MD Process Monitoring
MD Process Monitoring is a part of ONE Runtime Server Admin (see ONE Runtime Server Admin) that shows information about ongoing and finished MDM processes, runtime parameters, and data statistics.
Operation Plan
Shows the order of load operations defined in the Model (see Model) used as an internal workflow of the MDM engine. You can also download the operations list for using Executor (see Executor).
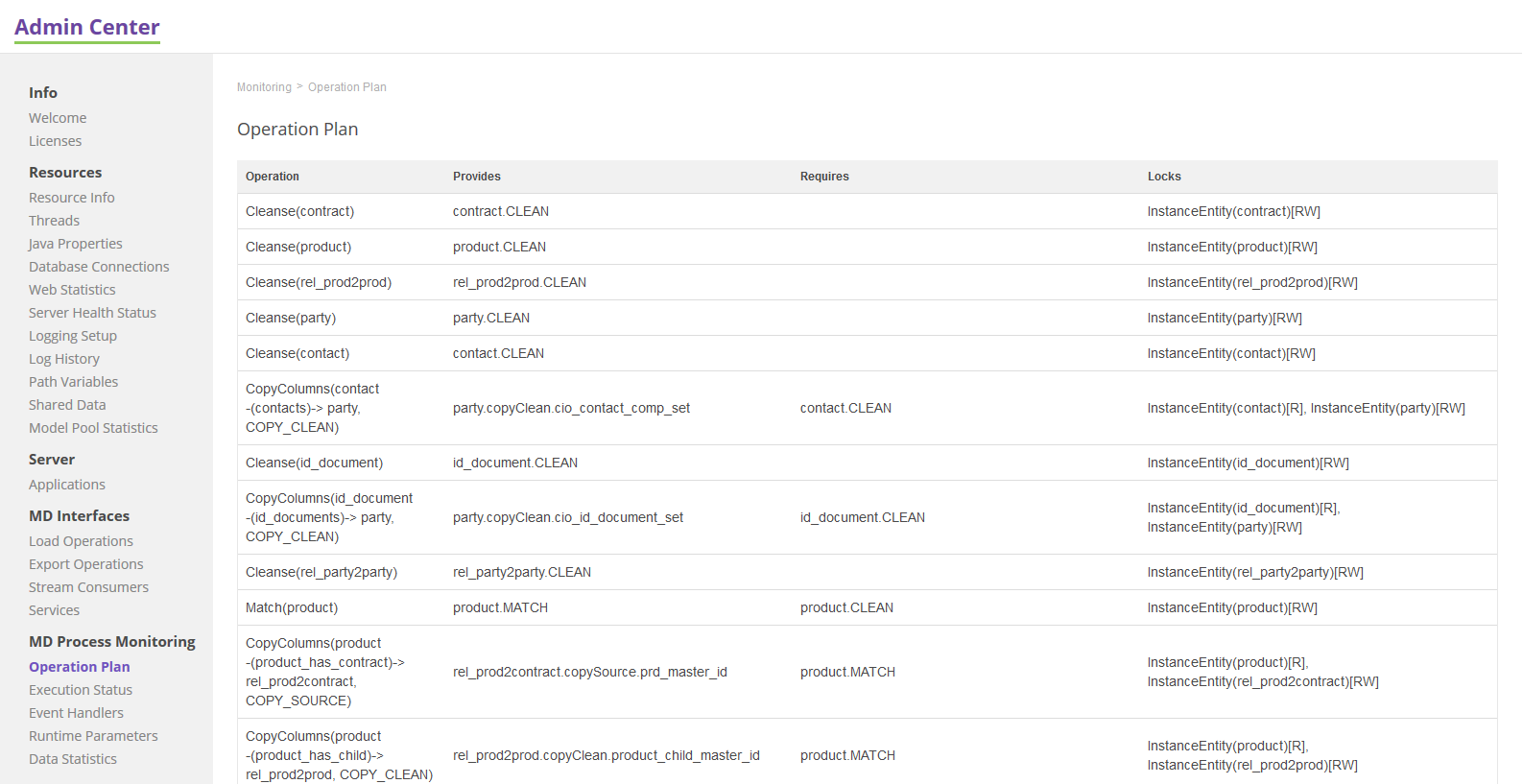
Columns have the following meaning:
-
Operation: Name of the operation.
-
Provides: Refers to the result of the operation.
-
Requires: Refers to the result of entity processing, which must be completed before processing the current one.
-
Locks: Similar to database locks; useful for parallel processing (Read or ReadWrite access shown as well).
Execution Status
Shows a list of already processed operations for both load and export operations.
