Nodes
mmd.json5 defines all nodes that appear as separate entities in the web application and connections between them.
Nodes section structure
Below is a general structure of the nodes part of mmd.json5:
{
...
"nodes":{
"metadata":{ },
"nodeName1": { },
"nodeName2":{ }
}
}Metadata node
The first node has to be metadata.
This is a root node that holds the entities (nodes) displayed in the web application’s left menu.
All other entities are displayed as sections and input fields in the web application’s screens.
An exception: Catalog Items are always present in the web application’s left menu, they do not have to be listed under the metadata node.
|
|
To add an entity (node) to the web application’s left menu, embed the node (here named
Full configuration example: Click here to expand example configuration |
Nodes hierarchy
Each node defines a section in the web application.
Where it is displayed depends on its position within the mmd.json5 hierarchy: the nodes embedded under the metadata node are displayed in the left navigation menu; the nodes embedded under or referred from other nodes are displayed as child sections/pages of the embedding page/section.
Defining Nodes
Definition of each node contains the following parts:
-
properties: Defines the input fields available in the web application. See Properties. -
extends(optional): Extends a node functionality with additional functionalities inherited from another node. See Extends. -
plugins(optional): Defines plugins that are applicable only within the node. To use a plugin in the whole ONE 2.0 web application, add it to the top-levelpluginssection. -
constraints(optional): Defines additional validations that are applied to the property. See Constraints. -
traits(optional): Properties that are defined by plugins and add additional functionality or change the appearance of the entity.
{
"plugins":{ },
"root":"metadata",
"nodes":{
"metadata":{ },
"nodeName1": { },
"nodeName2":{
"extends":"entityName",
"properties":{ },
"plugins":{ },
"constraints":[ ]
}
}
}Properties
Each property defines an input field available to the web application.
The properties do not need any additional configuration to enable the correct work of the application.
Currently, there is no option for the customizable configuration of properties in the mmd.json file.
|
In the web application, properties are displayed according to the following rules:
-
Property names in the web application are derived from the property names in the
mmd.json5file, e.g.,propertyName is displayed as Property Name in the web application.The front end transformation will consider camel cases as separate words and will automatically take out any punctuation. For example, "profilingLimitEnabled" will be displayed as Profiling limit enabled. -
All scalar properties are displayed in the General / General Information section, in the same order in which they appear in the
mmd.json5file. -
Each embedded or single reference entity has a separate section within the embedding/referring page.
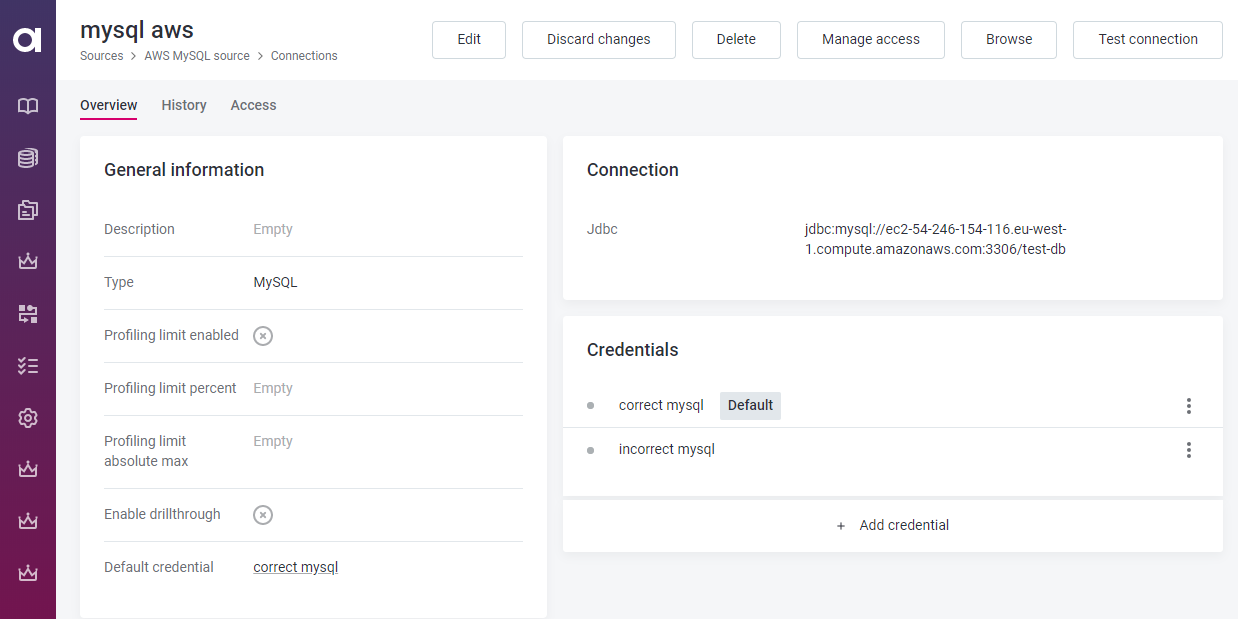
Property definition in mmd.json5 has the following structure:
"properties":{
"propertyName":{
"type":{ },
"constraints": [],
"description":"propertyDescription"
"valueProvider":{ }, / "defaultValue":"defaultValue"
}
}-
propertyName: Property name displayed in the web application -
type: Defines a type of property linkage in the web application -
constraints: Defines validations that are applied to the property -
description: Property description -
valueProvider: Used in properties where to define the list of possible values. -
defaultValue: Used in properties where the user selects the default value from one or multiple pre-defined values.
