Unstructured Data Governance
| This feature is currently in beta and is turned off by default. To enable it, contact your Customer Success Manager. |
Unstructured data governance lets you catalog and govern unstructured documents, such as PDF, DOCX, or TXT files, stored in your connected sources using the same concepts that apply to structured data.
How it works
When you add files to a document collection, ONE uses AI to analyze their content. You define what the AI looks for using two components:
-
Document categories specify the types of documents the AI should recognize. When a document matches a category, ONE assigns the linked glossary term. See Create document categories.
-
Extraction entities specify what information the AI should detect within documents. Detected entities are also linked to glossary terms. See Create extraction entities.
Based on this configuration, the AI can:
-
Classify documents into categories (for example, invoices, contracts, receipts).
-
Detect assets such as PII, financial data, or product codes.
-
Organize documents for compliance, governance, or downstream processing.
Supported sources and file formats
- Sources
- File formats
-
PDF, DOCX, DOC, PPTX, PPT, XLSX, ODT, RTF, HTML, MD, TXT, LOG
Work with unstructured data
Document files from a source
To add files from a source to a document collection:
-
Navigate to Catalog > Sources and open your source.
-
Switch to the Connections tab and expand the browser to view available files.
-
Select the files you want to add:
-
For a single file, select the Document file button next to it.
-
For multiple files, select the files and choose Document files from the dropdown menu.
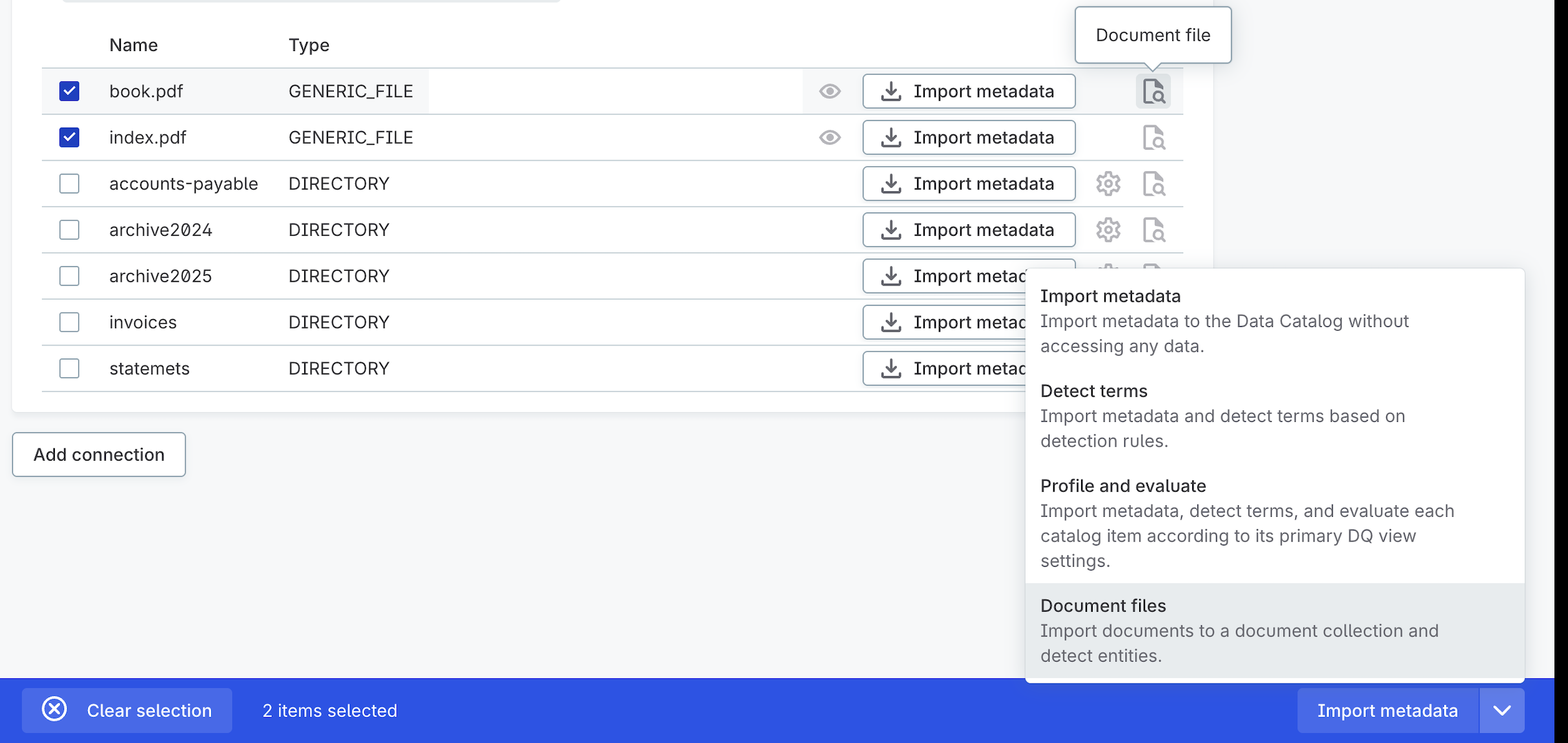
-
-
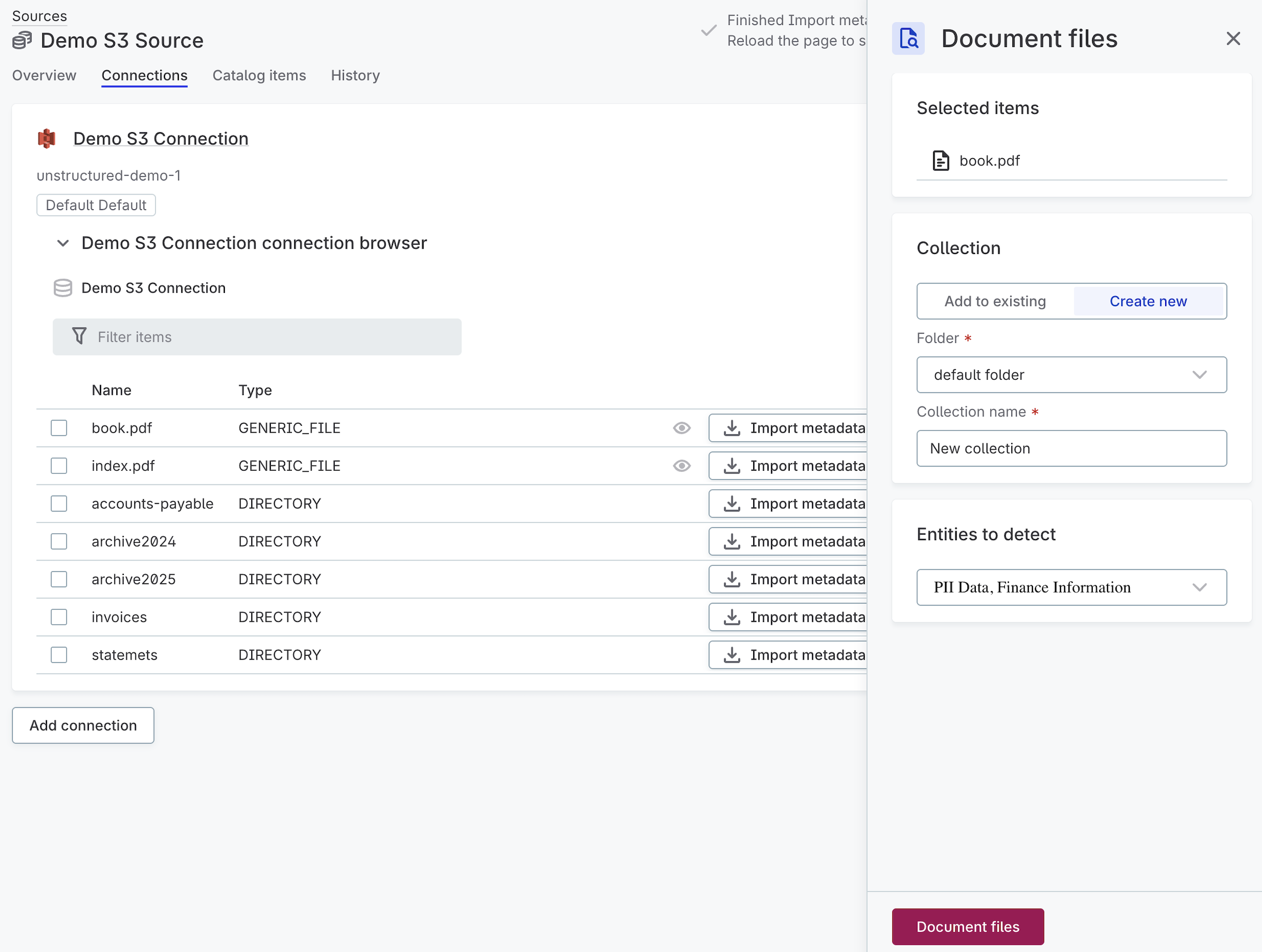
In Document files, configure the following:
-
Collection: Add files to an existing collection or create a new one. For a new collection, specify the folder and name.
