Configuring Permissions Frequent Scenarios
Current page is describing the examples of the most frequent scenarios of configuring permissions.
Scenario 1: Removing default permissions on entity
Permissions, that are not propagated from the metadata, can be revoked from the Access table by hovering over permission and clicking on the bin sign:
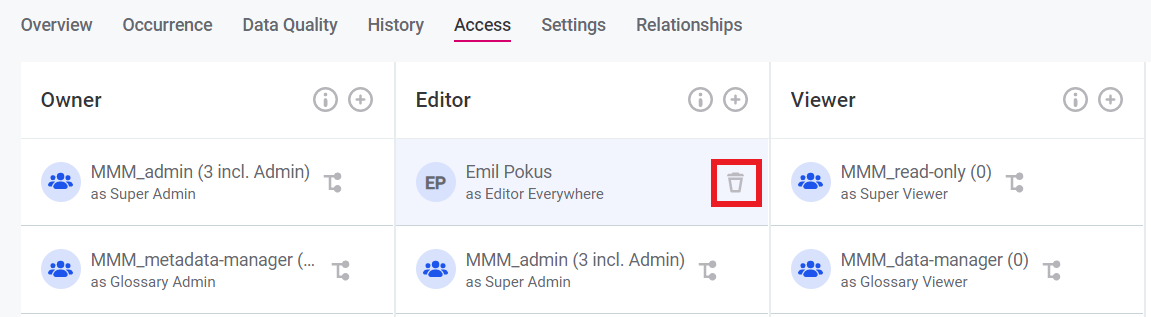
However, those permissions that were propagated from the metadata and have a corresponding node icon, can not be deleted that way. To delete entity permissions that were propagated from the Metadata, the GraphQL mutation needs to be used:
| For more information on GraphQL usage see ONE API. |
-
Open the Playground by adding
/playground/to the URL line of the page. -
Run the following mutation query, where:
-
Specify the <UnassignCapability> you would like to revoke
-
Specify the <capabilityID> you would like to revoke.
-
Specify the <gid> of the source of the permission, which in case of Metadata is
"00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001". -
Specify the <roleID> or <userID> you would like to remove permission from.
mutation metadataUnassign { <UnassignCapability>( capabilities: "<capabilityID>" gid: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001" grantingStrategy: GRANT roles: "<roleID>" // or users: "<userID>" ) { result { gid } } }For example, to remove Viewer rights from Emil Pokus on a specific Catalog Item, the following mutation is used:

-
|
To run the queries correctly, the IDs of users, roles, capabilities and source of permissions granting ( It is possible to get the
It is possible to get all default permissions assignments in Metadata by running the following query: Click here to expand…It is possible to get permissions assignments on specific source, for example, Catalog Item, by running the following query, where GID is the ID of the Catalog Item: Click here to expand… |
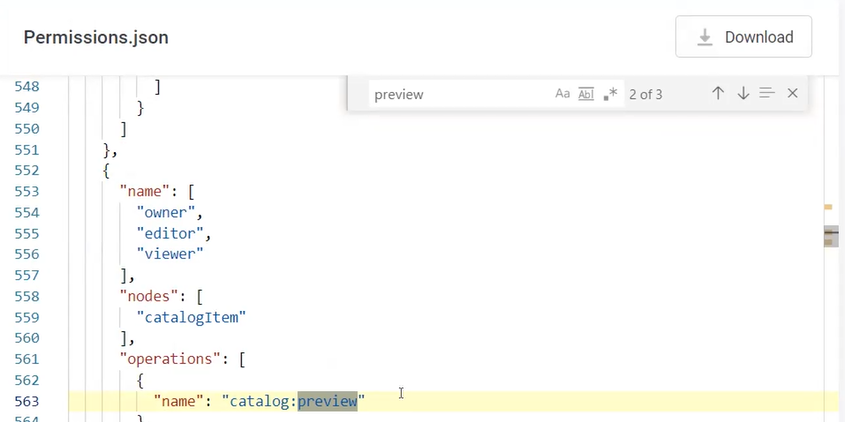
Scenario 2: Restricting permissions on data preview
There are three major ways how to restrict preview of the data:
To revoke permission on previewing data from all Viewers, go to Organization > Permissions Model and remove the viewer Operation Set where preview operation is added.
To revoke preview permission from a specific user, the user’s roles needs to be managed. If the user is already assigned to a role that has a permission to see the preview of data, the permission cannot be revoked for a user while saving his role and the role’s permissions.
