Relational Database Connection
Follow this guide if you want to connect to a relational database such as Oracle, PostgreSQL, or Snowflake. For a full list of supported relational databases, see Supported Data Sources.
Create a source
To connect to a relational database:
-
Navigate to Knowledge Catalog > Sources.
-
Select Create.
-
Provide the following:
-
Name: The source name.
-
Description: A description of the source.
-
Deployment (Optional): Choose the deployment type.
You can add new values if needed. See Lists of Values.
-
| Alternatively, add a connection to an existing data source. See Connect to a Source. |
Add a connection
-
Select Add Connection.
-
In Connection type, choose Relational Database > [your database type].
-
Provide the following:
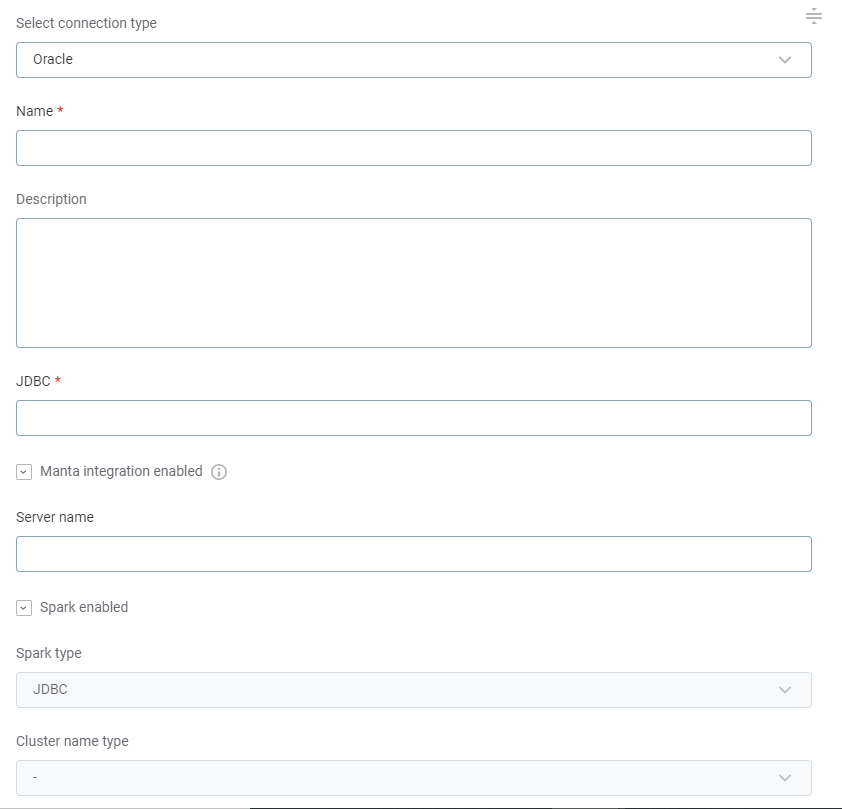
-
Name: A meaningful name for your connection. This is used to indicate the location of catalog items.
-
Description (Optional): A short description of the connection.
-
JDBC: A JDBC connection string pointing to the IP address or the URL where the data source can be reached. For a list of supported sources and JDBC drivers, see Supported Data Sources.
Depending on the data source and the authentication method used, additional properties might be required for successful connection. See Add Driver Properties. -
Manta integration enabled: Select this option to enable using MANTA, which is needed to calculate Lineage.
Manta is a data lineage platform bringing data lineage capabilities to ONE and is integrated during ONE deployment. -
Server name (related to Manta integration): The server of the database. This value is automatically filled after a successful connection to MANTA has been established.
-
Spark enabled: Enable Spark if you want to process large volumes of data using your Spark cluster. This improves how ONE works with relational databases during profiling and data quality tasks.
-
If selected, choose the Spark processing method:
-
JDBC: ONE Spark DPE creates a number of JDBC connections directly to the database to process data in parallel.
-
SPARK_CONNECTOR: ONE Spark DPE sources the data via another data provider, such as an ADLS Gen2 container or Amazon S3 bucket. This method might be faster for very large datasets.
-
-
Select the Spark cluster to process your data.
Only previously configured clusters are shown in ONE.
To add and configure a new cluster, refer to Metastore Data Source Configuration and Metastore Connection.
-
-
-
If you are connecting to Snowflake and want to use pushdown processing, proceed with Configure Snowflake pushdown processing.
Otherwise, go to step Add credentials.
Configure Snowflake pushdown processing
If pushdown processing is enabled, profiling is run entirely using Snowflake data warehouse. In addition, AI fingerprints used to calculate term suggestions are also computed in Snowflake.
During query pushdown, profiling results and data samples are sent to Ataccama ONE. To learn more, see Snowflake Pushdown Processing.
| Full profiling does not include domain detection, which is always executed locally by Data Processing Engine (DPE). |
| For pushdown processing to function, the credentials added for this connection need to be for a Snowflake user with write permissions, as pushdown processing involves writing into the working database (including creating tables). |
-
Select Pushdown processing enabled.
-
In Working database, provide the name of the database you want to use for storing the stage, functions, and temporary tables created during profiling. You have two options:
-
Use the database that is being processed (default).
-
Create a custom database (recommended).
Additional setup in Snowflake is required. See Create the working database in Snowflake.
-
-
In Grant to roles, add a JDBC role if you need to share the Snowflake pushdown setting across different credentials (for example, to a common underlying role).
Otherwise, you can leave the field empty.