-
Entities to detect: Select entity types to detect (for example, PII Data, Finance Information).
-
-
Select Document files: The files are added to the collection and analyzed by the AI. Once complete, you can view the results in the Catalog.
View results in the Catalog
Document collections appear in the Catalog as catalog items. To view a collection, navigate to Catalog > Data catalog and open it.
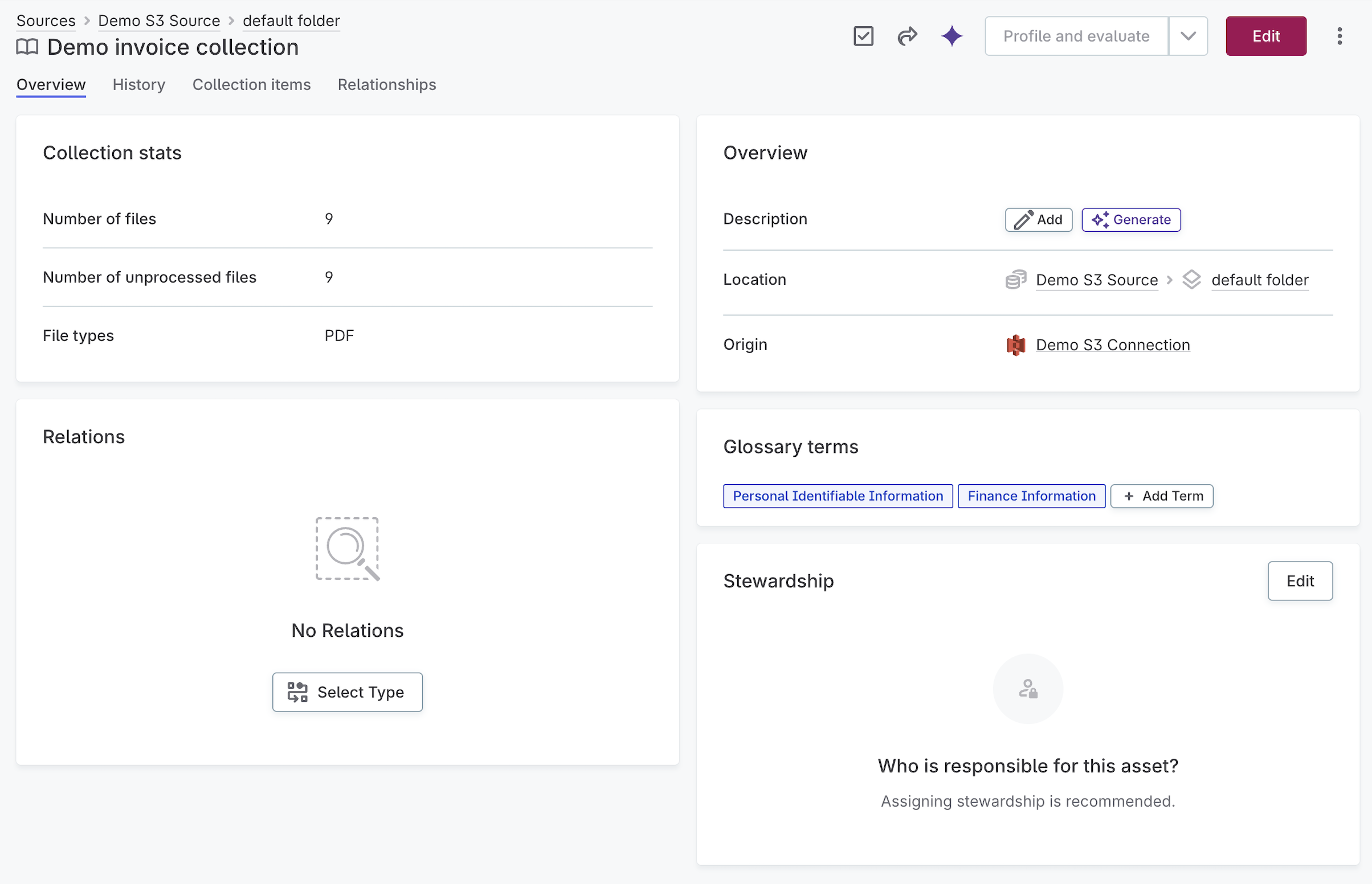
The collection overview displays:
-
Collection stats: Number of files, unprocessed files, and file types.
