How to Deploy an RDM Web App Configuration
After defining the RDM model for the first time or making changes to the existing one, the model configuration needs to be deployed to the RDM web application.
| For compatibility reasons, the RDM web application is initially loaded with a default, empty configuration that needs to be replaced by following the steps described. |
Before you start
Before you deploy the model configuration, keep in mind the following:
When a new configuration is being deployed:
-
The RDM web application is not available.
-
The RDM web application performs all configured validations on all data in all tables that changed since the last configuration.
-
The RDM web application checks the structure of the RDM repository and compares it to the model currently being deployed.
In addition, how long the application remains unavailable for generally depends on the following factors:
-
Application server hardware and memory.
-
Database server hardware and memory.
-
Network capacity and availability.
-
The number of records in tables.
-
The number of columns.
-
The number of relationships and their depth (parent > child 1 > child 2 >…).
-
The number of mn-references.
-
The number and complexity of validations. SQL validations are generally faster than online (ONE plans or components) validations.
Procedure
-
In ONE Desktop, right-click the App Configuration node and select Generate.
-
Keep the Default location option selected (the default location is the
etcfolder) and select Generate. AconfigurationFiles.zipfile is generated. -
Open your browser.
-
Navigate to the RDM Admin console:
http://{rdm_url}:8060/admin.Do not delete the active configuration: it is needed when deploying a new configuration in the following steps. Even after the new configuration is made active, there is no need to delete the preceding configuration - it might even be useful as a fallback in case of any errors during the deployment of the new one. -
Select Add configuration.
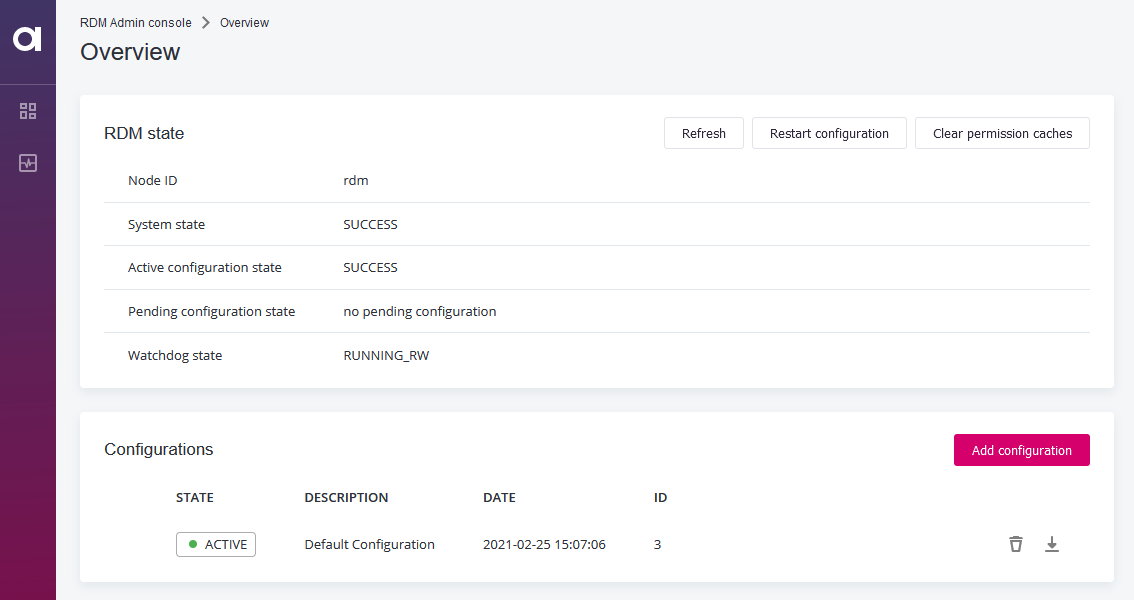
-
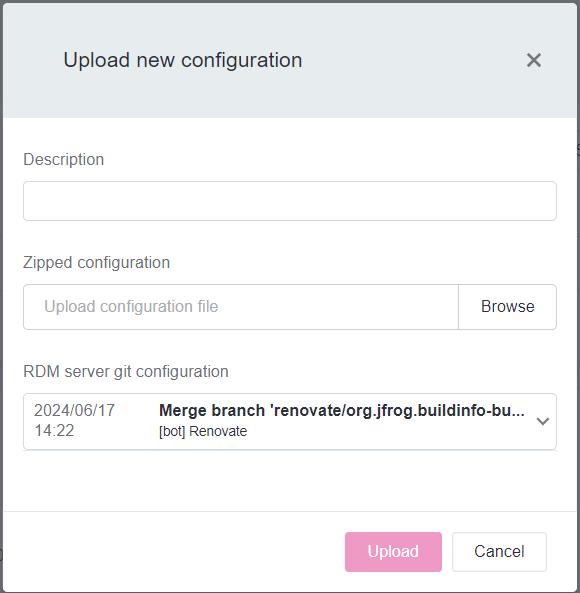
In the Upload new Configuration dialog:
-
Enter a description.