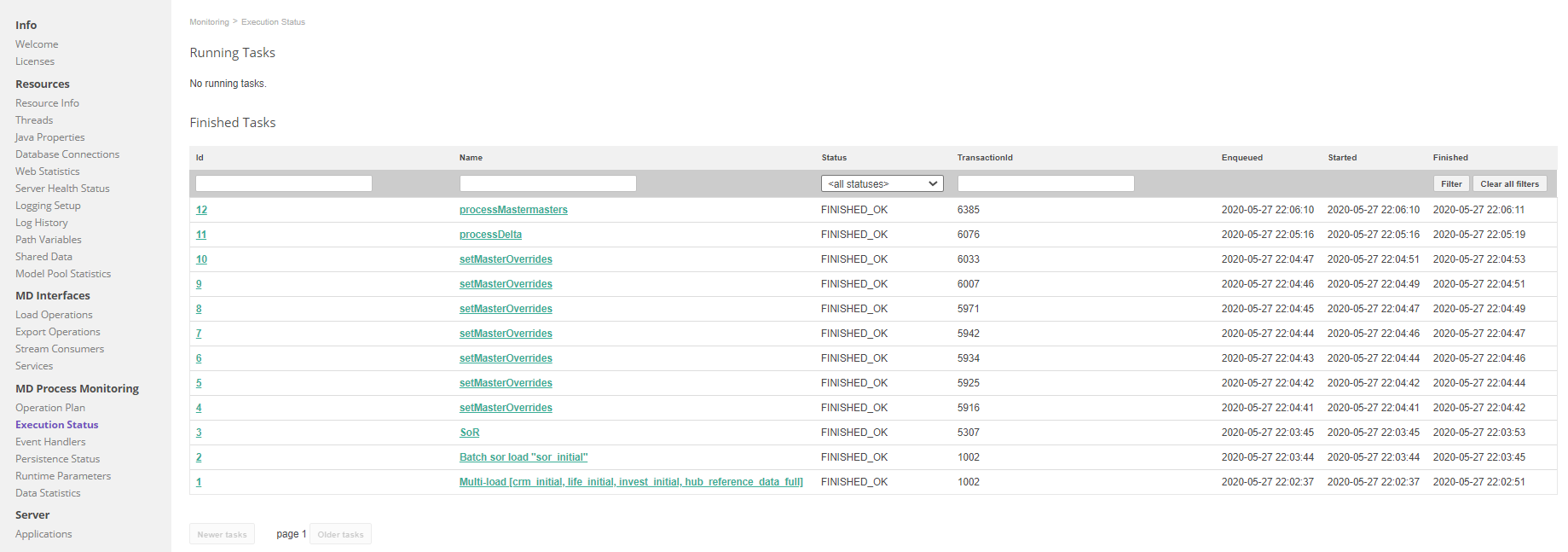
Clicking on any one operation will open more information about it.
Load Operation
The image below shows a details screen of a load operation.
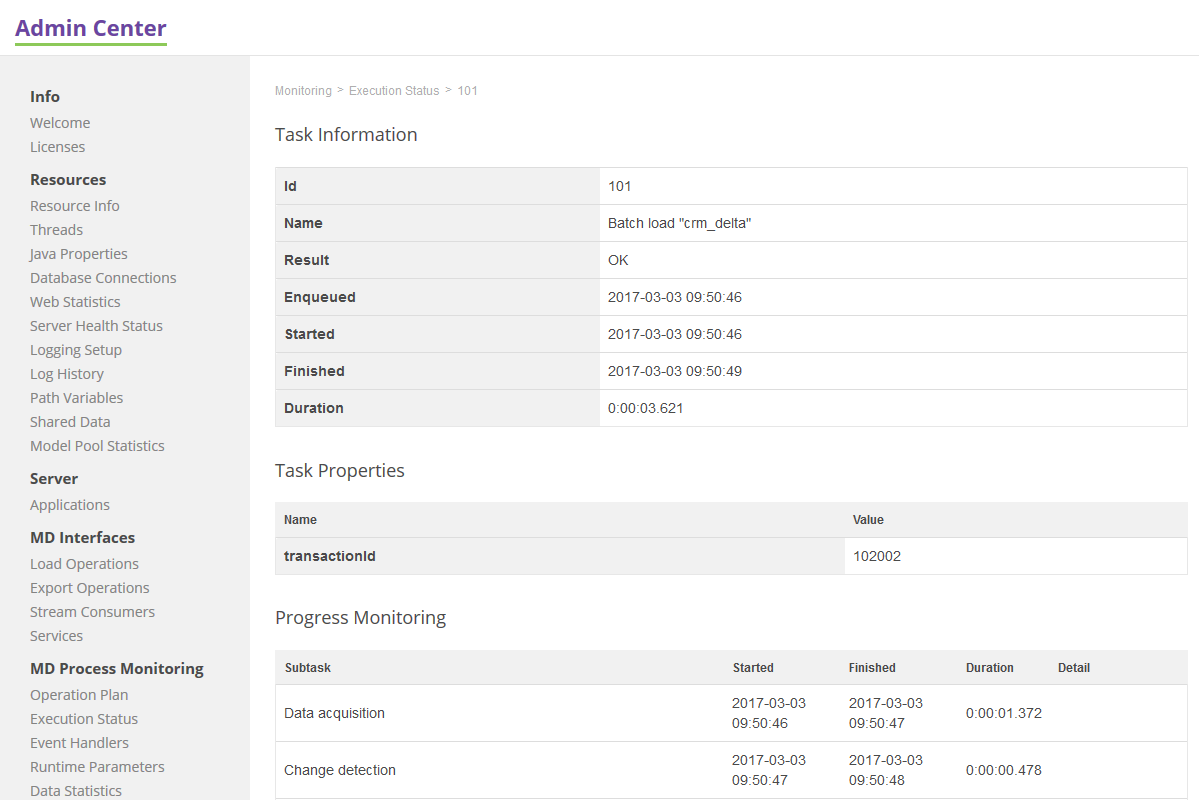
Progress monitoring displays each step of the operation providing the following detail:
-
Subtask name
-
Start date and time
-
Finish date and time
-
Duration
-
Detail
-
Number of changed records, total number of incoming records (change detection)
-
Number of records at the start of a subtask (cleanse)
-
Number of records at the start of a subtask + number of records affected by processing (match, copyColumns)
-
Number of records at the start of a subtask + number of records affected by processing → number of record at the end of the subtask (merge)
-
Batch load subtasks are the following:
| Subtask Name | Description |
|---|---|
Data acquisition |
Subtask refers to a process and transformation in a load plan, while a load operation launched. |
Change detection |
"Real" change detection (also known as delta detection) of incoming data against data already stored in MDM repository. Since this point only the changed data is processed. |
Master data consolidation |
Cleansing, match, copyColumns and merge subtasks per an entity are processed in a given order. |
Committing |
Writing down the data into the MDM repository. |
Export Operation
The image below shows a details screen of an export operation.