-
Overview: Description, location, and origin connection.
-
Glossary terms: Terms detected in the collection (for example, PII, Finance Information).
-
Relations: Connections to other catalog items.
-
Stewardship: Assigned owner and roles.
To view details for a specific file, switch to the Collection items tab and select a file.
Create document categories
Document categories define how the AI classifies your files. The AI uses the category name and definition to determine the best match for each document, then assigns the linked term.
To view document categories, navigate to Glossary > Unstructured data > Document categories.
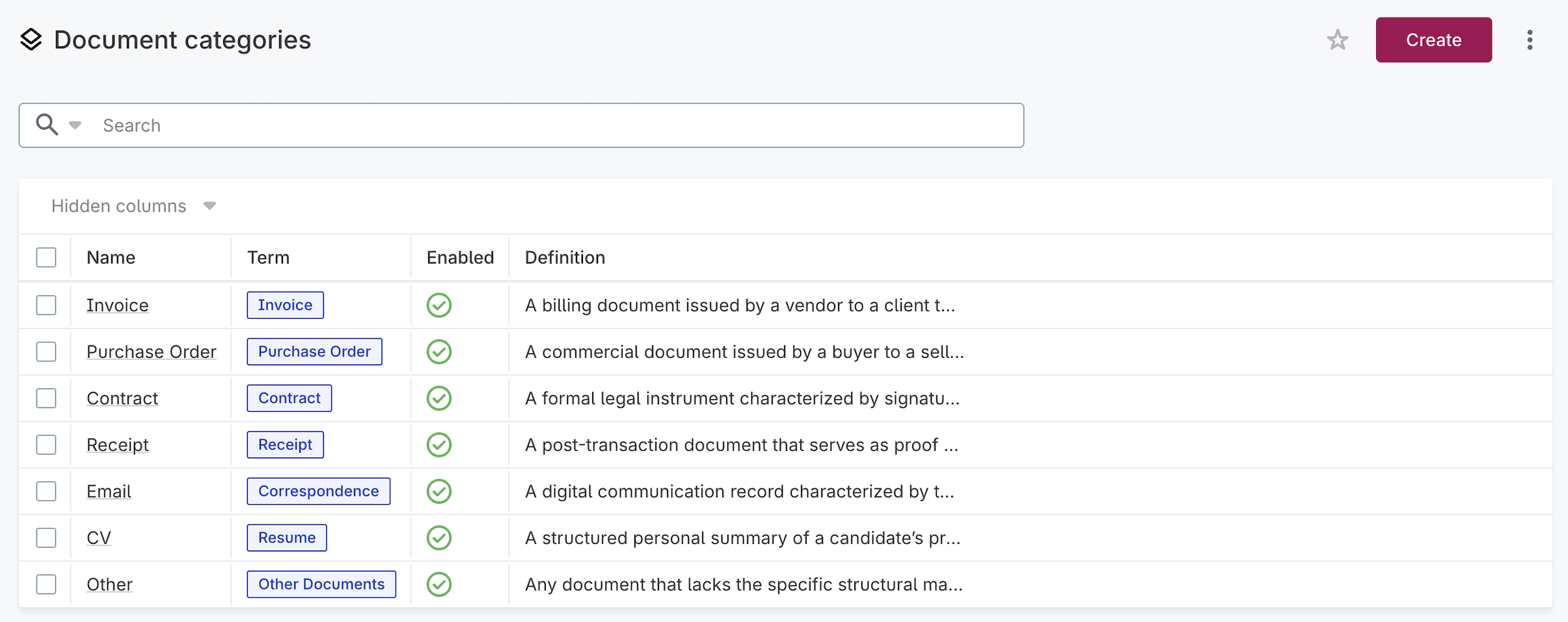
To create a new category, select Create and provide:
-
Name: The category name (for example, Invoice, Contract, Receipt).
