AI Agent
The ONE AI Agent is designed to radically transform data management by providing a general purpose tool for automating many of the most tedious tasks. The current version of the ONE AI Agent focuses primarily on data quality.
Before you start
Take a moment to get familiar with the recommended practices for using Generative AI capabilities of ONE, described in Gen AI Best Practices. This will help you use Generative AI more effectively.
Using the AI Agent requires specific identity provider roles. See Identity Provider Roles.
What is an AI agent
An AI agent is an intelligent system that uses Large Language Models (LLM) to perform complex tasks on the behalf of users.
In contrast to AI assistants or chatbots that primarily answer questions, AI agents have the ability to dynamically plan, refine, and execute plans that utilize API-based tools. These plans are not rigid workflows but are rather dynamic steps that are planned and validated as the agent works.
ONE AI Agent
| The AI model is not trained using your data or metadata. |
In ONE, the AI Agent is a general purpose tool that can handle both atomic tasks and questions like a typical AI assistant as well as manage and plan for complex, multi-step tasks. This means the Agent is capable of completing a broad array of tasks across the platform.
The AI Agent plays a key role in optimizing data management through:
- Intelligent task planning
-
Creating and executing plans for complex tasks across the platform, not limited to just data quality.
- Specialized tool utilization
-
Leveraging various tools for searching, accessing metadata and data, modifying content, and performing utility functions.
- Automated data management
-
Reducing manual effort by handling tasks like data quality checks, rule generation, and catalog management.
- Data exploration and analysis
-
Finding specific information in your data and generating insights based on patterns and trends.
- Documentation assistance
-
Answering questions about platform functionality directly from documentation.
By integrating automation, intelligence, and compliance capabilities, the AI Agent in Ataccama ONE enhances data governance, decision-making, and operational efficiency, which in turn helps you manage data with greater confidence and precision.
AI Agent capabilities
The AI Agent uses the following tools to form plans that can execute complex work:
|
Complex requests can take longer than simple queries. For example, bulk creation of data quality rules could take three minutes and more to fully run. Be clear about your question and expectations. |
Search capabilities
-
Catalog search: Search for database catalog items based on keywords.
-
Business terms search: Search for business terms in the business glossary.
-
Rule search: Find existing rules in the catalog.
-
Documentation search: Ask questions about the documentation.
Metadata and data access
-
Catalog metadata search: Retrieve metadata of a catalog item.
-
Attribute fetcher: Fetch attributes of a catalog item.
-
Profiling tool: Access existing profiling data about attributes from the catalog.
-
Data sample tool: Get a data sample of a catalog item.
-
SQL query tool: Retrieve data of a catalog item using an SQL query.
Data modification tools
-
SQL catalog item creation: Create a new SQL catalog item based on a SQL query.
-
DQ rule creation: Create a new DQ evaluation rule.
-
DQ rule assignment: Assign a rule to attributes of a catalog item.
-
Description generation: Generate or improve a description for a catalog item, attribute, rule, or term.
Reference data tools
-
Search reference data tables: Search for reference data tables by name substring.
-
Fetch reference data table attributes: Fetch the schema (attributes/columns) of a reference data table.
-
Fetch reference data table data sample: Fetch sample data rows from a reference data table.
-
Generate reference data table description: Generate an AI-powered description for a reference data table.
-
Create reference data table: Create a new empty reference data table.
-
Rename reference data table: Rename an existing reference data table.
-
Set reference data table description: Set or update the description of a reference data table.
-
Apply reference data table metadata changes: Apply pending schema changes to a reference data table.
-
Create reference data table attribute: Create a new attribute (column) in a reference data table.
-
Rename reference data table attribute: Rename an attribute (column) in a reference data table.
-
Delete reference data table attribute: Delete an attribute (column) from a reference data table.
-
Change reference data table attribute data type: Change the data type of an attribute in a reference data table.
-
Connect reference data table attribute: Connect an attribute to reference another table’s attribute, creating a foreign key relationship.
-
Assign DQ rule to reference data table attribute: Assign a data quality rule to reference data table attributes.
-
Upsert reference data table records: Create new records or update existing records in a reference data table.
-
Edit reference data table: Modify data in a reference data table using SQL UPDATE queries.