Type
Defines a type of property linkage in the web application:
-
Scalar type property, no linkage.
-
An embedded entity; is contained within another entity.
-
Reference entity; refers to another entity.
| Property type | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Scalar |
Defines a property (input field) with no linkage to another entity. Definition in In the web application, a scalar type property is represented as an input field (
|
||||
Embedded entity |
(Single or Array) Embedded entity is contained within another entity (property) and is in a parent-child relationship with it. If a parent stops to exist, the child is deleted as well; but the parent can exist without a child (e.g., a data source pointing to a catalog item, the catalog item cannot exist without a data source). A single embedded entity can store a single value, an array embedded entity can store multiple values. Definition in
In the web application, property representation depends on its type:
|
||||
Single reference entity |
A single reference entity is independent of the entity (property) that refers to it, the entities just point to each other. If one of the entities is deleted, the other one continues to exist (e.g., a catalog item referring to a term, the term can exist without a catalog item). Definition in
In the web application, a single reference entity is represented as a dropdown menu listing the instances of the referred entity (for terms) or a section with a table listing the referred entities.
|
Examples
Scalar type entity:
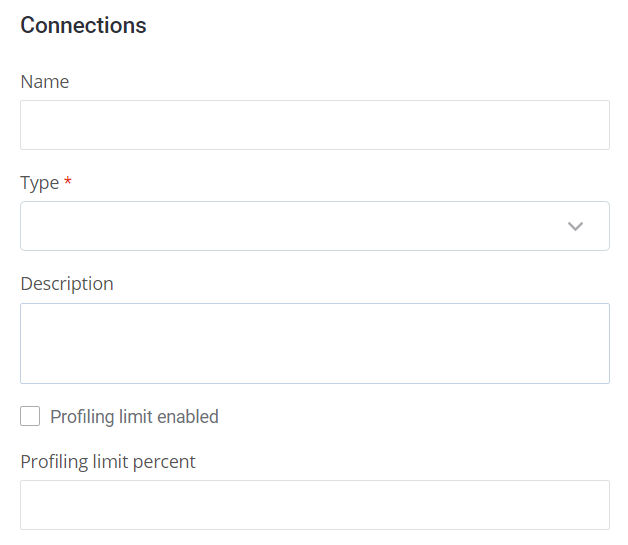
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
Click here to expand example configuration
"connection":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":{
"type":"string"
},
"description":"source name"
},
"type":{
"type":{
"type":"string"
},
"constraints":[
{
"type":"REQUIRED"
}
],
"valueProvider":{
"type":"dataSourceDriverTypes"
}
},
"description":{
"type":{
"type":"string"
}
},
"profilingLimitEnabled":{
"type":{
"type":"boolean"
}
},
"profilingLimitPercent":{
"type":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
}Single reference entity: Term relationship referring to the Abstract term entities in the Source field:
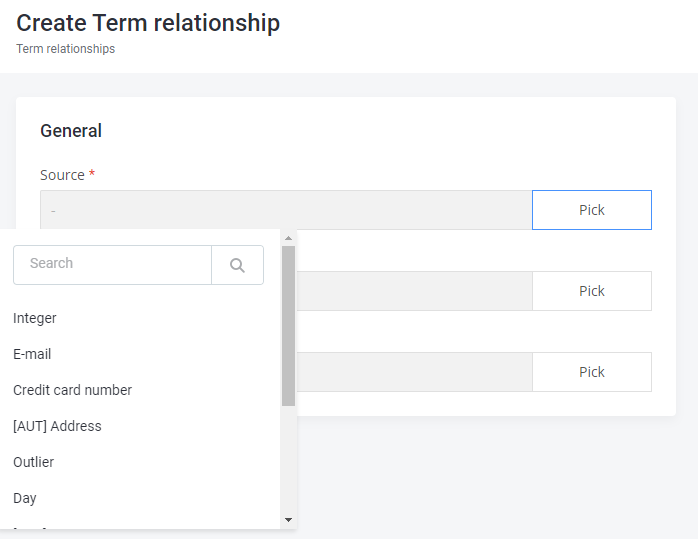
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
"abstractTerm":{ },
"termRelationship":{
"properties":{
...