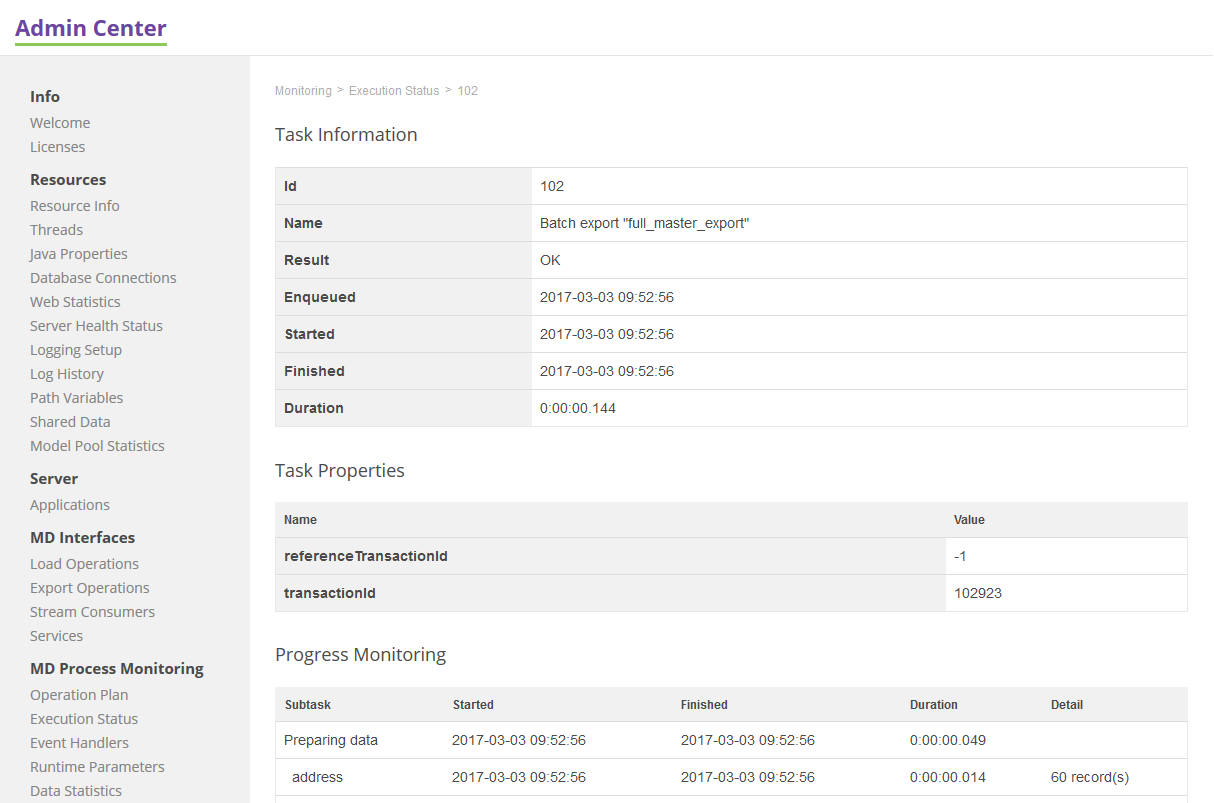
Progress monitoring displays each step of the operation providing the following detail:
-
Subtask name
-
Start date and time
-
Finish date and time
-
Duration
-
Detail: Number of records at the start of the subtask.