-
Delete reference data table records: Delete records from a reference data table using filters.
-
Discard reference data table records changes: Discard draft record changes and restore data from the published state.
AI Agent use cases
Here are the key use cases you can perform with the AI Agent:
Data quality management
-
Generate DQ rules in bulk from table:
-
Example: "Implement all DQ rules listed in table [table_with_DQ_rules] and apply them on table [Catalog item]."
-
Example: "Generate one expression checking if the value matches this pattern. First two letters 'AB' and 5 numbers. Use regular expressions."
-
-
Apply DQ rules in bulk:
-
Example: "Create a DQ rule for validation of product codes. The product code needs to start with 3 capital letters, followed by optional dash, followed by 3 to 6 digits."
-
-
DQ evaluation of a catalog item:
-
Example: "Assess data quality of table [Catalog item]."
-
Data exploration and analysis
-
Find information in data and metadata:
-
Example: "Find conference attendees that were not from United States."
-
Example: "What is the percentage of null values in zipcode in table [Catalog item]."
-
Example: "What is the longest company name in attribute company_name in table attendees?"
-
Catalog management
-
Catalog search:
-
Example: "Find all tables related to [topic]."
-
-
Create SQL catalog item:
-
Example: "Create SQL CI selecting amount and payment day columns from payments table from pgs_testdata source."
-
-
Generate description for a table:
-
Example: "Generate description for table [table_name]."
-
-
Catalog item comparison:
-
Example: "What are the differences between these two tables, party and party01?"
-
-
Catalog item source understanding:
-
Example: "Is it possible to join this CREDIT_CARDS_ATTRITED table and CREDIT_CARDS table?"
-
Knowledge management
-
Chat with documentation:
-
Example: "How do I enable automated detection of a business term?"
-
-
Term search by owner:
-
Example: "Find Terms which are owned by Data Office."
-
-
Find appropriate rule:
-
Example: "What rule should I use if I want to validate email values?"
-
Reference data
-
Create and configure reference tables:
-
Example: "Create a new reference data table for currency codes with columns code, name, and symbol."
-
Example: "Add a new attribute 'region' to the country_codes reference table."
-
-
Manage reference data content:
-
Example: "Add these 5 new country codes to the countries reference table."
-
Example: "Update the status field to 'inactive' for all products with price less than 10."
-
-
Reference data exploration:
-
Example: "Show me sample data from the product_categories reference table."
-
Example: "What attributes does the customer_segments reference table have?"
-
-
Reference data quality:
-
Example: "Assign data quality rules to the email attribute in the contacts reference table."
-
Example: "Generate a description for the payment_methods reference table."
-
-
Reference data relationships:
-
Example: "Connect the country_id attribute in orders table to the id attribute in countries reference table."
-
-
Bulk reference data operations:
-
Example: "Import data from the product_catalog catalog item into the products reference table."
-
Limitations
The AI Agent can intelligently chain together the tools and capabilities listed in AI Agent capabilities. When these tools are combined in agentic workflows, you can address different use cases in the platform. Since there is no technical limit to the requests you can send, there is no strict limit to what you can achieve.
While we can’t provide an exhaustive list of possible use cases, we actively test and support those listed in AI Agent use cases. Results for unlisted use cases can’t be guaranteed.
