ONE Metadata Model Reference
This guide describes the metadata model configuration files.
ONE configuration files
Configuration files for ONE are located in the ONE product package, in the <ONE-core>/mmd folder.
| For information on installing the ONE product package, see installation-guides.adoc. |
mmd.json5
The main configuration file for the ONE web application is mmd.json5.
It defines the structure for ONE web application metadata (i.e., it defines the web application):
-
Functionalities available within the application (defined by plugins)
-
Entities displayed in the application and connections between them, application layout (defined by nodes)
-
Connections between entities and functionalities (defined by applying plugins to the entities)
Even though the layout is defined as a flat structure, it is stored as a tree, and viewing it as such can ease the process of writing a proper, functional configuration.
To configure ONE web application, use the default <ONE-core>/mmd/mmd.json5 file as a template. The default file contains all ONE webapp configuration options.
File structure
The file is a .json5 that provides the list of entities and their metadata to the backend.
The general structure of the mmd.json5 file is as follows:
{
"plugins":{ },
"root":"metadata",
"nodes":{ }
}Plugins
| All plugins available are enabled by default. While it is possible to add or remove them, in the current state it may result in loss of basic functionality. |
The plugins section lists all plugins (functionalities) that can be used by the web application.
To add/remove functionality to the web application, add/remove the plugin to/from the list of plugins in mmd.json5.
To add/remove functionality that should be available to a single entity, add/remove the abovementioned plugin to the entity definition.
| For more information, see Nodes. |
Root
Specifies the name of the root node.
It has to be metadata, otherwise, the web application will crash.
| For more information about nodes and their configuration, see Nodes. |
relationships.json5
The main configuration file for visualizing relationships of all nodes in ONE Web Application. It defines what objects will be included in the graph of relationships.
relationships.json5 configures all the relationships between the catalog object added to the Catalog.
| External lineage represents the relationships between the entities which are not present in Catalog but can be reached in Manta. To enable external relationships, follow the configuration instructions for external lineage. |
To configure relationships, select the nodes which should be allowed or skipped in ONE web application visualization.
|
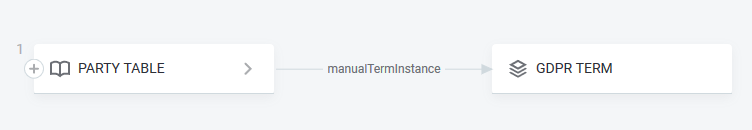
For example, if there are two objects which are connected through the allowed third, "connecting", one, the visualization will be possible with three of them:
If the connecting node is not included in allowed, only the first node will be recognized for visualization. If the connecting node is skipped, this node will be not visible at visualization, other two will be shown:
|
Relationship components can be used in different places and each of them has a custom configuration.
Currently, the component is used in Catalog only.
It is configured by the configuration with the catalogLineage key.
If there is no custom configuration, the default configuration key will be used.
To select nodes that should be present as objects at the visualization, specify the allowedNodes settings.
