Relationships
The Relationships sub-node in the RDM Logical Model node allows adding, modifying, and deleting parent-child relationships between tables of the RDM logical model.
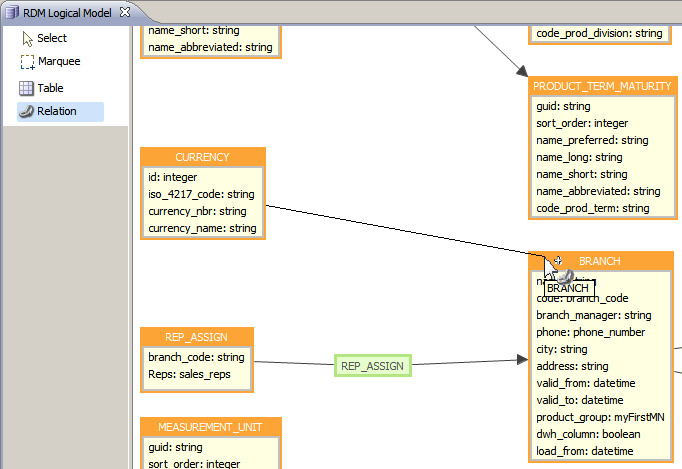
In the Data Model Editor, the relationship is marked by an arrow from the child table to the parent table, with the relationship name in between.
| Creating MN relationships is described in How to Create an MN Relationship in RDM. |
Add a new relationship in the Model Explorer
-
Right-click Relationships > New relationship.
-
Fill in the attributes.
-
Select OK to save changes.
Add a new relationship in the Data Model Editor
-
Right-click RDM Logical Model > Edit schema. The canvas of the Data Model Editor opens, with the elements palette on the left.
-
Select Relationship from the palette and connect the child table with the parent table (the arrow should go from the child to the parent).
-
Double-click the newly created relationship.
-
Fill in the attributes.
-
Select OK and save changes.
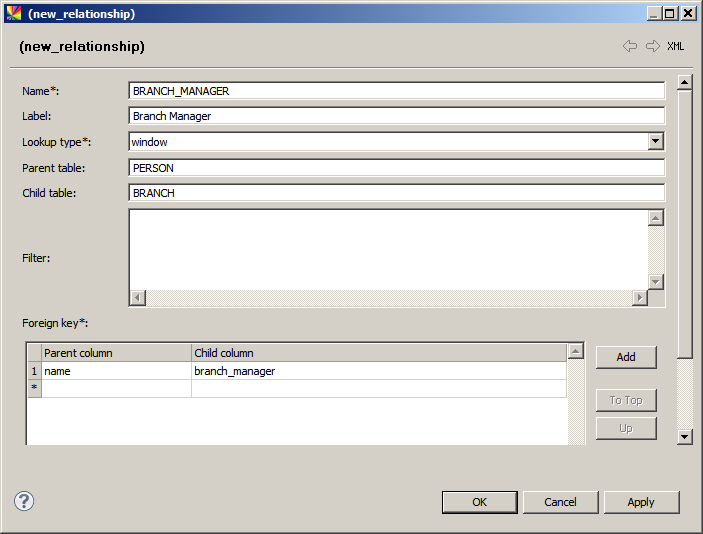
Relationship attributes
| Attribute | Required | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Name |
Y |
Name of the relationship used in the model configuration process. The maximum length of the name is determined by the database type. The database type is set in the App Variables node.
|
||||
Label |
N |
Name of the relationship as shown in the web application. |
||||
Lookup type |
Y |
Determines the appearance of the lookup to the parent table in the Create/Edit Detail dialog. See Working with Records in RDM, section Lookups. Lookup types:
|
||||
Parent table |
Y |
Name of the parent table (the relationship arrow leads here). |
||||
Child table |
Y |
Name of the child table (the relationship arrow starts here). |
||||
Filter |
N |
SQL condition that makes only a subset of parent records satisfying this condition to be available for the child table. |
||||
Foreign key |
Y |
Defines the columns of the parent and child table that create the relationship.
|
The condition should contain the part of an SQL query following the where logical operator.
The syntax generally depends on the database type used, with one important distinction: child table column names should be put between dollar signs ($), for example,$child_column_name$.
|
Multiple relationships between two tables
| While one child table can have several relationships to the same parent table, the connection must be via different child columns, that is, you cannot connect both PARENT_COLUMN A to CHILD_COLUMN A and PARENT_COLUMN B to CHILD_COLUMN A. |
Was this page useful?
