Domains
Domains are custom constraints, assigned to table columns. For example, you want to limit the values entered into a given column to letters or to a phone number in a particular format. You can configure these and other business requirements for dictionary columns via domains by creating custom limitations by format, regular expressions, string size, and values ranges for numeric data types.
For all definition options, see Domain attributes.
Preconfigured domains
Six default domains are preconfigured in a blank RDM project: BOOLEAN, STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT, DATE, and DATETIME.
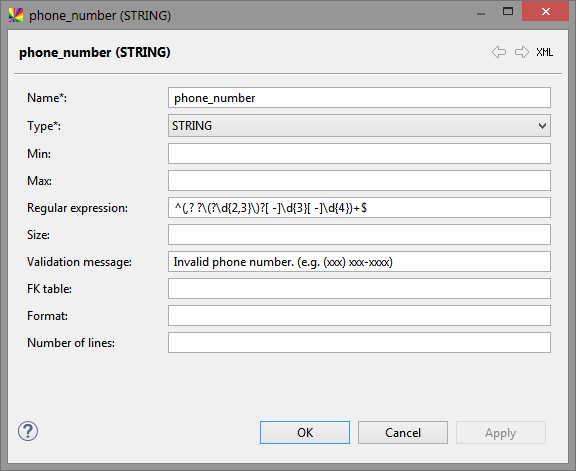
Create a new domain
-
Expand RDM Logical Model > Domains.
-
Right-click Domains and select New domain.
-
Fill in the attributes (see the following sections).
-
Select OK to save changes.
The domain is defined and can be assigned to an attribute in an RDM table. See Tables.
Domain attributes
| Attribute | Required | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Name |
Y |
Name of the domain. |
||
Type |
Y |
ONE Desktop data type to which the domain is mapped. The following values are possible:
|
||
Min |
N |
Definition of the minimum value. |
||
Max |
N |
Definition of the maximum value. |
||
Regular expression |
N |
A regular expression that validates the input. See Regular Expressions. |
||
Size |
N |
Limits the number of characters that can be entered into the field; used primarily for string values; float and integer attributes will be converted to string to check their size. |
||
Foreign key table |
N |
Name of the referenced table (required for mnreferences type). |
||
Format |
N |
Custom formats to change the way RDM displays the domain. See Format definitions for information about the possible format definitions depending on the data type. |
||
Number of lines |
N |
Determines the number of rows that are displayed in the create and edit dialog in the RDM web application (specified only for string data type).
|
||
Validation message |
N |
A message that appears in the web application when domain-defined constraints are violated.
|
The following table specifies which domain attributes are available for each data type:
| Domain Type | Min | Max | Regular expression | Size | Validation message | FK table | Format | Number of lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
boolean |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
date |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
datetime |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
float |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
integer |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
long |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
mnreferences |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
string |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
Format definitions
This section specifies what custom formats can be configured for each data type, including how the data is displayed in the web application.
Datetime data type
Definition of the format for dates uses the following pattern letters:
-
y - year
-
M - month
-
d - day
-
H - hours
-
m - minutes
-
s - seconds
-
S - milliseconds
The number of pattern letters used for defining each part of the date influences the format. See the following examples.
| Definition | Result |
|---|---|
dd.MM.yyyy |
01.02.2015 |
dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss |
01.02.2015 03:04:05 |
dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS |
01.02.2015 03:04:05.600 |
yyyy-MM-dd |
2015-02-01 |
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
2015-02-01 03:04:05 |
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS |
2015-02-01 03:04:05.600 |
If the format is not defined, the following default definition (for English as the web application language) is used from Google Web Toolkit:
| Definition | Result |
|---|---|
yyyy MMM d HH:mm:ss |
2015 Jan 1 01:02:03 |
For detailed information, see:
Numeric data types
Definition of the format for numbers in the integer, long, and float formats uses the following symbols:
-
# - Stands for one digit. If a displayed number does not contain a digit in the position of a hash, the position is empty.
-
0 - Stands for one digit; used to display a zero.
-
Before the decimal point for fractions like 0.25 instead of .25.
-
After the decimal point for setting the number decimal places.
-
-
, - A thousands separator (the actual separator symbol depends on the RDM web application language settings).
-
. - Decimal mark (the actual decimal mark symbol depends on the RDM web application language settings).
If the format is not defined, the following default definition (for English as the web application language) is used from the Google Web Toolkit: #,##0.###.
|
Examples for float
| Format | 123456789.0 | .9 | .99 | .994 | .995 | .996 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[empty] |
123 456 789 |
0.9 |
0.99 |
0.994 |
0.995 |
0.996 |
####.## |
123456789 |
0.9 |
0.99 |
0.994 |
1 |
1 |
#,###.## |
123 456 789 |
0.9 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
1 |
1 |
#,##0.## |
123 456 789 |
0.9 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
1 |
1 |
#,##0.00 |
123 456 789.00 |
0.90 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0,000.00 |
123 456 789.00 |
0 000.90 |
0 000.99 |
0 000.99 |
0 001.00 |
0 001.00 |
Was this page useful?