By default, the following nodes are shown:
-
catalogItem -
attribute -
term -
location -
source
default: {
nodeConfiguration: {},
edgeConfiguration: {
"defaultEdgeLabels": {},
"customEdgeLabels": []
},
skipNodes: []
},By default, external relationships are allowed for the attribute node only:
catalogLineage: {
externalRelationshipsEnabled: true,
nodeConfiguration: { },
"edgeConfiguration": { },
skipNodes: []
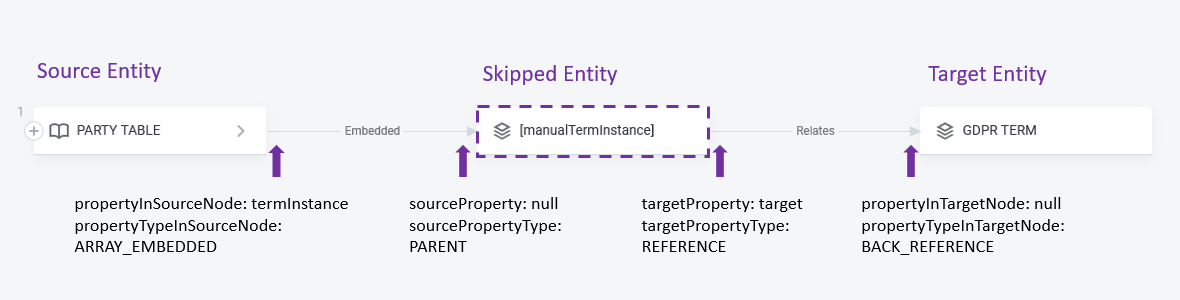
},To select nodes that should be shown as edges at relationships visualization, specify the skipNodes settings:
-
Set the entity that you want to skip in the
entityType, e.g."termInstance". -
Set source entity,
sourceNodeEntityType, from which the relationships are defined. -
Set the target entity,
targetNodeEntityType, that you want to see the relationship with. -
Specify the
sourcePropertyandtargetProperty,propertyInSourceNodeandpropertyInTargetNodeto indicate the correct property types for"source"and"target". -
Set
sourcePropertyTypeandtargetPropertyType,propertyTypeInSourceNodeandpropertyTypeInTargetNodethat indicate connection (relationship) type with another entity (property) and can be one of the following:-
SINGLE_EMBEDDEDtype of property which stores a single value (parent-child relationship). -
ARRAY_EMBEDDEDtype of property which stores multiple values (parent-children relationship). -
REFERENCEtype of property which points to another entity but is independent of it. -
PARENTthe parent-children relationship (the current entity is the child). -
BACK_REFERENCEindicates this entity is pointed to by another entity (property).
-
|
For example, the property type assignment can be as follows:
|
skipNodes: [
{ entityType: "termInstance",
sourceNodeEntityType: "attribute",
targetNodeEntityType: "term",
sourceProperty: null,
sourcePropertyType: "PARENT",
targetProperty: "target",
targetPropertyType: "REFERENCE",
propertyInSourceNode: "termInstances",
propertyTypeInSourceNode: "ARRAY_EMBEDDED",
propertyInTargetNode: null,
propertyTypeInTargetNode: "BACK_REFERENCE" }
]permissions.json
Permissions are defined in permissions.json.
It defines what Owner, Editor and Viewer can do on each mmd node and how these are combined together, as well as which nodes can be shared.
permissions.json also defines the mapping for some mandatory roles, such as application roles and admins on metadata.
These roles are default (Application User) and MMM_admin (Application Admin) in Keycloak.
|
It is possible now to configure the
|
The permissions are defined for the following nodes:
-
sources -
credentials -
connections -
catalogItem -
attribute -
entities related to
catalogItemandattribute -
term -
location -
source -
statistics -
rule -
component -
lookup -
project -
rdm
In the Capabilities part of the file, the capabilities of the users are defined on different levels, such as:
-
special - that provides full access to the application and its configuration.
-
simple - that specifies Viewer, Editor, and Owner capabilities on the application.
-
extra-locations - that applies additional user role capabilities on the specified application locations.
-
source - that applies specific capabilities on sources.
-
global-source-related - that specifies roles on the global source.
-
global - that lists the global application capabilities.
rootRoleMapping.json5
In this file, the roles mapping is defined. The mapping is made on three levels:
-
super
-
application
-
compositions
users.json
Currently users.json defines how the Keycloak roles are shown on the frontend (user roles and company roles).
users.json is obsolete, users can be configured directly in Keycloak.
profilingConfig.json5
In this file, the default profiling configurations are specified. The configurations include:
-
Full profiling, where the type of profiling is "FULL" and anomaly detection is enabled.
-
Sample profiling, where the type of profiling is "SAMPLE" with limits set to 10000 on Count and 20 on Percentage, and anomaly detection is disabled.
-
Profiling of the last partition, where the type of profiling is "LAST_PARTITION" and anomaly detection is enabled.
Was this page useful?