"source":{
"type":{
"reference":"true",
"array":"false",
"object":"abstractTerm"
}}}}Array embedded entity: Catalog item containing Term instance entities (for a particular catalog item) in a Term Instances section:
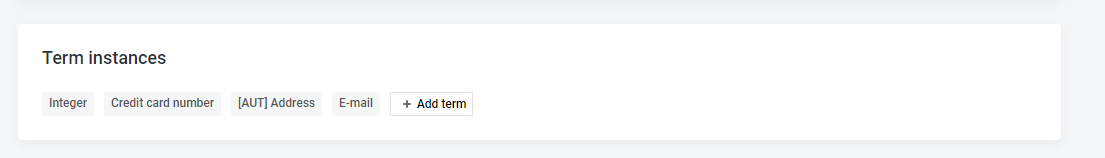
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
"termInstance":{ },
"catalogItem":{
"properties":{
...
"termInstances":{
"type":{
"reference":"false",
"array":"true",
"object":"termInstance"
}}}}Array embedded entity: Source containing Connection entities in a Connections section:
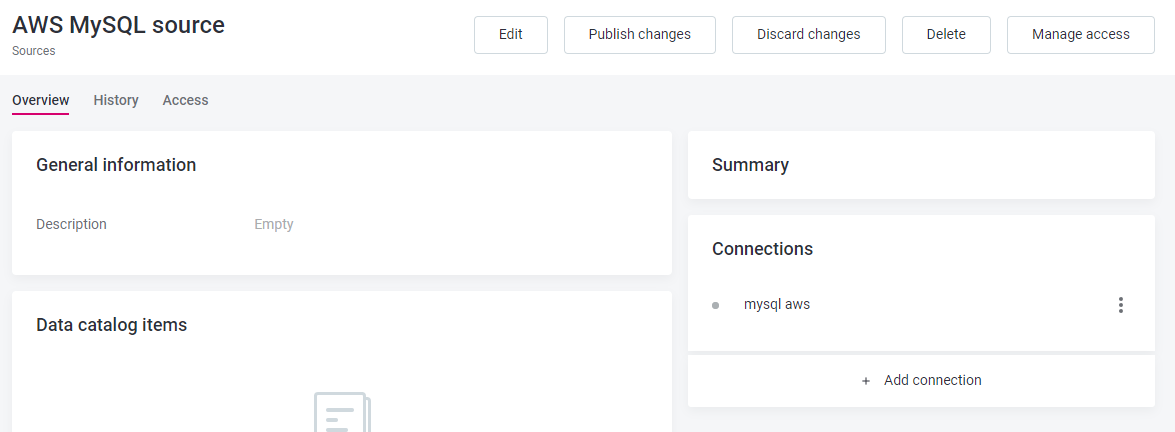
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
"connection":{ },
"source":{
"properties":{
...
"connections":{
"type":{
"reference":"false",
"array":"true",
"object":"connection"
}}}}Single embedded entity: Attribute profile containing Anomaly State entity in the Anomaly State section:
"attributeProfile":{
"properties":{
"anomalyState":{
"type":{
"reference":"false",
"array":"false",
"object":"anomalyState"
}}}}property constraints
Defines additional validations that are applied to the property.