-
Select the
configurationFiles.ziparchive. -
(Optional) Select the preferred RDM server git configuration.
This option is only available for Cloud deployments. For more information, see RDM Deployment Guide.
-
Select Upload.
-
-
Select Apply configuration and confirm your selection.
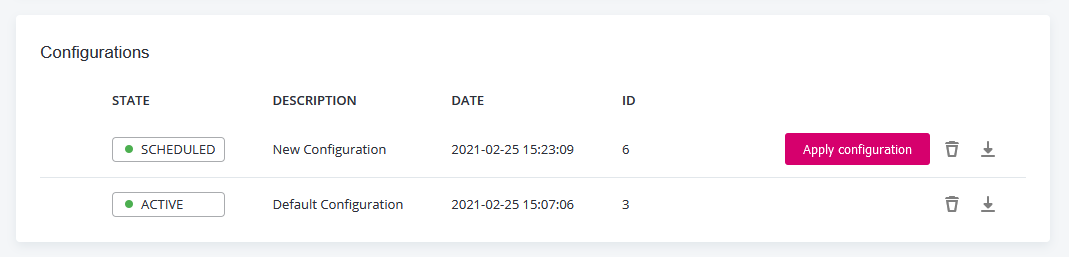
The configuration is restarted and the old (active) and new (scheduled) configurations are compared.
If you try to access the RDM application at this time, an error message appears:
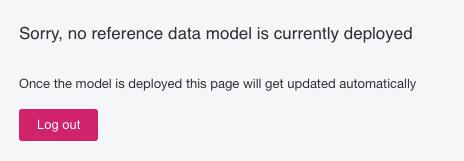
-
Select Review proposed configuration to view the comparison.
-
Review changes to the model and select Accept configuration proposal.
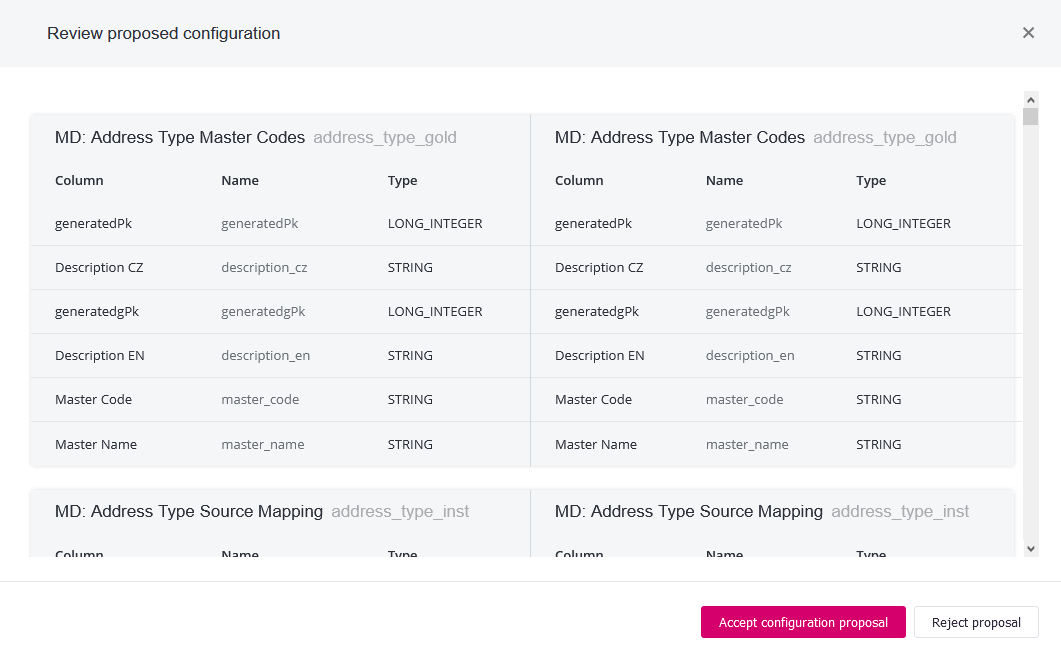
If the new configuration is in any way unsuitable, the Reject proposal option is the last chance to safely delete it and start the process anew. The last previously used configuration is reinstated if you choose to reject the new one. Once a configuration is accepted and made active, we firmly recommend not deleting it. This could lead to critical validation errors and may result in the need for advanced troubleshooting by expert users. -
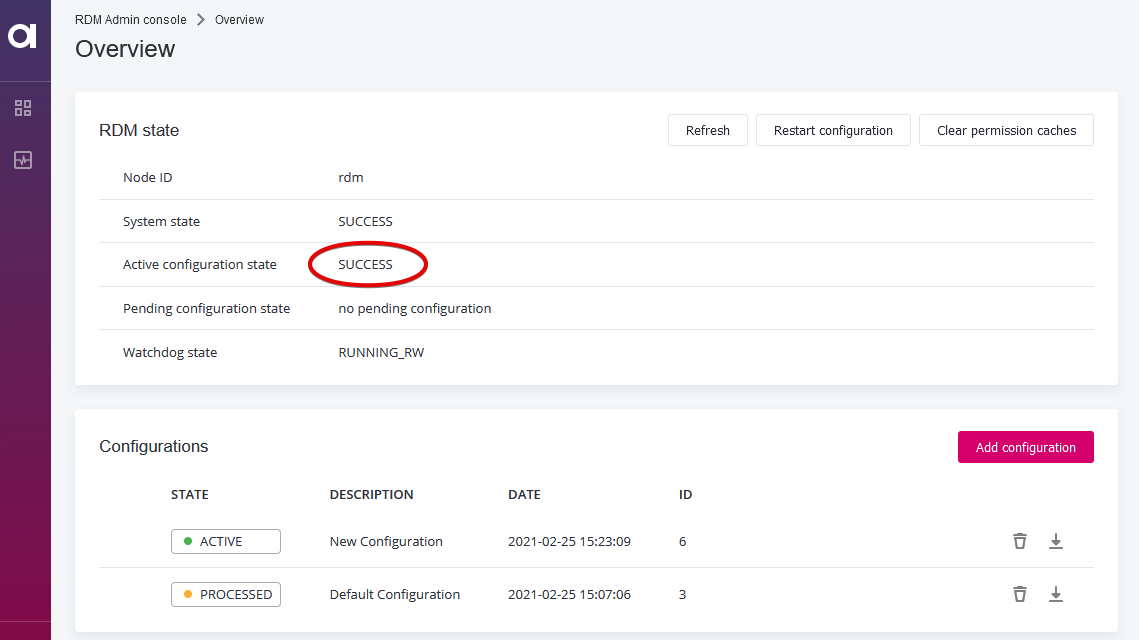
Back on the Overview screen, the Active configuration state section shows Success. This means the application is ready to be used again.
Advanced troubleshooting
The following information can be useful when dealing with failed configuration uploads and is meant for expert users.
RDM configuration concepts
When you deal with and troubleshoot RDM configurations, keep the following principles in mind:
-
When deployed without errors or when dealing with the default configuration, the active configuration is consistent with the database structure. This means that what is defined in the configuration exists in the database.
-
When you upload and accept a new configuration, the structure of the database has to be altered to reflect the new configuration. The needed changes are computed against the previously active configuration, and put in place when the new model is applied.
-
If there is no previous active configuration to compute needed changes against, the new configuration is accepted without performing any database alterations.