Batch exports subtasks are the following:
| Subtask Name | Description |
|---|---|
Preparing data |
Subtask refers to a process of loading (and filtering) data from the MDM repository when an export operation is launched. |
Exporting |
Process of working with data in an export plan. |
Committing |
Writing down the data. |
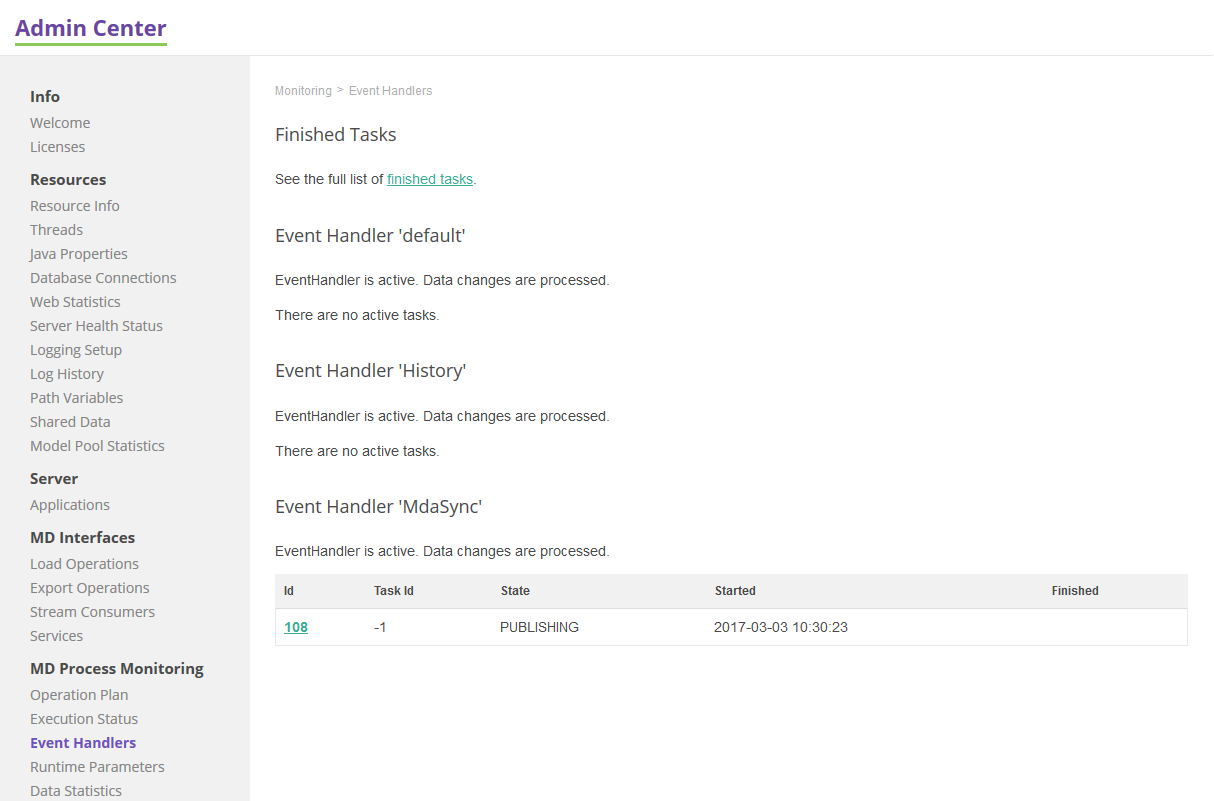
Event Handlers
As a part of a load operation, there can be an event handler and event publisher configured. It is possible to see finished and ongoing tasks.
Ongoing Handles show the status of currently running handlers:
-
Id: Event handler processing id, link to detailed information (details shown depend on Event Handler Name).
-
Task Id: Task if of the related load operation’s execution status.
-
State: Information about current processing phase (see the list of available statuses above).
-
Started: Time of task start.
-
Finished: Time of task finish.
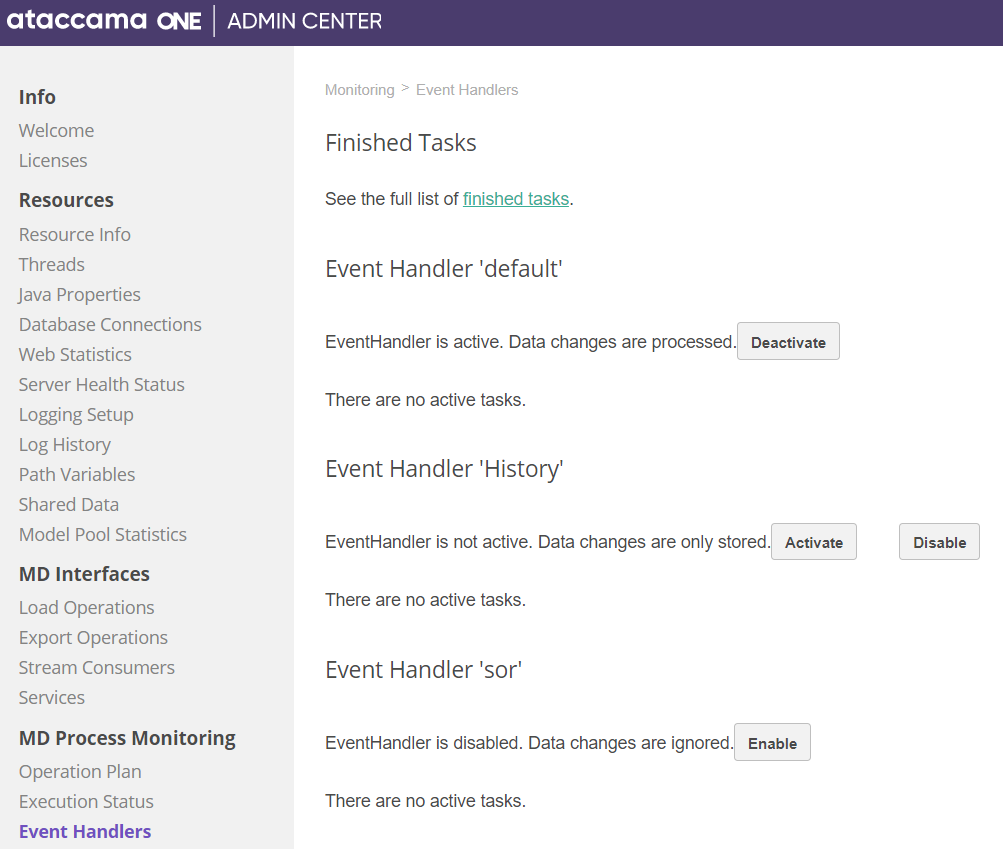
You can also perform the following actions on Event Handlers from the Admin Center:
-
Deactivate: Events are captured by
EventHandlerand stored topersistenceDirbut are propagated by publishers only after activation. -
Activate: Event handler will start propagating events by publishers, only available if event handler has been deactivated due to publishing failure.
