimal table structure.
-
Manual editing available: After import, you can modify the table structure on the Data structure tab.
-
Data type limitation: Data types are autodetected from your file and cannot be changed during import. To use different data types, complete the import first, then change them on the Data structure tab.
For next steps after creating your table, see:
Generate table descriptions
After creating your table, you can automatically generate comprehensive descriptions using AI. The AI analyzes your table structure and sample data to create meaningful, contextual descriptions that help users understand the purpose and content of each table.
AI generation options
The AI assistant provides multiple generation options:
-
Generate complete descriptions from scratch: Creates new descriptions based on table structure and data.
-
Fix grammar and improve existing descriptions: Enhances existing descriptions with better grammar and clarity.
-
Improve writing style and word choice: Refines the language and style of existing descriptions.
Generate a table description
To generate an AI-powered table description:
-
The table should contain some data records for better AI analysis.
-
You must have Editor or Owner permissions for the table.
-
Go to Reference data > Reference data.
-
Select the table you want to add a description to.
-
In the table overview, select the AI description generator button.
-
Choose your preferred generation option:
-
Generate from scratch for new descriptions
-
Fix grammar to improve existing content
-
Improve style to enhance writing quality
-
-
Review the generated description.
-
Select Apply to use the generated description, or Regenerate to create a new version.
-
The AI-generated description will be added to your table metadata and will be visible to all users who have access to the table.
You can also access the AI description generator during the file import process to add descriptions as you create tables.
Best practices
-
Ensure your table contains representative data before generating descriptions.
-
Review and customize AI-generated descriptions to match your organization’s terminology.
-
Use the "Fix grammar" option to improve existing descriptions written by team members.
-
Consider regenerating descriptions when your table structure or data significantly changes.
Next steps
After creating your table, you can continue with other workflows:
-
Manage access: Set Up Access and Governance - Control who can access and modify your data
-
Publish your data: Publish and Approve Reference Data - Make your reference data available across the platform
-
Update data: Import Data into Existing Tables - Keep your table current with data imports
-
Use your data: Work with Published Reference Data - Access your published data throughout ONE
For advanced scenarios, explore:
-
Export to Databases - Write reference data to external systems
-
Create Validation Rules - Enforce data quality
-
Deduplicate Data - Extract clean unique values
Was this page useful?