For example, if the user is assigned to a role that has rights to see all catalog items, it is impossible to restrict the user’s permission to one specific catalog item. Restrict the user’s permissions in that case is only possible via the following way:
-
Remove the mapping of user and role in Keycloak or another identity management system you are using.
If there are several users who should not be able to preview the same catalog items, another role can be created for them. -
Create a capability in permissions.json, that has no operation
"preview". -
Assign the capability to a user on each location one by one where the user needs to have permissions.
For example, if Emil Pokus is assigned to the role catalog_adminbut it appears that he should not be seeing the data preview of one specific Catalog Item, he should be unassigned from the rolecatalog_adminand assigned to all catalog items he needs to have access to via Access tab on each Catalog Item.
Scenario 3: Creating custom capability and assigning it to a Keycloak role
For guidelines on how to create a new capability see Manage Permissions of Users and Roles, Configuring custom permissions section. Capabilities are applied to a specific location, or in other words, entities, such as Catalog Items or DQ Projects.
To assign a Keycloak role to a newly created capability, go to the location the capability refers to, and map role and capability on the Access tab. For more information see Manage Permissions of Users and Roles, Granting, sharing and revoking permissions section.
Scenario 4: Restricting user permissions to one DQM project
To revoke permission from a specific user, the user’s roles needs to be managed. If the user is already assigned to a role that has a permission to DQ Project, the permission cannot be revoked for a user while saving his role and the role’s permissions. For example, if the user is assigned to a role that has rights to edit all DQ Projects, it is impossible to restrict the user’s permission to one specific project. Restrict the user’s permissions in that case is only possible via removing the mapping of user and role in Keycloak or another identity management system you are using.
For example, if Emil Pokus is assigned to the role dq_admin but it appears that he should not be able to edit some specific DQ projects, the following should be done:
-
Emil Pokus should be unassigned from the role.
-
He should be assigned to all DQ projects as an owner where he needs to have access to via Access tab on each DQ project. Assign the editors rights to a user on each project one by one where the user needs to have permissions, and ignore projects where the user should not be an editor.
Scenario 5: Restricting user editor permissions to attributes
There are two options to restrict users' edit rights on attributes. Currently it works as "all or nothing", which means you can either edit all attributes or you don’t edit any for all users.
-
The first option is to restrict users' edit rights from all attributes on a catalog item. To do that, follow these steps:
-
Remove the user from the role which has the capability to perform editors actions on a catalog item everywhere.
-
Create a specific capability on attributes, for example, without the operation
"name": "core:edit". -
Then attributes need to be shared one by one. But this case will be deprecated in the next ONE versions.
-
-
To revoke editing permissions from users on the attributes, do the following:
-
Remove the user from the role which has the capability to perform editors actions on a catalog item everywhere.
-
Create a new capability on a catalog item that would restricting editing of all attributes, for example, without
"name": "core:edit"operation. -
Assign new capability on a Catalog Item to a user on an Access tab. Grant permissions to a user again on all other Catalog Items that he needs to have access to.
-
Scenario 6: Configuring and assigning access to a custom entity
When creating top-level custom entity (the one that goes to the left hand menu), ownership permissions to this entity on metadata need to be set first.
Example in permissions.json, source_admin has permissions on root ( "/") which means source admin on metadata can create new drafts and therefore can create new sources.
Similar capability is needed for new top-level entity creation.
Other custom entities that are located underneath other sections, like Glossary, Catalog, etc. inherit permissions of the source. Permissions can be changed on the Access tab of the newly created entity.
Scenario 7: Configuring and assigning permissions to work with SQL catalog items
To be able to work with SQL Catalog Items, two parts of configuration need to be fulfilled:
-
The permissions need to be granted to the users who will work SQL Catalog Items in the application. For the default configuration, see Default permissions in permissions.json file.
-
Data source connection need to have specific properties that would allow working with SQL. For more information and the default configuration, see Data Sources Configuration for the plugin that allows the feature and Add a JDBC Driver to DPE for the configuration properties on a JDBC driver connection and Metastore Data Source Configuration for the configuration properties on a Metastore connection.
Default permissions in permissions.json file
The default permissions on working with SQL Catalog Items are the following:
-
The operations that allow users working with SQL catalog items need to be set. By default, these permissions are assigned to Owner and Editor.