-
Disable: Event handler will stop capturing events, only available if event handler is already deactivated.
-
Enable: Event handler will start capturing events but still will be inactive, that is no publishing yet, and monitor the health status of both Event Handlers and Publishers.
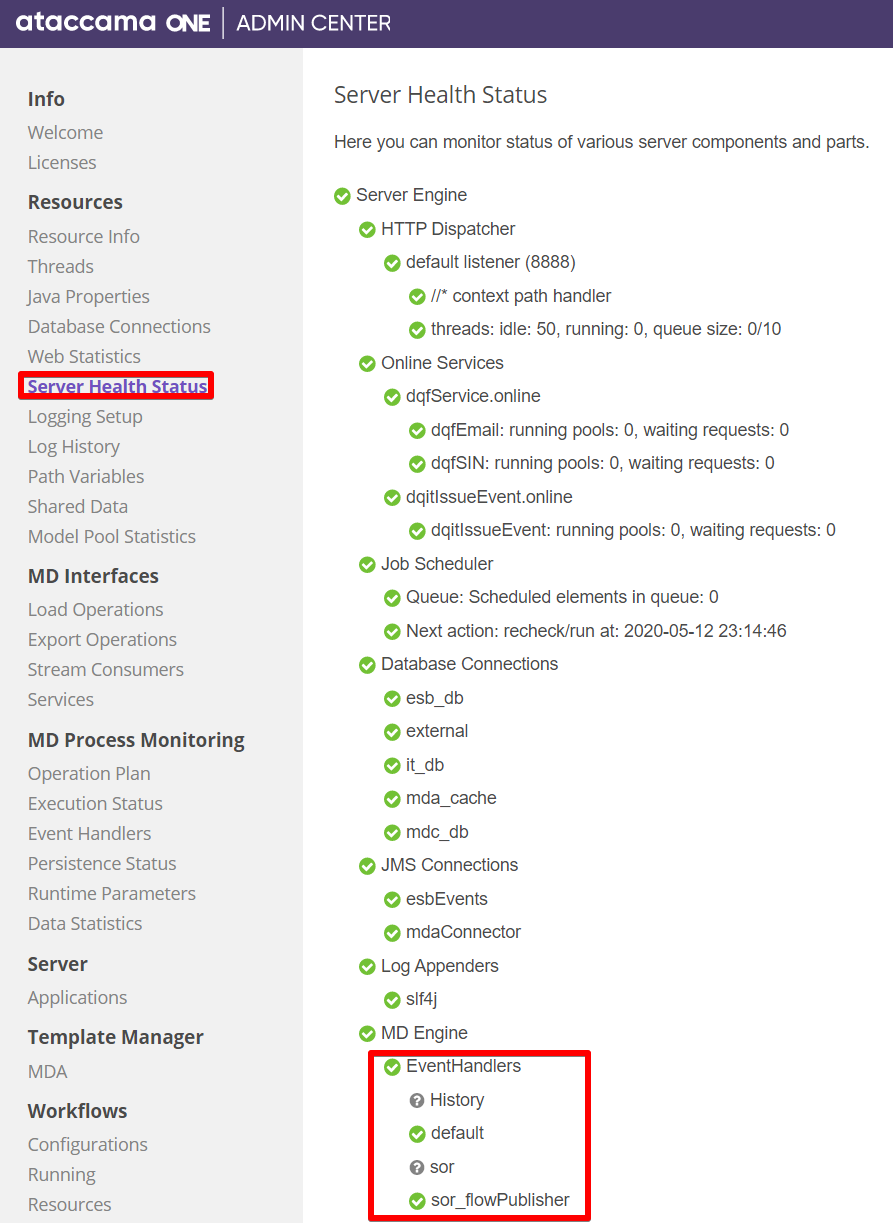
| Event Handler status in Server Health Status reflects also the state of its publishers (publisher cannot be monitored or restarted on their own). If you need to run and monitor two publishers independently, you will need to create more event handlers, that is ensure that each event handler uses only one publisher. For more information, see Adding a Data Event Handler and Publisher. |
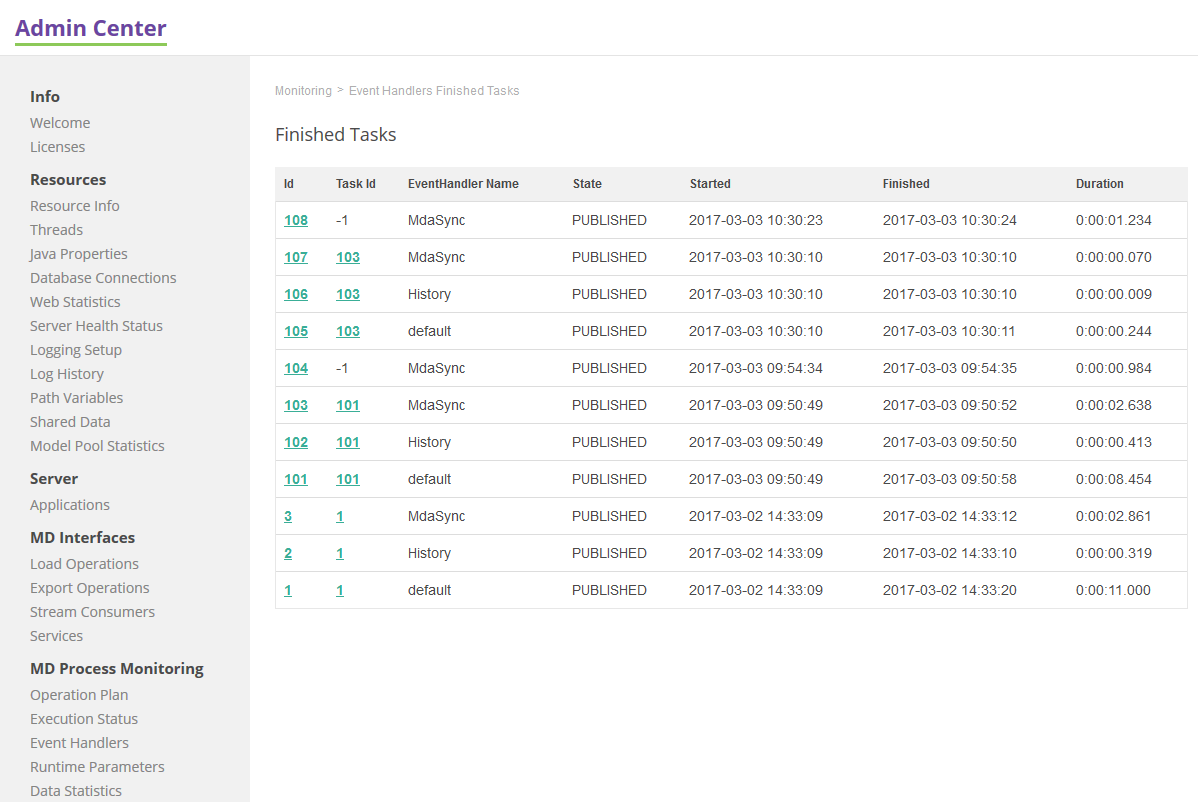
Finished Tasks
History of all finished event handlers displayed together:
-
Id: Event handler’s processing id, link to detailed information (details shown depends on Event Handler Name).
-
Task Id: Relates to related load operation’s execution status.
-
Event Handler Name
-
MdaSync (if applicable)
-
History
-
EventHandlerAsync (or a different name)
-
-
State: Information about the current processing phase
-
RECEIVING: Receiving events from an ongoing transaction.
-
READY: Ready for publishing.
-
PUBLISHING: Ongoing publishing process.
-
PUBLISHED: Publishing is finished.
-
CORRUPTED: Temporary files are corrupted.
-
CRASHED_RECEIVING: MDM processing or Event Handler failed - temporary files will be removed.
-
CRASHED_PUBLISHING: Publishing was not successful - when a publisher is activated, publishing continues.
-
-
Started: Time of task start.
-
Finished: Time of task finish.
-
Duration: Task duration.