-
Definition: A description of this document type.
-
Term reference: The glossary term to assign when this category is detected.
-
Enabled: Select to activate the category.
Create extraction entities
Extraction entities define what information the AI should detect within documents. Entities are grouped into lists by domain (for example, PII Data, Finance Information).
To view extraction entity lists, navigate to Glossary > Unstructured data > Extraction entity lists.
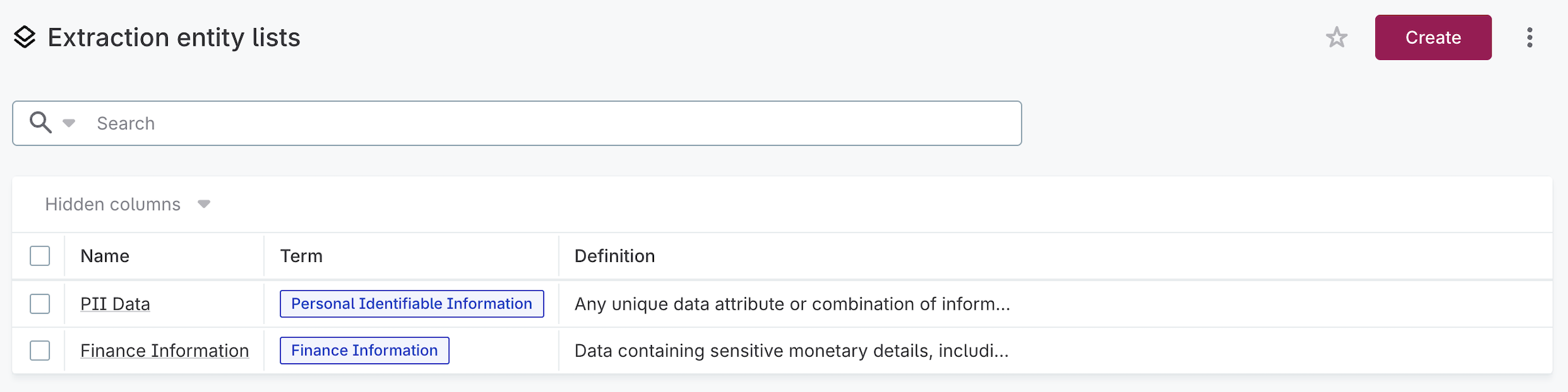
To create a new entity list, select Create and provide:
-
Name: The list name (for example, PII Data).
-
Definition: A description of what this entity list covers.
-