-
Optional:
"name": "datasource: dslQueryPreview". It allows to see the preview of the data after clicking the Run query button. -
"name": "datasource: dslQueryMetadataImport". It is required to allow metadata import, thus creating and editing SQL catalog items.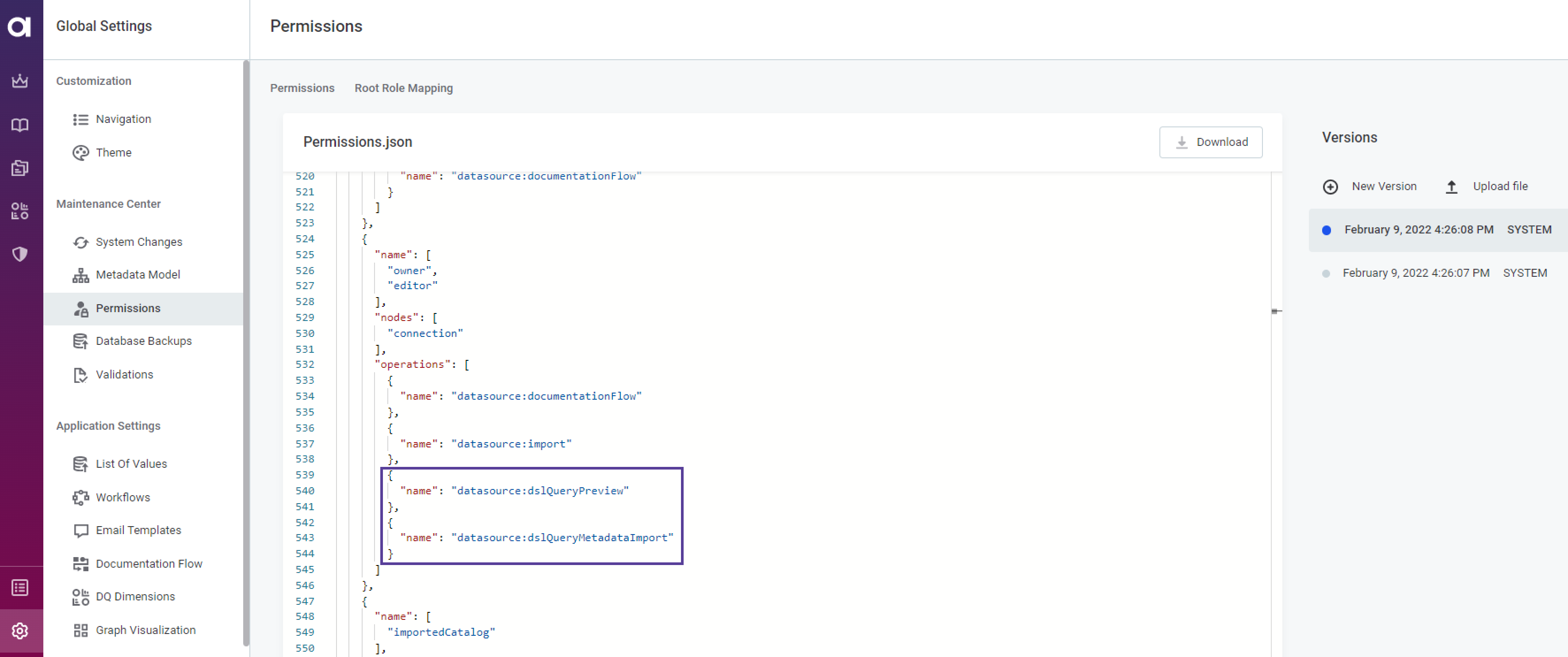
-
The capability that toggles the whole feature needs to be set. Check if the capability
dsl-query-catalog-itemsis configured in thepermissions.jsonfile.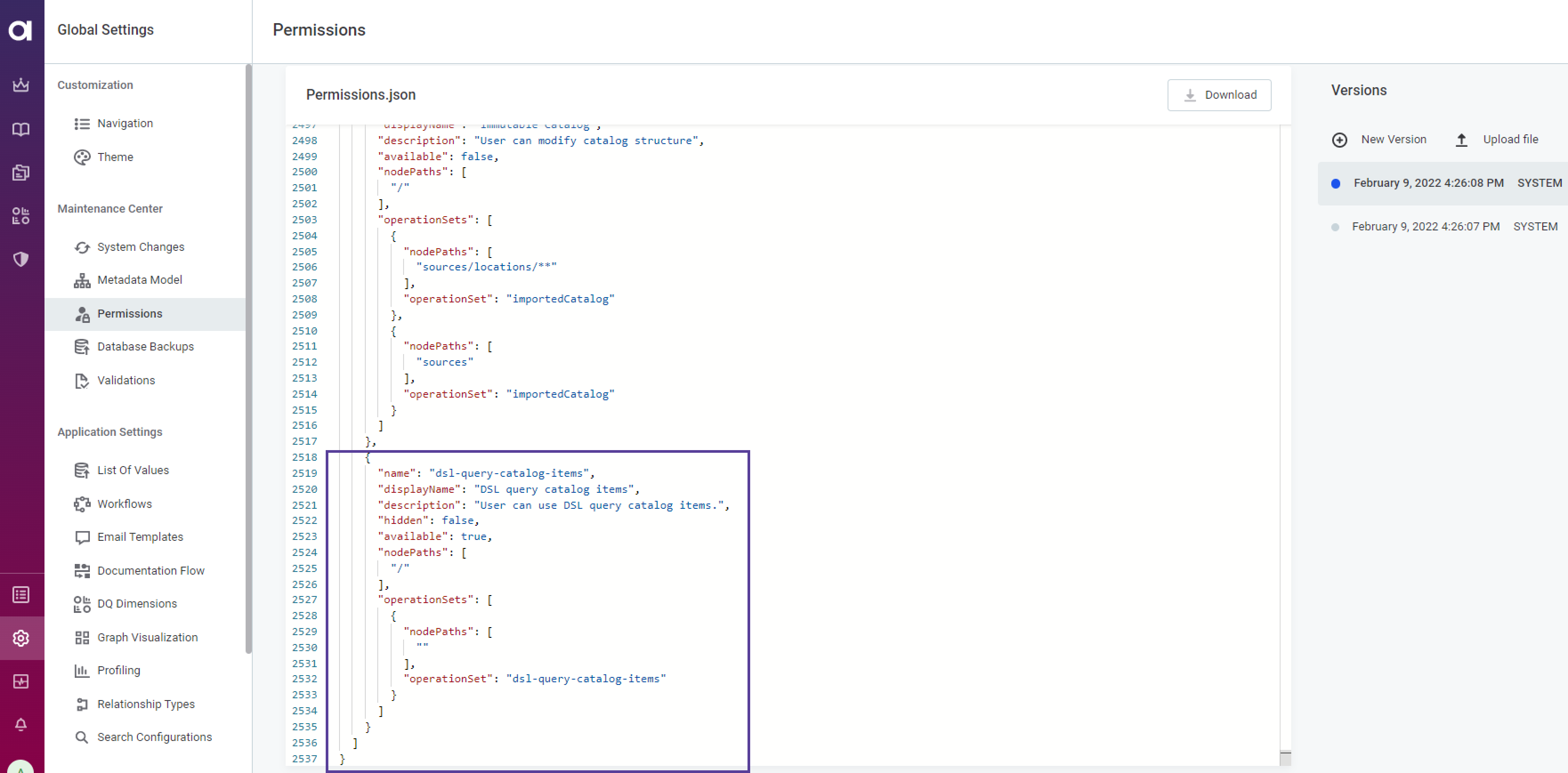
By default it is assigned to
MMM_adminandMMM_data-managerroles. Other roles cannot see the Create SQL catalog item button and change existing SQL catalog items' queries. To check on who has the capability assigned, use the following GraphQL:Click here to expand…
query GetCapabilities_metadata { metadata(gid: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001") { gid assignedIdentities{ grantingStrategy capability { name id } identity { ... on Role { name } ... on Person { username userId email id } } } } }
-
In addition to the SQL feature permissions, the users need to have permissions on a connection to the data source from which the data need to be imported to the SQL catalog item.
Granting permissions to a user
To grant permissions to a user use the playground.
| For more information on GraphQL usage see the first scenario or ONE API. |
-
Open the Playground by adding
/playground/to the URL line of the page. -
Run the following mutation query:
mutation metadataAssignCapabilities($roles: [String!]!, $users: [String!]!) { metadataAssignCapabilities( gid: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001" capabilities: ["dsl-query-catalog-items@/"] roles: $roles users: $users grantingStrategy: GRANT ) { success } }
Revoking permissions from a user
To remove permissions from a user, remove the role’s capability using the playground.