-
Uploading a new configuration can result in one of the following outcomes:
-
Success: The resulting database structure is successfully altered and matches up with the now active model.
-
Failure: The resulting database structure could not be successfully altered and is inconsistent with the configuration.
-
-
Data is protected during the process of uploading a new configuration. This means that even if application of a new configuration fails no data is lost or broken. Database structure and the previous configuration is preserved and can still be used to start and run RDM. In such cases the failed configuration is marked as
SCHEDULEDin RDM Admin Console, and the associated logs can be used to troubleshoot the detected problems. It is safe to deleteSCHEDULEDconfigurations. -
You cannot upload a new model if the current active model is not working correctly and if RDM is not able to fully start with the old active model. RDM detects the active configuration does not match database structures and cannot safely compute needed structure alterations against such a configuration. In such cases the following section walks you through possible solutions.
RDM cannot start with active configuration
Usually when RDM fails to start even with an active previously accepted configuration, there is an error in validations of database structure. In such cases, there are two approaches to consider:
-
Switch to repairingmode: TheSwitch to repairingmode is an action RDM Admin Console that lets you start RDM even with validation errors reported. When this mode is active only system users can log in and attempt to fix the reported validation errors directly to make the data in RDM consistent with the configuration. After the errors are resolved, you can selectResume repairing modeto attempt to restart RDM. -
Fix the configuration ZIP file and upload it as the only configuration. For this approach, all previous configurations including the default one have to be deleted first. This is to force RDM to accept this configuration because there is no other configuration to compute database structure alterations against.
Was this page useful?