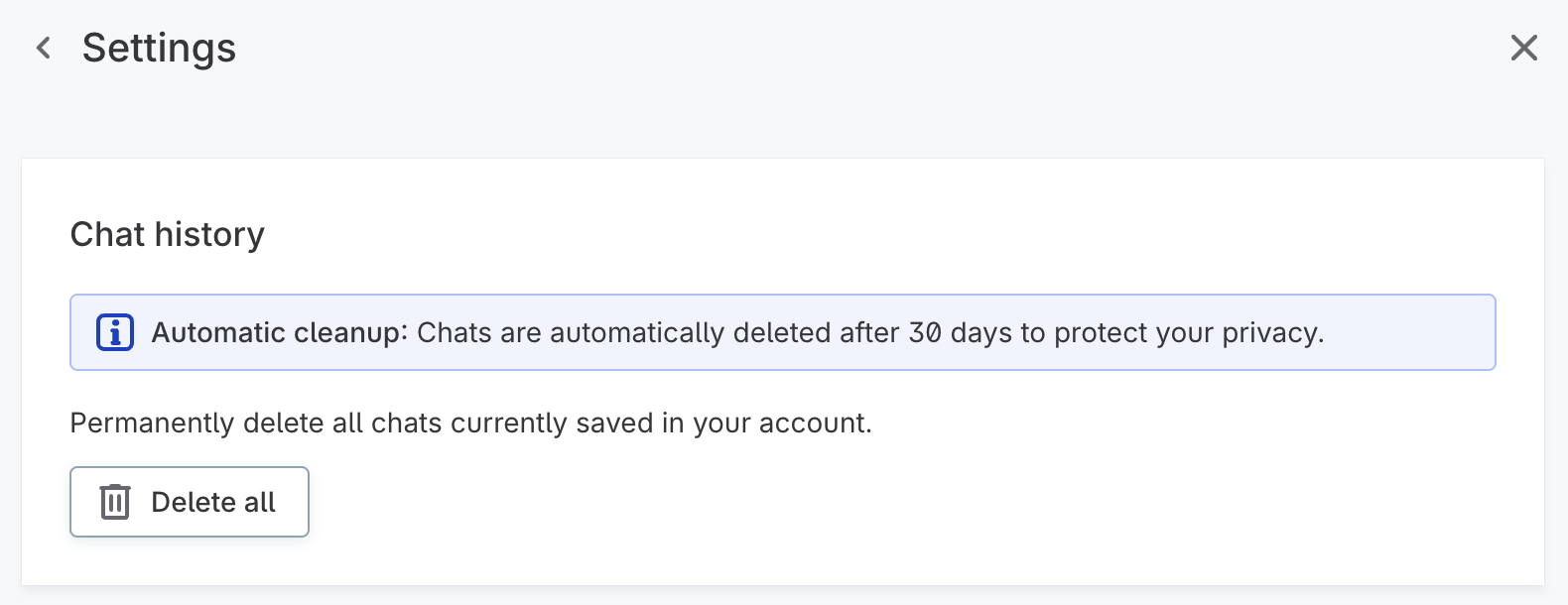
How to use AI Agent
Open the AI Agent chat window at any time from the left-side navigation menu.
Additionally, the AI Agent is available throughout the platform, for example in the Catalog or Glossary. When accessed from these locations, the AI Agent can provide context-aware assistance relevant to the assets.
| Look for the star icon in the upper-right corner to open the AI Agent from these locations. |
AI Agent interface
When you open the AI Agent, a chat window appears with a field where you describe your task.
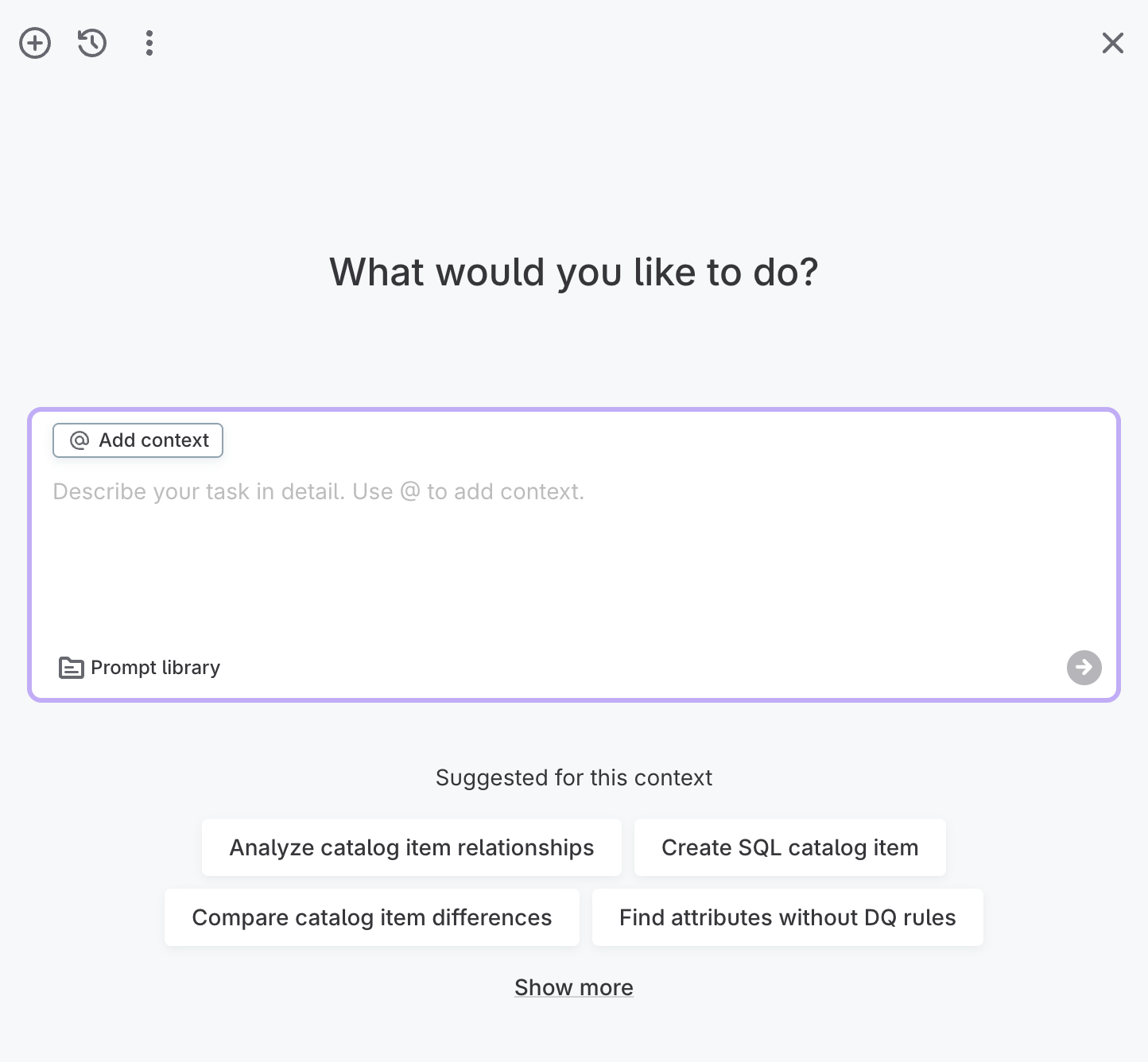
The interface includes the following elements.
Top toolbar
-
New chat (plus icon): Open a new chat.
-
Chat history (clock icon): Access previous chats.
-
More options (three dots): Access Prompt library or Settings.
-
Close (X icon): Close the AI Agent window.
Start a new chat
To start a new chat, select the new chat icon. Write a query in natural language and press Enter or select the arrow.
You can also choose from the prompt library or select one of the suggested prompts.
In the following example, we ask the AI Agent to find attributes of a specific catalog item, and let it suggest rules for it.
Find attributes of @DQ_CI_DIMENSIONS_FACTS with no rules applied, and suggest appropriate rules for them.
| Use @ to select entities and data assets when writing queries. |
I have identified that all attributes of the catalog item
DQ_CI_DIMENSIONS_FACTS do not have any rules assigned to them. Based on their data types, I have suggested appropriate rules for each attribute:
STRING Attributes: For attributes like REPORT_ID, PROCESSING_ID, CONFIGURATION_ID, CONFIGURATION_NAME, CATALOG_ITEM_ID, CATALOG_ITEM_NAME, DIMENSION_ID, and DIMENSION_NAME, I suggest a rule to check that the value is not empty.
DATETIME Attributes: For attributes like PROCESSING_STARTED_AT and PROCESSING_FINISHED_AT, I suggest a rule to check that the value is a valid date format.
LONG Attributes: For attributes like FAILED_COUNT, PASSED_COUNT, and TOTAL_COUNT, I suggest a rule to check that the value is non-negative.
Interact with AI Agent responses
After you submit a query, the AI Agent processes your request and displays the response.