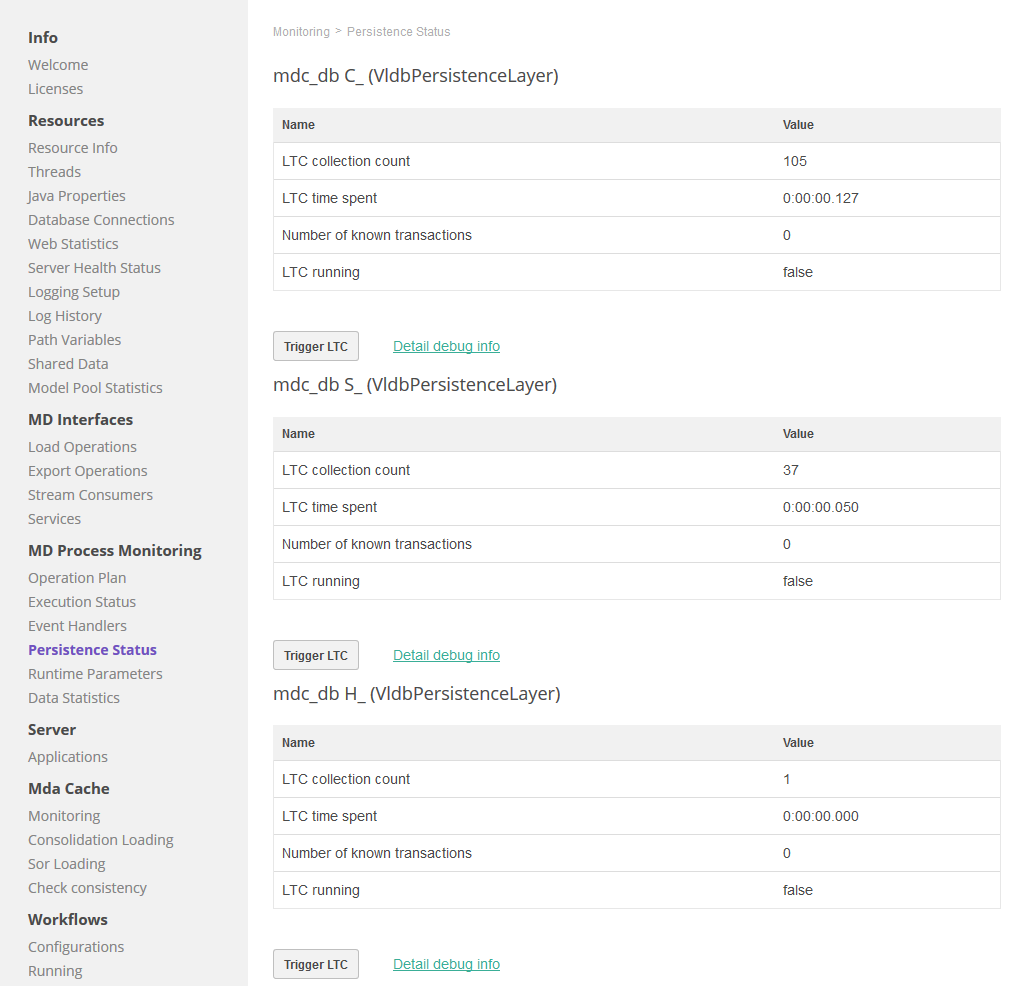
Persistence Status
Persistence Status is a monitoring section for the VLDB persistence type (at least one has to be defined). It displays the list of defined VLDB persistencies, typically for Consolidation and History. For each VLDB persistence there are following details available:
-
LTC count: Number of executions of the Logical Transaction Collector (LTC).
-
LTC time spent: Total time spent cleaning up the obsolete records (since MDM server start up).
-
Number of known transactions: Represents the number of active or finished transactions that have not yet been collected by LTC.
-
LTC running: Boolean flag indicating the current LTC activity.
-
Trigger LTC: Manual action to start collection of obsolete records - run the LTC. To know more about VLDB in Persistence Layer, see Persistence Layer.
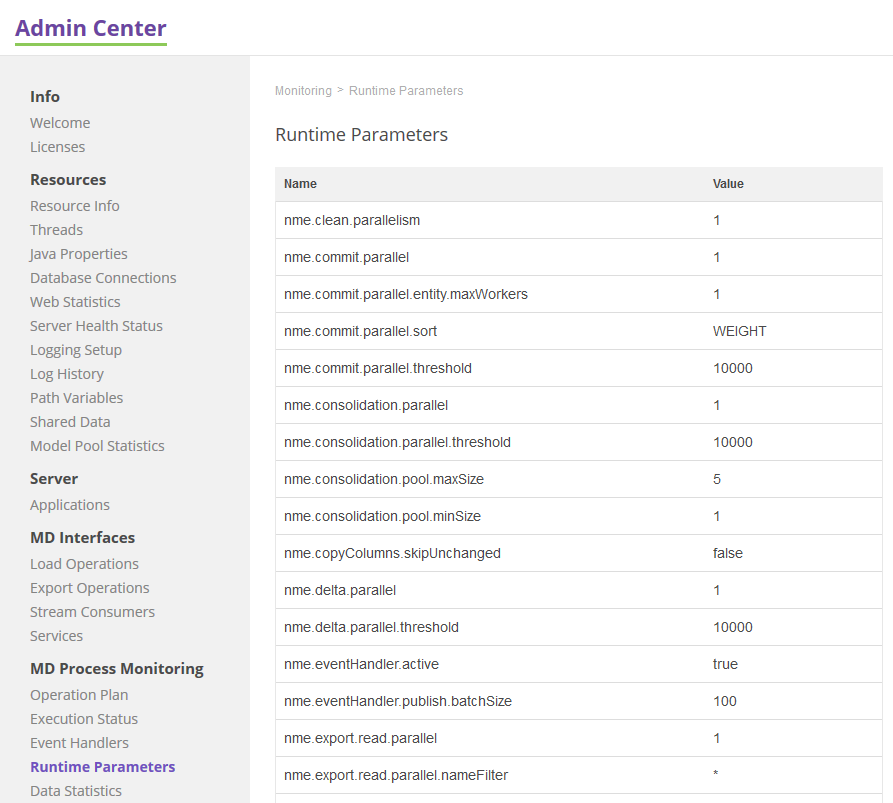
Runtime Parameters
Shows all runtime parameter values that are used by the engine as configured in Runtime Parameters (see Runtime Parameters).