Create the working database in Snowflake
In ONE, you only need to enter the working database name, as described in the previous step. However, you need to execute a script in Snowflake independently before proceeding, so that Snowflake allows Ataccama to transfer functions.
In Snowflake, select + Worksheet, and follow these instructions. The following script creates the working database and grants access to defined user roles.
-
Working database name (represented by
<working_db>placeholder in the example script): The name of the temporary database that is created to store Ataccama domain lookups and other temporary data. The database can be deleted after you finish using ONE.Multiple users can reuse the same database if they have access to it.
-
Roles (represented by
<pushdown_role>in the example script): Specify the Snowflake roles that can access the Ataccama working database. If no roles are specified here, all users have the access to the database. -
Users (represented by
<sample_user>and<another_user>in the example script): Assign the created role to users as required.
-- Create working database and stage
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS <working_db>;
CREATE STAGE IF NOT EXISTS _ATC_ONE_STAGE;
-- Create role
CREATE ROLE IF NOT EXISTS <pushdown_role>;
-- Assign role to user
GRANT ROLE <pushdown_role> TO USER <sample_user>;
GRANT ROLE <pushdown_role> TO USER <another_user>;
-- Grant access to database
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE <working_db> TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
-- Grant access to schema
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
GRANT CREATE TABLE ON SCHEMA public TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
GRANT CREATE SEQUENCE ON SCHEMA public TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
GRANT CREATE FUNCTION ON SCHEMA public TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
-- Grant access to stage
GRANT READ ON STAGE _ATC_ONE_STAGE TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
GRANT WRITE ON STAGE _ATC_ONE_STAGE TO ROLE <pushdown_role>;
----Add credentials
| OAuth 2.0 authentication can only be used for Snowflake. |
-
Select Add Credentials.
-
Choose an authentication method and proceed with the corresponding step:
-
Username and password: Basic authentication using your username and a password.
Select this method if you are connecting to an MS SQL data source using Kerberos authentication to Azure Active Directory (AD). For further instructions, see How to Connect to MS SQL Using Kerberos Authentication to Windows Active Directory. -
Integrated credentials: For some data sources, you can use, for example, Azure AD or Azure Key Vault. This requires configuring additional driver properties.
-
OAuth credentials: Use OAuth 2.0 tokens to provide secure delegated access. Available only for some data sources.
-
[OAuth user SSO credentials]: Use an external identity provider Single Sign-On (SSO). Available only for some data sources.
-
Username and password
-
Provide the following:
-
Name (Optional): A name for this set of credentials.
-
Description (Optional): A description for this set of credentials.
-
Username: The username for the data source.
-
Password: The password for the data source.
To access the password directly from the Azure Key Vault storage:
-
Set the password to
keyvault:SECRET:<name_of_stored_secret>. Make sure to provide the actual name of the secret instead of the placeholder. -
Authenticate to Azure Key Vault (see Azure Active Directory Key Vault Authentication).
-
-
-
If you want to use this set of credentials by default when connecting to the data source, select Set as default.
One set of credentials must be set as default for each connection. Otherwise, monitoring and DQ evaluation fail, and previewing data in the catalog is not possible. -
Proceed with Test the connection.
Integrated credentials
| As a prerequisite, you need to set up additional driver properties. See Add Driver Properties. |
-
Provide the following:
-
Name (Optional): A name for this set of credentials.
-
Description (Optional): A description for this set of credentials.
-
-
If you want to use this set of credentials by default when connecting to the data source, select Set as default.
One set of credentials must be set as default for each connection. Otherwise, monitoring and DQ evaluation fail, and previewing data in the catalog is not possible. -
Proceed with Test the connection.
OAuth credentials
| If you are using OAuth 2.0 tokens, you also need to supply the Redirect URL to the data source you’re connecting to. This information is available when configuring the connection. |
-
Provide the following:
-
Name (Optional): A name for this set of credentials.
-
Description (Optional): A description for this set of credentials.
-
Redirect URL: This field is predefined and read-only. This URL is required to receive the refresh token and must be provided to the data source you’re integrating with.
-
Client ID: The OAuth 2.0 client ID.
-
Client secret: The client secret used to authenticate to the authorization server.
-
Authorization endpoint: The OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint of the data source. It is required only if you need to generate a new refresh token.
-
Token endpoint: The OAuth 2.0 token endpoint of the data source. Used to get access to a token or a refresh token.
-
Refresh token: The OAuth 2.0 refresh token. Allows the application to authenticate after the access token has expired without having to prompt the user for credentials.
Select Generate to create a new token. Once you do this, the expiration date of the refresh token is updated in Refresh token valid till.
-
-
If you want to use this set of credentials by default when connecting to the data source, select Set as default.
One set of credentials must be set as default for each connection. Otherwise, monitoring and DQ evaluation fail, and previewing data in the catalog is not possible. -
Proceed with Test the connection.
Test the connection
To test and verify whether the data source connection has been correctly configured, select Test Connection.
If the connection is successful, continue with the following step. Otherwise, verify that your configuration is correct and that the data source is running.
Save and publish
Once you have configured your connection, save and publish your changes. If you provided all the required information, the connection is now available for other users in the application.
In case your configuration is missing required fields, you can view a list of detected errors instead. Review your configuration and resolve the issues before continuing.
Next steps
You can now browse and profile assets from your connection.
In Knowledge Catalog > Sources, find and open the source you just configured. Switch to the Connections tab and select Document. Alternatively, opt for Import or Discover documentation flows.
Or, to import or profile only some assets, select Browse on the Connections tab. Choose the assets you want to analyze and then the appropriate profiling option.
Was this page useful?