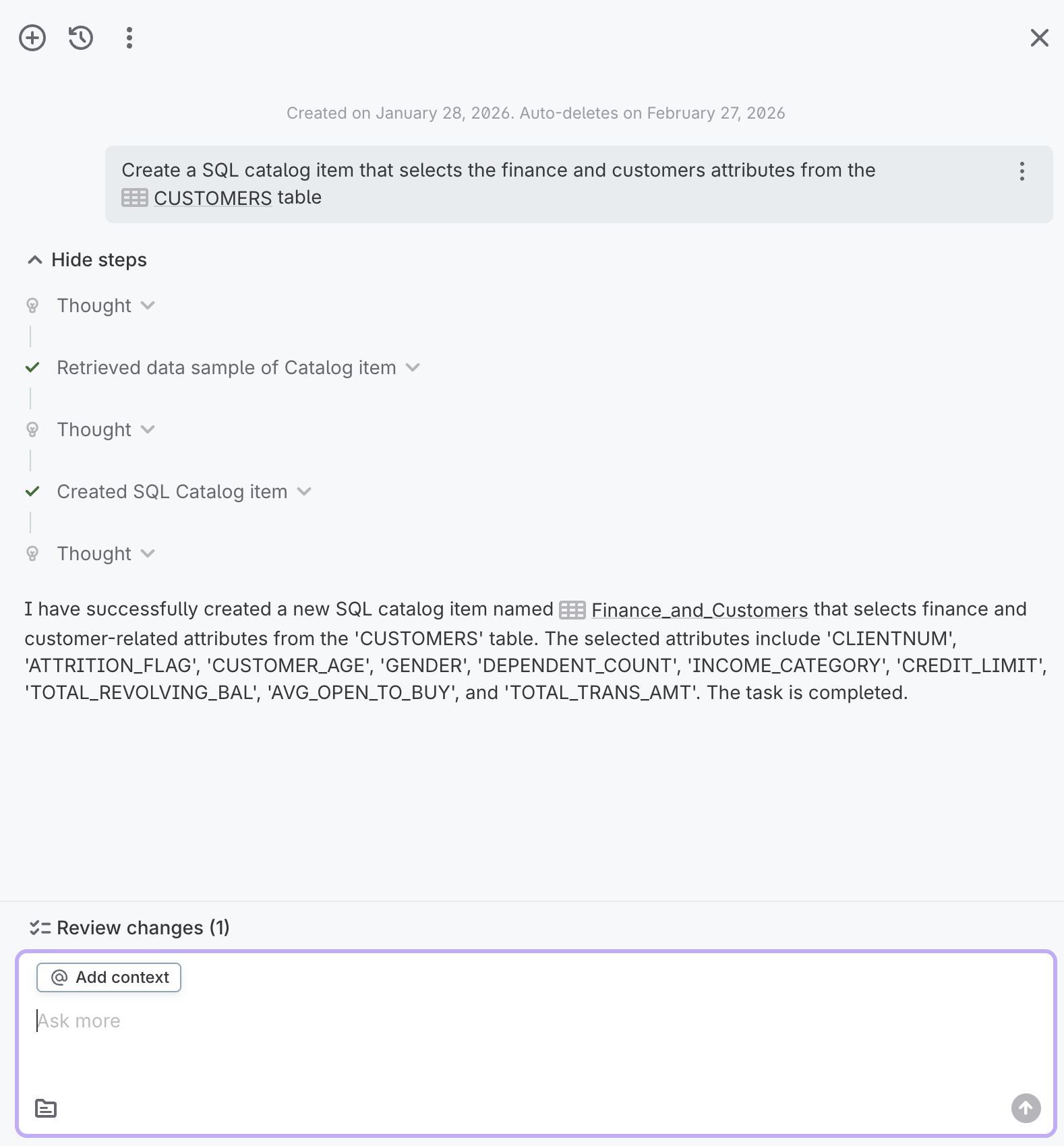
You can interact with the results in one of several ways:
-
Steps: Select Show steps to see the steps the AI Agent took to complete your request. Each step shows the action taken, such as retrieving data or creating items. Select Hide steps to close this view.
-
Review changes: If the AI Agent made changes during the conversation, you can see a summary in Review changes.
-
Continue the conversation: Use the query field to ask follow-up questions or refine your request. Select Add context to reference additional entities using the
@symbol.
Was this page useful?