The validations are verified by the application upon publishing the entity. If the application detects validation errors, a validation message is displayed with a list of errors. The application does not allow publishing until all errors are resolved.
| Note that the application validates only the subset you are currently publishing, not all metadata in the application. |
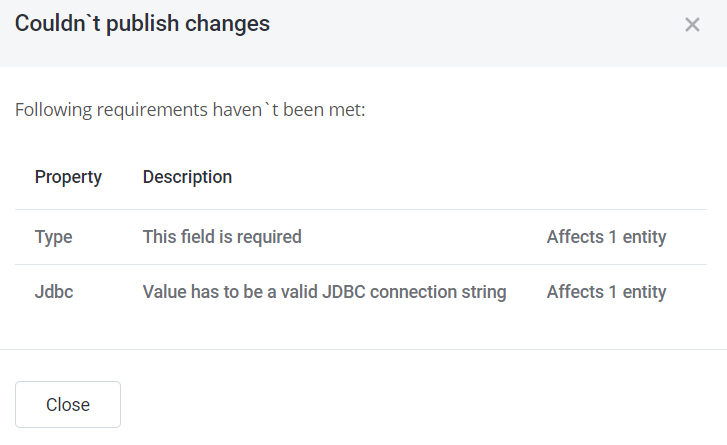
Default constraints:
Reference existence is validated implicitly by the backend and does not require the user to manually indicate it in the configuration file.
Configurable constraints:
The following table lists the available constraints:
| Type | Description | Enabled by |
|---|---|---|
REQUIRED |
Required field.
It is not possible to create/edit/save an entity if this field is empty.
In the web application, required fields are marked with a star The validation message is hard-coded: "This field is required". Definition in
|
default |
REGEXP |
The field input has to comply with the regular expression defined in the Definition example in
|
default |
UNIQUE |
A combination of properties that are listed under the The validation message will be hard-coded and has not been defined yet. Definition example in
For example, when defining a data source locations, we want each location to have a unique name.
To achieve this, we have to set a constraint that Click here to expand example configurationDepending on the |
default |
JDBC_DATA_SOURCE |
Validates whether the string on input (defined by property listed in the The validation message is hard-coded: "DRIVER_DOES_NOT_SUPPORT". Definition example in
Click here to expand example configuration |
|
Example constraint:
An example of defining a constraint in one property and reusing it in another:
Click here to expand example configuration
"propertyName1":{
"type":{ },
"constraints":[
{
"type": "REGEXP",
"id": "CONTAINS_AT_LEAST_ONE_ALPHA_NUM",
"pattern": "^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$",
"message": "Name can only have alphanumeric characters"
}
]
},
"propertyName2":{
"type":{ },
"constraints":[
{
"type":"REGEXP",
"id":"CONTAINS_AT_LEAST_ONE_ALPHA_NUM",
}
]
},description
Property description. The description is not displayed in the web application.
"propertyName":{
"type":{ },
"description":"propertyDescription"
},valueProvider, defaultValue
Value providers are used in properties where the user selects from multiple pre-defined values. The values can be either pre-defined on the backend or by a user in the web application.
In the web application, it shows a filterable dropdown menu with all available values (instances of the entity). There are three types of value providers:
-
COMPLETE: A list of available values is provided by the
typeproperty. Only values from this list can be assigned. -
DEFAULT: Default property value that is offered to the user.
Default value providers
Definition in mmd.json5:
"name":{
"type":{ },
"defaultValue":"defaultValue",
}defaultValue: default value displayed in the web application.
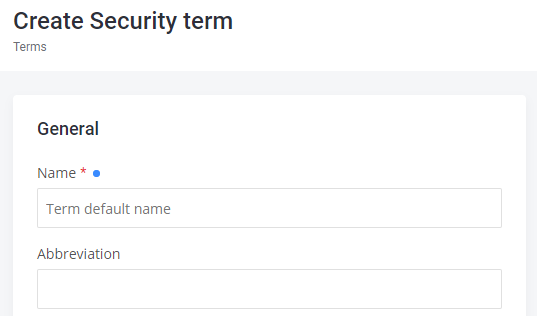
Example:
"term":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":{ },
"defaultValue":"Term default name",
"constraints":[ ]
},
Complete value providers
Definition in mmd.json5:
"propertyName":{
"type":{ },
"valueProvider":{
"type":"valueProviderType"
}}valueProviderType: select the value provider.