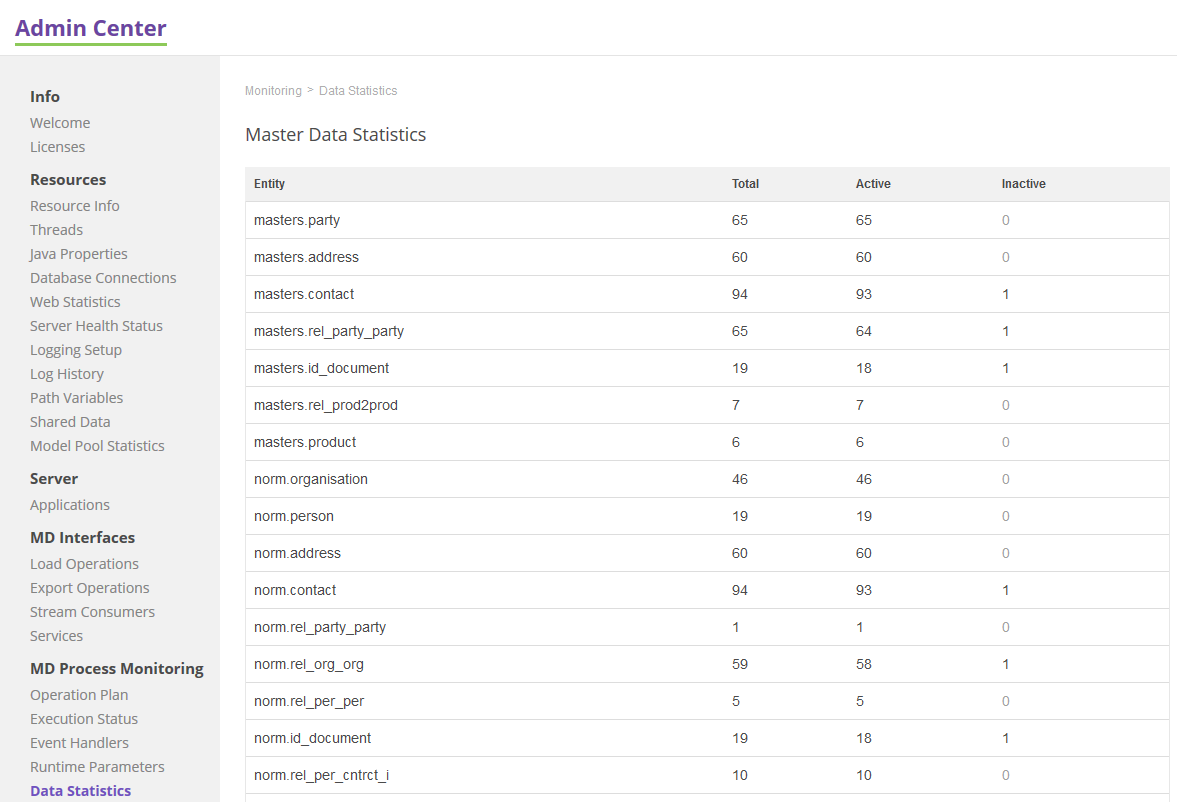
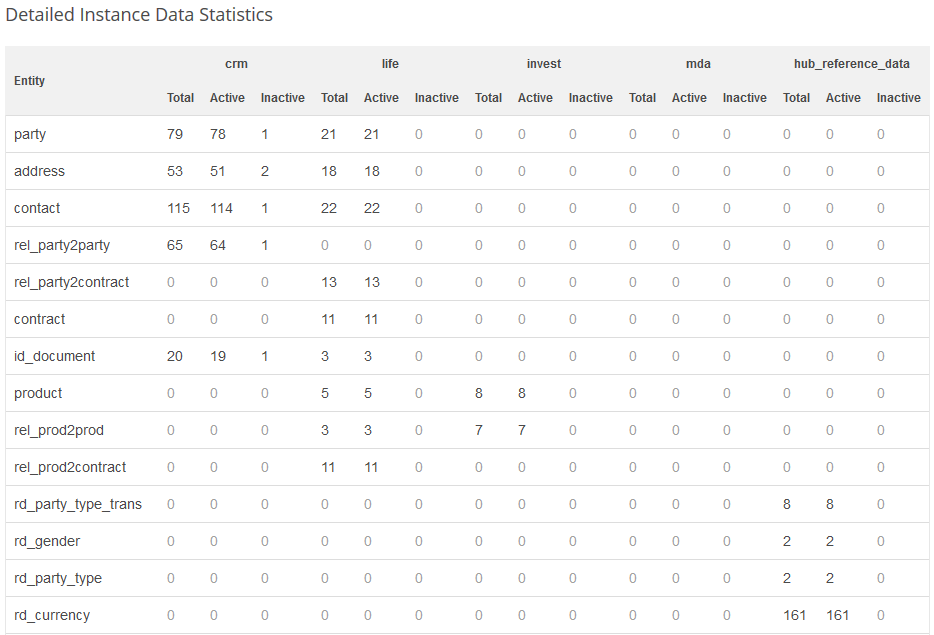
Data Statistics
Was this page useful?