| For more information on GraphQL usage see the first scenario or ONE API. |
-
Open the Playground by adding
/playground/to the URL line of the page. -
Run the following mutation query:
mutation metadataUnassignCapabilities($roles: [String!]!, $users: [String!]!) { metadataUnassignCapabilities( gid: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001" capabilities: ["dsl-query-catalog-items@/"] roles: $roles users: $users grantingStrategy: GRANT ) { success } }
This will restrict the user with this role to be able to see the button Create SQL item and change anything on existing SQL catalog items:
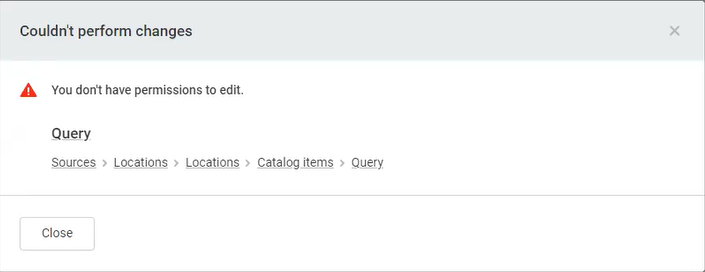
Scenario 8: Removing editors rights on a specific property from a user
It is possible to restrict a user with editor rights from editing specific fields. For example, it is possible to have a term editor, who can edit terms, but is not allowed to touch Owner and Steward properties.
To do that, three steps should be followed:
-
Creating of a new suitable capability for editor on terms. To do that, in Global Settings> Permissions, add the following capability to the
permissions.jsonfile:{ "name": "term-editor", "displayName": "Glossary Editor", "description": "The user has edit permissions to all glossary terms as well as their relationships.", "available": true, "nodePaths": [ "/" ], "operationSets": [ { "nodePaths": [ "terms/**", "termRelationships/**" ], "operationSet": "editor" } ] }, -
Find the existing editor operationSet configuration on terms and termRelationships. To do that, find the places in operation sets which influence terms by searching for
core:edit:{ "name": [ "owner", "editor" ], "nodes": [ ".*" ], "operations": [ { "name": "core:edit", "properties": [ ".*" ] }, { "name": "core:createNewDraft", "properties": [ ".*" ] -
Remove the
core:editoperation for properties that should not be edited. Add a new definition in operationSets section that was found in the previous step:{ "name": [ "editor" ], "nodes": [ "term" ], "operations": [ { "name": "!core:edit", "properties": [ "owner", "steward" ] } ] }
Scenario 9: Limited access rights configuration
You can configure the following teams of users:
-
Team of users that cannot create new sources and has access only to its sources.
-
Team of users that can create new sources and sees sources from all teams.
-
Team of users that cannot create new sources and sees sources from all teams.
We expect that the roles TeamA, TeamB, TeamC exist in Keycloak and were synchronized into MMM. A user who has such the TeamA will belong to the team TeamA.
There will also need to be a role/team responsible for creating sources/terms/rules.
It can be a separate role, or it can be performed by admin - using the role MMM_admin (which will not need extra setup).
No changes in permissions.json are needed.
Workaround manual solution
First, the correct set up should be configured.
You need to replace some already existing assignments on the metadata entity.
You can do this through GraphQL. Most default sharing will be replaced on metadata:
-
Remove assignments for all roles except for
MMM_admin,MMM_user,MMM_read-only,MMM_application-admin. Those will stay the same. -
If you are using a separate Creators role, assign it capabilities on the nodes that you expect will be possible to create for this role, for example,
source_admin@/,term_admin@/andrule_admin@/. If not,MMM_adminis already configured correctly. -
dsl-query-catalog-itemsshould be given to roles (teams) that need creating a special type of catalog item. For more information see Manage Users and Roles.
To configure the set up correctly, follow these steps:
-
Run the following query:
query listAssignments { metadata(gid: "root") { assignedIdentities { capability { id } identity { ... on Role { name } } } } } -
To assign and change capabilities use the following GraphQL:
mutation assign { metadataAssignCapabilities( # or metadataUnassignCapabilities gid: "root" grantingStrategy: GRANT capabilities: ["source-viewer@/"] # you can list multiple at once roles: ["MMM_data-governor"] # you can list multiple at once ) { success } }
The workaround is to delegate the creation of nodes (catalog items, terms, sources, rules, etc.) to a dedicated team, which is either a Keycloak role or a person. This Keycloak role or person will get the Creators rights. This dedicated team of Creators will create a new node upon request and share it with TeamA, TeamB, or TeamC with the Owner’s capability. After that teams can work with the node normally:
-
TeamA can edit sources, profile catalog items, and assign terms.
-
TeamC can share anything with TeamA or TeamB.
The only restriction is that teams cannot create new node on their own.
Was this page useful?