See the following table for a list of options.
| Type | Description | Enabled by | Values defined by |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Offers data sources to which you can connect. Available values: PostgreSQL, MySQL, RDM Datasource, MDA application data, File system. |
|
backend |
|
Offers data types that you can assign to a column. Available values: STRING, INTEGER, DATE, DATETIME, BOOLEAN, LONG, FLOAT. |
|
backend |
|
A security tag that you can assign to a term. Available values: INTERNAL, PUBLIC, SENSITIVE. |
|
backend |
|
Term suggestion status. Changes according to web application user’s action. Available values: Pending, Approved, Rejected. |
|
backend |
|
Source of the suggestion. Assigned automatically. Available values: Manual, Profiling, AI. Currently, only AI is used, when AI core sends suggestions to the application. |
|
backend |
|
Shows a list of values defined by the web application user for the entity specified by the Definition in mmd.json5: |
default |
web app user |
Value provider examples
dataSourceDriverTypes value provider:
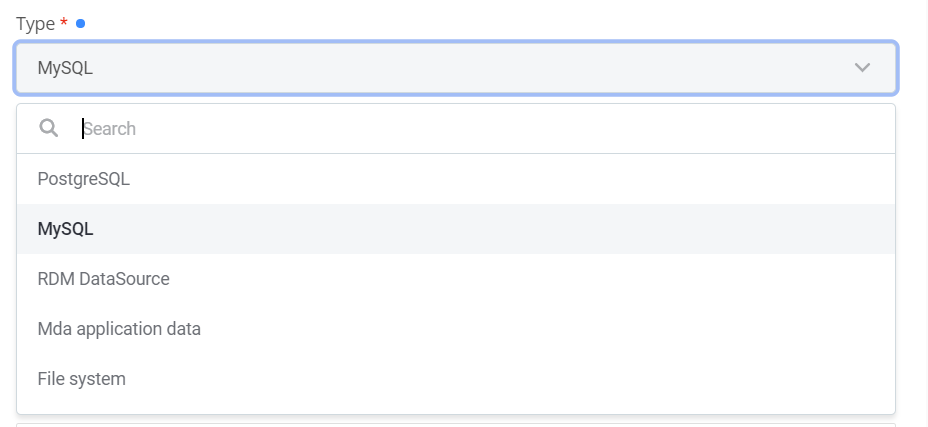
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
"type":{
"type":{ },
"valueProvider":{
"type":"dataSourceDriverTypes"
}
},sameParent value provider: when selecting default credentials for a data source connection, the application offers all credentials saved for the connection:
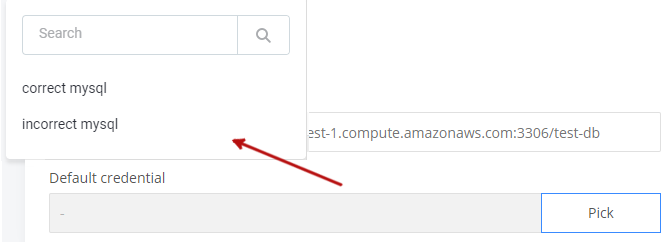
Corresponding configuration in mmd.json5:
"connection":{
"properties": {
"credentials":{ },
"defaultCredential":{
"type":{ },
...
"valueProvider":{
"type":"sameParent",
"name":"credentials"
}}}}Extends
Extends the node/entity functionality with the functionality of the entity specified by the extends attribute (so-called "superentity").
The extended entity inherits all characteristics (properties, constraints) from the superentity, in addition to its own.
For example, the extendedEntity in the code below contains property1 defined in its superentity, as well as its own property2 and property3.
| It is not possible to overwrite existing properties. |
"nodes":{
...
"superEntity":{
"properties":{
"property1":{ },
},
},
"extendedEntity":{
"extends":"superEntity",
"properties":{
"property2":{ },
"property3":{ },
}
}Constraints
Defines additional validations that are applied to the node (entity).
On the node level, you can use the following constraint: UNIQUE, where properties lists the properties to which the constraint applies.
"roleReference":{
"properties":{ },
"constraints":[
{
"type":"UNIQUE",
"id":"ROLE_REFERENCE_UNIQUE_ROLE",
"scope":"WITHIN_PARENT",
"properties":[
"role"
]
}
]
}The other constraints (REGEX, REQUIRED, JDBC_DATA_SOURCE) can be assigned to scalar properties only.
See the preceding property constraints section.
Traits
Traits are properties that are defined by plugins and add additional functionality or change the appearance of the entity. For more information, see Traits.
|
Traits are properties that are defined by plugins and would alter the appearance of the entity, eg. 'Searchable': They add additional functionality to the entity. Currently, you can add only the core:displayName
|
Was this page useful?