Term reference: The term to associate with this entity list.
-
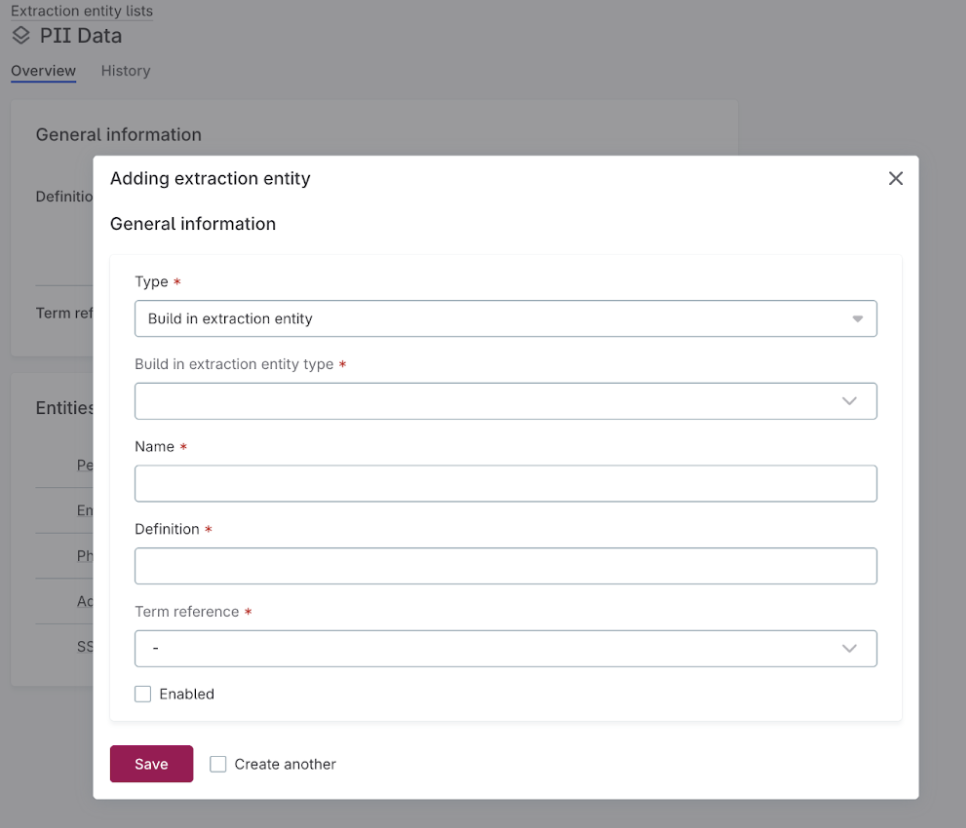
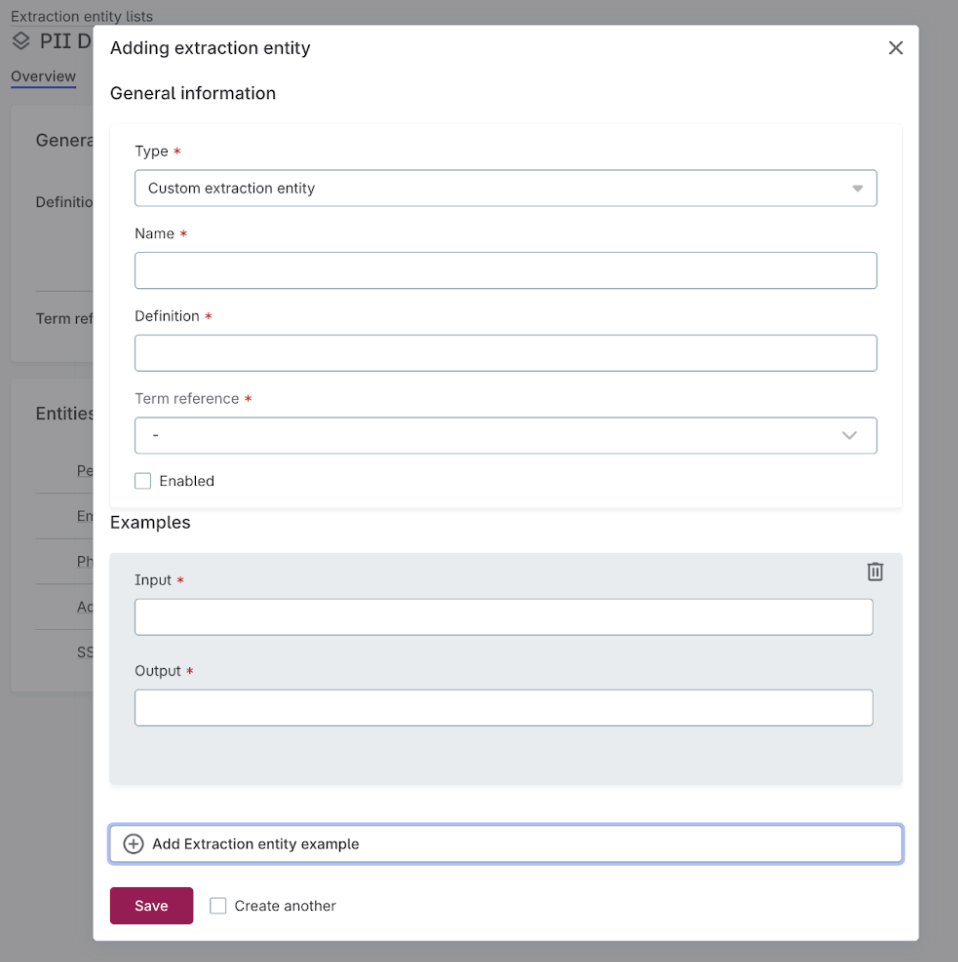
Extraction entities: Add extraction entities. Entities can be either built-in or custom:
-
Built-in: Select a predefined entity type that the AI recognizes automatically. The name and definition are for display purposes only—the model uses the built-in type for detection.
-
Custom: Define entities using a name, definition, and examples. The definition should describe the format and purpose of the entity (for example, "A unique, short-form alphanumeric string such as an SKU, EAN, or UPC"). Add examples of values the AI should detect.
-
Was this page useful?
